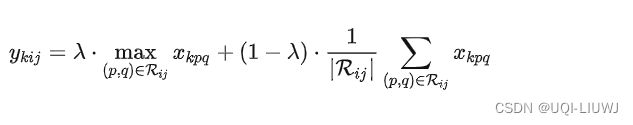机器学习/pytorch笔记 池化
1 全局池化
1312.4400.pdf (arxiv.org)
1.1 理论部分
- 将某个channel中所有的元素取平均,输出到下一层
- 全连接层的替代操作,剔除了全连接层中黑箱的特征,直接赋予了每个channel实际的类别意义。
- 使用GAP代替全连接层,可以实现任意图像大小的输入
- 对整个特征图求平均值,可以用来提取全局上下文信息
1.2 pytorch实现
全局平均池化
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
m = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1))
input = torch.randn(2,2,3)
print(input)
'''
tensor([[[-1.1367, -1.9247, -2.0963],
[-1.5315, 1.5207, 1.1702]],
[[-0.7293, 0.7023, 1.2145],
[ 1.1222, 0.1508, -1.2018]]])
'''
output = m(input)
print(output)
'''
tensor([[[-0.6664]],
[[ 0.2098]]])
'''
torch.mean(input,dim=[1,2])
'''
tensor([-0.6664, 0.2098])
'''2 混合池化
LNCS 8818 - Mixed Pooling for Convolutional Neural Networks (psu.edu)
随机采用了最大池化和平均池化方法
λ是0或1的随机值,表示选择使用最大池化或平均池化
混合池化优于传统的最大池化和平均池化方法,并可以解决过拟合问题来提高分类精度。
3 随机池化
1301.3557.pdf (arxiv.org)
随机池化对特征图中的元素按照其概率值大小随机选择,即元素值大的被选中的概率也大,而不像max-pooling那样,永远只取那个最大值元素,这使得随机池化具有更强的泛化能力。
3.1 步骤
- 方格中的元素同时除以它们的和sum,得到概率矩阵
- 按照概率随机选中方格
- pooling得到的值就是选择到的方格相应位置的值。
3.2 举例
3.2.1 training时的情况
假设特征图中各元素值如下:
| 0 | 1.1 | 2.5 |
| 0.9 |
2.0 | 1.0 |
| 0 | 1.5 | 1.0 |
我们对特征图元组求和,并然每个元素除以这个和,得到概率矩阵:
| 0 | 0.11 | 0.25 |
| 0.09 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 0 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
每个元素值表示对应位置处值的概率,现在只需要按照该概率来随机选一个
比如最后选择了第三行第二个元素,那么最终的pooling的值就是1.5
3.2.2 testing时的情况
对矩阵区域求加权平均即可得到相应的平均池化结果
3.3 pytorch实现
3.3.1 逐步实现
x=torch.Tensor([[0,1.1,2.5],
[0.9,2.0,1.0],
[0,1.5,1.0]])
x_avg=x/torch.sum(x)
x_avg
'''
计算概率
tensor([[0.0000, 0.1100, 0.2500],
[0.0900, 0.2000, 0.1000],
[0.0000, 0.1500, 0.1000]])
'''
num=torch.distributions.Categorical(x_avg.flatten()).sample()
num
//tensor(7)
//采样一个点
x[num//x.shape[0],num%x.shape[0]]
//tensor(1.5000)
3.3.2 包装成类
class StochasticPooling(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self,x):
x_avg=x/torch.sum(x)
if(self.training):
//判断是training还是testing
num=torch.distributions.Categorical(x_avg.flatten()).sample()
return x[num//x.shape[0],num%x.shape[0]]
else:
return torch.sum(x*x_avg)
sp=StochasticPooling()
sp(x)
//tensor(0.9000)4 power average pooling 幂平均池化
使用了一个学习参数p
- p=1——>局部求和
- p—>∞ ——>最大池化
5 自适应池化
给定经过池化的输出feature map大小,自适应地求得stride和kernel_size
5.1 pytorch 实现
5.1.1 AdaptiveAvgPool1d
torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(output_size)
输入为(N,C,Lin) or(C,Lin),输出为(N,C,Lout) or (C, L_{out}),其中Lout=output_size.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# target output size of 5
m = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(5)
input = torch.randn(1, 64, 8)
output = m(input)
print(output.shape)
'''
torch.Size([1, 64, 5])
'''5.1.2 ADAPTIVEAVGPOOL2D
-
Input: (N,C,Hin,Win) or (C,Hin,Win).
-
Output: (N,C,S0,S1) or (C,S0,S1), where S=output_size.
# target output size of 5x7
m = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((5,7))
input = torch.randn(1, 64, 8, 9)
output = m(input)
print(output.shape)
'''
torch.Size([1, 64, 5, 7])
'''# target output size of 7x7 (square)
m = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(7)
input = torch.randn(1, 64, 10, 9)
output = m(input)
print(output.shape)
'''
torch.Size([1, 64, 7, 7])
'''# target output size of 10x7
m = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 7))
input = torch.randn(1, 64, 10, 9)
output = m(input)
print(output.shape)
'''
torch.Size([1, 64, 10, 7])
'''参考内容
一文看尽深度学习中的各种池化方法! - 知乎 (zhihu.com)