RabbitMQ 的五种消息队列
1.简单模式
RabbitMQ 工具类
public class MQUtils {
public static final String QUEUE01 ="queue01";
public static final String QUEUE02 ="queue02";
public static final String EXCHANGE01="exchange01";
public static final String EXCHANGE02="exchange02";
public static final String EXCHANGE03="exchange03";
//返回连接
public static Connection getConnection(){
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
//设置主机
factory.setHost("localhost");
//设置虚拟主机
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
//设置账号密码
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
//设置端口
factory.setPort(5672);
try {
return factory.newConnection();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
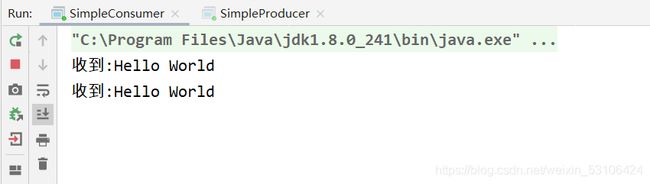
生产者
public class SimpleProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列,会在MQ服务上创建新的队列
channel.queueDeclare(MQUtils.QUEUE01,false,false,false,null);
//发送消息,到队列中,参数2,是队列名,参数4是消息的内容
channel.basicPublish("",MQUtils.QUEUE01,null,"Hello World".getBytes());
}
}
消费者
public class SimpleConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列,会在MQ服务上创建新的队列
channel.queueDeclare(MQUtils.QUEUE01,false,false,false,null);
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE01,true,consumer);
while (true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("收到:"+new String(delivery.getBody()));
}
}
}
2.工作队列模型
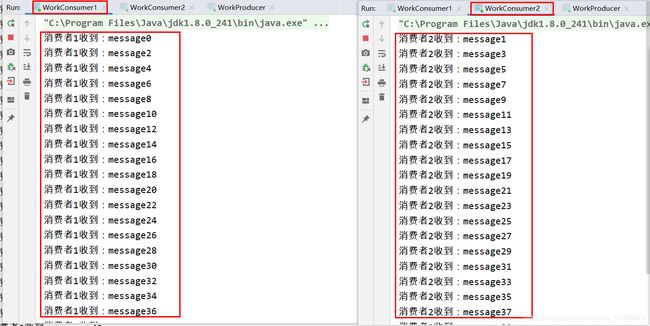
工作队列,生产者将消息分发给多个消费者,消费者会平分这些消息。
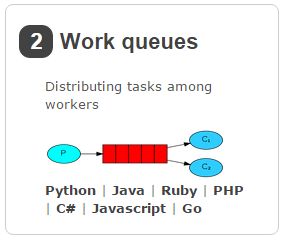
例:如果生产者生产了100条消息,消费者1消费50条,消费者2消费50条。
生产者
public class WorkProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列,会在MQ服务上创建新的队列
channel.queueDeclare(MQUtils.QUEUE01,false,false,false,null);
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++){
//发送消息,到队列中,参数2,是队列名,参数4是消息的内容
channel.basicPublish("",MQUtils.QUEUE01,null,("message"+i).getBytes());
}
}
}
消费者1
public class WorkConsumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得连接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列,会在MQ服务上创建新的队列
channel.queueDeclare(MQUtils.QUEUE01, false, false, false, null);
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息,参数2 是否自动确认 true自动 false 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE01,true,consumer);
while(true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者1收到:" + new String(delivery.getBody()));
//睡眠500 看他们是否会存在着处理消息能力的不同
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
}
消费者2
public class WorkConsumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得连接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列,会在MQ服务上创建新的队列
channel.queueDeclare(MQUtils.QUEUE01, false, false, false, null);
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息,参数2 是否自动确认 true自动 false 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE01,true,consumer);
while(true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者2收到:" + new String(delivery.getBody()));
//睡眠100 看他们是否会存在着处理消息能力的不同
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
}
问题:能者多劳
默认情况下,MQ服务为每个消费者分配相同数量的消息
处理快的消费者和处理慢的消费者处理一样多消息,存在效率问题
为什么不是能者多劳?
默认情况下,消息是自动确认的(发出去后MQ服务自动确认)
如何实现能者多劳?
改为手动确认,生产者发送消息后,需要消费者处理完一个消息后反馈给MQ服务,再处理下个消息。
消费者每次只处理一个消息
消费者
public class WorkConsumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得连接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//同一时刻服务器只发送一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
//声明队列,会在MQ服务上创建新的队列
channel.queueDeclare(MQUtils.QUEUE01, false, false, false, null);
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息,参数2 是否自动确认 true自动 false 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE01,false,consumer);
while(true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者1收到:" + new String(delivery.getBody()));
Thread.sleep(500);
//手动确认 参数1 消息的tag
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(),false);
}
}
}
3.发布/订阅模型
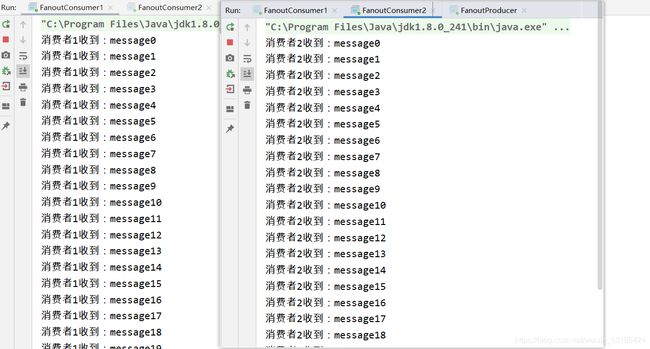
发布/订阅模式和Work模式的区别是:Work模式只存在一个队列,多个消费者共同消费一个队列中的消息;而发布订阅模式存在多个队列,不同的消费者可以从各自的队列中处理完全相同的消息。
实现步骤:
1.创建交换机(Exchange)类型是fanout
2.交换机需要绑定不同的队列
3.不同的消费者从不同的队列中获得消息
4.生产者发送消息到交换机
5.再由交换机将消息分发到多个队列

生产者
public class FanoutProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机, 参数1 交换机名称 参数2 交换机类型
channel.exchangeDeclare(MQUtils.EXCHANGE01,"fanout");
for (int i = 0; i <100 ; i++) {
//发送消息到队列中,参数1:交换机名称 参数4 内容消息
channel.basicPublish(MQUtils.EXCHANGE01,"",null,("message"+i).getBytes());
}
}
}
消费者1
public class FanoutConsumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列,会在MQ服务上创建新的队列
channel.queueDeclare(MQUtils.QUEUE01,false,false,false,null);
//队列和交换机进行绑定
channel.queueBind(MQUtils.QUEUE01,MQUtils.EXCHANGE01,"");
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息 ,参数二 是否自动确定 ,trur 确定 flase 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE01,true,consumer);
while (true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者1收到:"+new String(delivery.getBody()));
}
}
}
消费者2:
public class FanoutConsumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列,会在MQ服务上创建新的队列
channel.queueDeclare(MQUtils.QUEUE02,false,false,false,null);
//队列和交换机进行绑定
channel.queueBind(MQUtils.QUEUE02,MQUtils.EXCHANGE01,"");
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息 ,参数二 是否自动确定 ,trur 确定 flase 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE02,true,consumer);
while (true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者2收到:"+new String(delivery.getBody()));
}
}
}
4.路由模式

路由模式的消息队列可以给队列绑定不同的key,生产者发送消息时,给消息设置不同的key,这样交换机在分发消息时,可以让消息路由到key匹配的队列中。
可以想象上图是一个日志处理系统,C1可以处理error日志消息,C2可以处理info\error\warining类型的日志消息,使用路由模式就很容易实现了。
生产者
public class RoutingProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机, 参数1 交换机名称 参数2 交换机类型
channel.exchangeDeclare(MQUtils.EXCHANGE02,"direct");
//给交换机绑定队列和key
channel.queueBind(MQUtils.QUEUE01,MQUtils.EXCHANGE02,"hello");
channel.queueBind(MQUtils.QUEUE02,MQUtils.EXCHANGE02,"world");
for (int i = 0; i <100 ; i++) {
//发送消息到队列中,参数1 是交换机的名称 参数二 是key 参数4 是消息内容
channel.basicPublish(MQUtils.EXCHANGE02,"world",null,("message"+i).getBytes());
}
}
消费者1
public class RoutingConsumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息 ,参数二 是否自动确定 ,trur 确定 flase 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE01,true,consumer);
while (true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者1收到:"+new String(delivery.getBody()));
}
}
}
消费者2
public class RoutingConsumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息 ,参数二 是否自动确定 ,trur 确定 flase 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE02,true,consumer);
while (true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者2收到:"+new String(delivery.getBody()));
}
}
}
运行效果图:
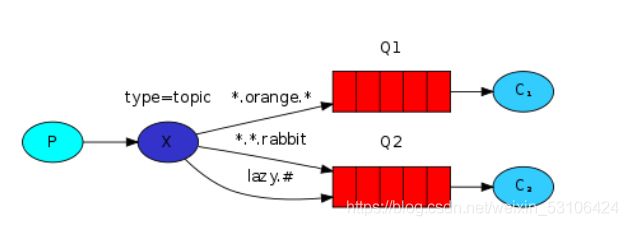
5.主题模型
主题模式和路由模式差不多,在key中可以加入通配符:
* 匹配任意一个单词
# 匹配逗号隔开的多个单词
public class TopicProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机, 参数1 交换机名称 参数2 交换机类型
channel.exchangeDeclare(MQUtils.EXCHANGE03,"topic");
//给交换机绑定队列和key
channel.queueBind(MQUtils.QUEUE01,MQUtils.EXCHANGE03,"hp.*cn");
channel.queueBind(MQUtils.QUEUE02,MQUtils.EXCHANGE03,"blb.#");
for (int i = 0; i <100 ; i++) {
//发送消息到队列中,参数1 是交换机的名称 参数二 是key 参数4 是消息内容
channel.basicPublish(MQUtils.EXCHANGE03,"blb.xx.xx.cn",null,("message"+i).getBytes());
}
}
}
消费者1
public class TopicConsumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息 ,参数二 是否自动确定 ,trur 确定 flase 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE01,true,consumer);
while (true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者1收到:"+new String(delivery.getBody()));
}
}
}
消费者2
public class TopicConsumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获得链接
Connection connection = MQUtils.getConnection();
//获得通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//创建消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//接受消息 ,参数二 是否自动确定 ,trur 确定 flase 手动
channel.basicConsume(MQUtils.QUEUE02,true,consumer);
while (true){
//取消息
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("消费者2收到:"+new String(delivery.getBody()));
}
}
}