第二章.线性回归以及非线性回归—多元线性回归
第二章.线性回归以及非线性回归
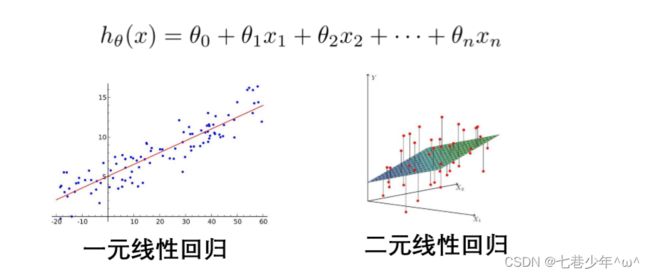
2.6 多元线性回归
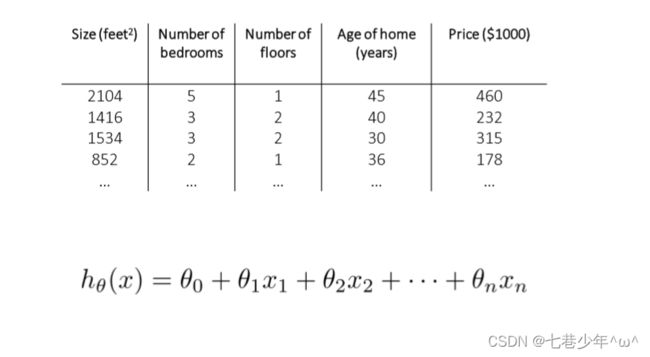
1.特征:
1).单特征:
2).多特征:
- 有多少个特征就有多少个未知数x
2.多元线性回归模型的使用场景:
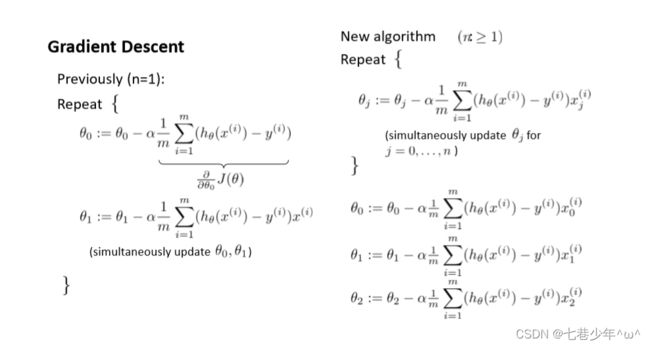
3.梯度下降法求解多元线性回归
1).公式:
4.实战1: 梯度下降法—多元线性回归:
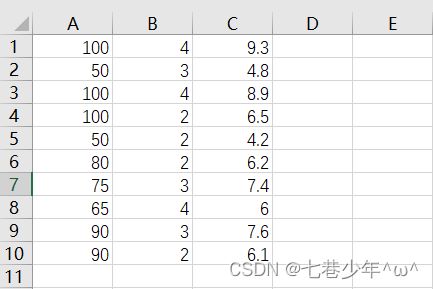
1).CSV中的数据:
以一家快递公司送货为例:X1-运货里程 X2-运货次数 Y:总运输时间
2).代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 加载数据
data = np.loadtxt('D:\\data\\Delivery.csv', delimiter=',')
# 切分数据
x_data = data[:, :-1]
y_data = data[:, -1]
# 学习率learning rate
lr = 0.0001
# 参数
theta0 = 0
theta1 = 0
theta2 = 0
# 最大迭代次数
epochs = 1000
# 代价函数:最小二乘法
def computer_error(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2):
totalerror = 0
for i in range(0, len(x_data)):
totalerror += ((theta1 * x_data[i, 0] + theta2 * x_data[i, 1] + theta0) - y_data[i]) ** 2
return totalerror / float(len(x_data)) / 2
# 梯度下降法
def gradient_descent(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2, lr, epochs):
# 数据集的总数量
m = float(len(x_data))
# 循环epochs次
for i in range(epochs):
grad_theta0 = 0
grad_theta1 = 0
grad_theta2 = 0
for j in range(0, len(x_data)):
# 梯度的计算
grad_theta0 += (1 / m) * ((theta1 * x_data[j, 0] + theta2 * x_data[j, 1] + theta0) - y_data[j])
grad_theta1 += (1 / m) * x_data[j, 0] * (
(theta1 * x_data[j, 0] + theta2 * x_data[j, 1] + theta0) - y_data[j])
grad_theta2 += (1 / m) * x_data[j, 1] * (
(theta1 * x_data[j, 0] + theta2 * x_data[j, 1] + theta0) - y_data[j])
# 更新grad_theta0,grad_theta1,grad_theta2
theta0 = theta0 - lr * grad_theta0
theta1 = theta1 - lr * grad_theta1
theta2 = theta2 - lr * grad_theta2
return theta0, theta1, theta2
print('初始参数:theta0={0},theta1={1},theta2={2},error={3}'.format(theta0, theta1, theta2,
computer_error(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2)))
theta0, theta1, theta2 = gradient_descent(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2, lr, epochs)
print('结果参数:theta0={0},theta1={1},theta2={2},error={3}'.format(theta0, theta1, theta2,
computer_error(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2)))
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
x0 = x_data[:, 0]
x1 = x_data[:, 1]
ax.scatter(x0, x1, y_data, c='r', marker='o', s=30)
# 生成网格矩阵
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1)
z = theta0 + theta1 * x0 + theta2 * x1
# 画3D图像
ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z)
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlabel('Miles')
ax.set_ylabel('Num of Delivery')
ax.set_zlabel('Time')
# 显示图像
plt.show()
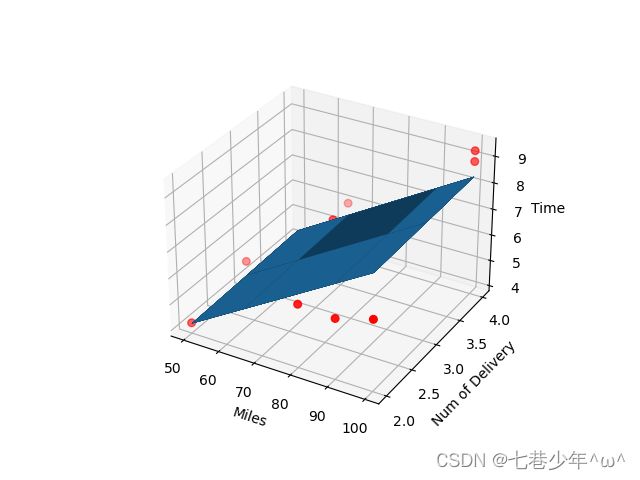
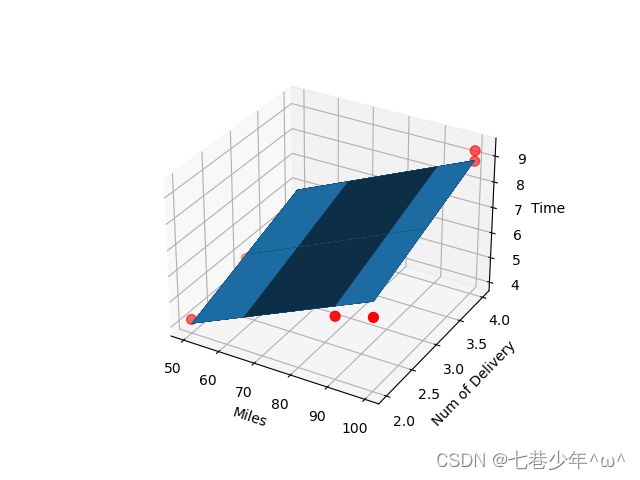
3).结果展示:
①.数据
5.实战2: sklearn—多元线性回归:
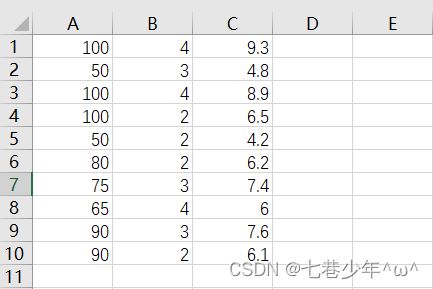
1).CSV中的数据:
以一家快递公司送货为例:X1-运货里程 X2-运货次数 Y:总运输时间
2).代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model
# 加载数据
data = np.loadtxt('D:\\data\\Delivery.csv', delimiter=',')
x_data = data[:, :-1]
y_data = data[:, -1]
# 创建模型
model = linear_model.LinearRegression()
# 拟合模型
model.fit(x_data, y_data)
# 回归系数
coeff = model.coef_
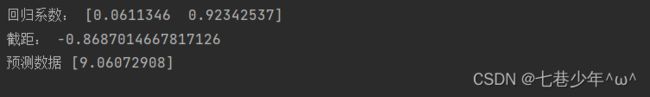
print('回归系数:', coeff)
# 截距
intercept = model.intercept_
print('截距:', intercept)
# 预测数据
x_test = [[102, 4]]
predict = model.predict(x_test)
print('预测数据', predict)
# 创建画布
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# 切分数据
x0 = x_data[:, 0]
x1 = x_data[:, 1]
# 画散点图
ax.scatter(x0, x1, y_data, c='r', marker='o', s=50)
# 生成网格矩阵
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1)
z = coeff[0] * x0 + coeff[1] * x1 + intercept
# 画3D图
ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z)
# 设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlabel('Miles')
ax.set_ylabel('Num of Delivery')
ax.set_zlabel('Time')
# 显示图像
plt.show()
3).结果展示:
①.数据