sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier 决策树-参数详解
sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier 决策树模型参数详解
决策树参数如下:
class sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(*, criterion='gini', splitter='best', max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, max_features=None, random_state=None, max_leaf_nodes=None, min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None, class_weight=None, presort='deprecated', ccp_alpha=0.0)
可选参数:
- criterion:分裂节点所用的标准,可选“gini”, “entropy”,默认“gini”。
- splitter:用于在每个节点上选择拆分的策略。可选“best”, “random”,默认“best”。
- max_depth:树的最大深度。如果为None,则将节点展开,直到所有叶子都是纯净的(只有一个类),或者直到所有叶子都包含少于min_samples_split个样本。默认是None。
- min_samples_split:拆分内部节点所需的最少样本数:如果为int,则将min_samples_split视为最小值。如果为float,则min_samples_split是一个分数,而ceil(min_samples_split * n_samples)是每个拆分的最小样本数。默认是2。
- min_samples_leaf:在叶节点处需要的最小样本数。仅在任何深度的分割点在左分支和右分支中的每个分支上至少留下min_samples_leaf个训练样本时,才考虑。这可能具有平滑模型的效果,尤其是在回归中。如果为int,则将min_samples_leaf视为最小值。如果为float,则min_samples_leaf是分数,而ceil(min_samples_leaf * n_samples)是每个节点的最小样本数。默认是1。
- min_weight_fraction_leaf:在所有叶节点处(所有输入样本)的权重总和中的最小加权分数。如果未提供sample_weight,则样本的权重相等。
- max_features:寻找最佳分割时要考虑的特征数量:如果为int,则在每个拆分中考虑max_features个特征。如果为float,则max_features是一个分数,并在每次拆分时考虑int(max_features * n_features)个特征。如果为“auto”,则max_features = sqrt(n_features)。如果为“ sqrt”,则max_features = sqrt(n_features)。如果为“ log2”,则max_features = log2(n_features)。如果为None,则max_features = n_features。注意:在找到至少一个有效的节点样本分区之前,分割的搜索不会停止,即使它需要有效检查多个max_features功能也是如此。
- random_state:随机种子,负责控制分裂特征的随机性,为整数。默认是None。
- max_leaf_nodes:最大叶子节点数,整数,默认为None
- min_impurity_decrease:如果分裂指标的减少量大于该值,则进行分裂。
- min_impurity_split:决策树生长的最小纯净度。默认是0。自版本0.19起不推荐使用:不推荐使用min_impurity_split,而建议使用0.19中的min_impurity_decrease。min_impurity_split的默认值在0.23中已从1e-7更改为0,并将在0.25中删除。
- class_weight:每个类的权重,可以用字典的形式传入{class_label: weight}。如果选择了“balanced”,则输入的权重为n_samples / (n_classes * np.bincount(y))。
- presort:此参数已弃用,并将在v0.24中删除。
- ccp_alpha:将选择成本复杂度最大且小于ccp_alpha的子树。默认情况下,不执行修剪。
可选函数:
- classes_:类标签(单输出问题)或类标签数组的列表(多输出问题)。
- feature_importances_:特征重要度。
- max_features_:max_features的推断值。
- n_classes_:类数(用于单输出问题),或包含每个输出的类数的列表(用于多输出问题)。
- n_features_:执行拟合时的特征数量。
- n_outputs_:执行拟合时的输出数量。
- tree_:
![]()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Aug 11 10:12:48 2020
@author: Admin
"""
# 引入数据
from sklearn import datasets
import numpy as np
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:,[2,3]]
y = iris.target
print("Class labels:",np.unique(y)) #打印分类类别的种类
## 画出决策边界图(只有在2个特征才能画出来)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_region(X,y,classifier,resolution=0.02):
markers = ('s','x','o','^','v')
colors = ('red','blue','lightgreen','gray','cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
# plot the decision surface
x1_min,x1_max = X[:,0].min()-1,X[:,0].max()+1
x2_min,x2_max = X[:,1].min()-1,X[:,1].max()+1
xx1,xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min,x1_max,resolution),
np.arange(x2_min,x2_max,resolution))
Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(),xx2.ravel()]).T)
Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1,xx2,Z,alpha=0.3,cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(),xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(),xx2.max())
# plot class samples
for idx,cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
plt.scatter(x=X[y==cl,0],
y = X[y==cl,1],
alpha=0.8,
c=colors[idx],
marker = markers[idx],
label=cl,
edgecolors='black')
# 切分训练数据和测试数据
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
## 30%测试数据,70%训练数据,stratify=y表示训练数据和测试数据具有相同的类别比例
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=1,stratify=y)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
## 估算训练数据中的mu和sigma
sc.fit(X_train)
## 使用训练数据中的mu和sigma对数据进行标准化
X_train_std = sc.transform(X_train)
X_test_std = sc.transform(X_test)
## 决策树分类器
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini',max_depth=4,random_state=1)
tree.fit(X_train_std,y_train)
plot_decision_region(X_train_std,y_train,classifier=tree,resolution=0.02)
plt.xlabel('petal length [standardized]')
plt.ylabel('petal width [standardized]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
tree_fit=tree.fit(X_train_std,y_train)
tree_fit.classes_ #array([0, 1, 2])
tree_fit.feature_importances_ #array([0.42708333, 0.57291667])
tree_fit.max_features_ #2
tree_fit.n_classes_ #3
tree_fit.n_features_ #2
tree_fit.n_outputs_ #1
tree_fit.tree_
![]()
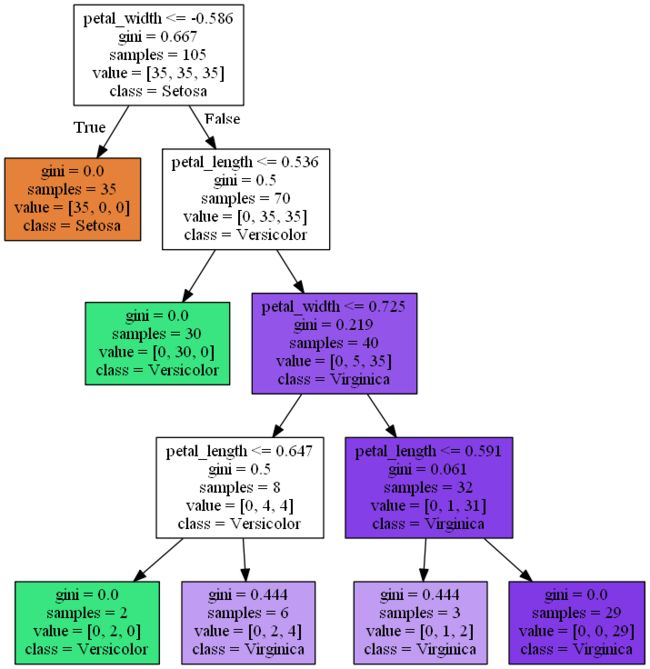
决策树可视化:
pydotplus的安装:在命令行输入conda install -c conda-forge pydotplus
## 决策树可视化
from pydotplus import graph_from_dot_data
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
dot_data = export_graphviz(tree,filled=True,class_names=['Setosa','Versicolor','Virginica'],
feature_names=['petal_length','petal_width'],out_file=None)
graph = graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_png('D:\\Users\\Desktop\\一部二部文件\\tree.png')
![]()
================================介绍2=====================
class sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion=’gini’, splitter=’best’, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, max_features=None, random_state=None, max_leaf_nodes=None, min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None, class_weight=None, presort=False)
一、参数
criterion:
特征选择标准,【entropy, gini】。默认gini,即CART算法。
splitter:
特征划分标准,【best, random】。best在特征的所有划分点中找出最优的划分点,random随机的在部分划分点中找局部最优的划分点。默认的‘best’适合样本量不大的时候,而如果样本数据量非常大,此时决策树构建推荐‘random’。
max_depth:
决策树最大深度,【int, None】。默认值是‘None’。一般数据比较少或者特征少的时候可以不用管这个值,如果模型样本数量多,特征也多时,推荐限制这个最大深度,具体取值取决于数据的分布。常用的可以取值10-100之间,常用来解决过拟合。
min_samples_split:
内部节点(即判断条件)再划分所需最小样本数,【int, float】。默认值为2。如果是int,则取传入值本身作为最小样本数;如果是float,则取ceil(min_samples_split*样本数量)作为最小样本数。(向上取整)
min_samples_leaf:
叶子节点(即分类)最少样本数。如果是int,则取传入值本身作为最小样本数;如果是float,则取ceil(min_samples_leaf*样本数量)的值作为最小样本数。这个值限制了叶子节点最少的样本数,如果某叶子节点数目小于样本数,则会和兄弟节点一起被剪枝。
min_weight_fraction_leaf:
叶子节点(即分类)最小的样本权重和,【float】。这个值限制了叶子节点所有样本权重和的最小值,如果小于这个值,则会和兄弟节点一起被剪枝。默认是0,就是不考虑权重问题,所有样本的权重相同。
一般来说如果我们有较多样本有缺失值或者分类树样本的分布类别偏差很大,就会引入样本权重,这时就要注意此值。
max_features:
在划分数据集时考虑的最多的特征值数量,【int值】。在每次split时最大特征数;【float值】表示百分数,即(max_features*n_features)
random_state:
【int, randomSate instance, None】,默认是None
max_leaf_nodes:
最大叶子节点数。【int, None】,通过设置最大叶子节点数,可以防止过拟合。默认值None,默认情况下不设置最大叶子节点数。如果加了限制,算法会建立在最大叶子节点数内最优的决策树。如果特征不多,可以不考虑这个值,但是如果特征多,可以加限制,具体的值可以通过交叉验证得到。
min_impurity_decrease:
节点划分最小不纯度,【float】。默认值为‘0’。限制决策树的增长,节点的不纯度(基尼系数,信息增益,均方差,绝对差)必须大于这个阈值,否则该节点不再生成子节点。
min_impurity_split(已弃用):
信息增益的阀值。决策树在创建分支时,信息增益必须大于这个阈值,否则不分裂。(从版本0.19开始不推荐使用:min_impurity_split已被弃用,以0.19版本中的min_impurity_decrease取代。 min_impurity_split的默认值将在0.23版本中从1e-7变为0,并且将在0.25版本中删除。 请改用min_impurity_decrease。)
class_weight:
类别权重,【dict, list of dicts, balanced】,默认为None。(不适用于回归树,sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeRegressor)
指定样本各类别的权重,主要是为了防止训练集某些类别的样本过多,导致训练的决策树过于偏向这些类别。balanced,算法自己计算权重,样本量少的类别所对应的样本权重会更高。如果样本类别分布没有明显的偏倚,则可以不管这个参数。
presort:
bool,默认是False,表示在进行拟合之前,是否预分数据来加快树的构建。
对于数据集非常庞大的分类,presort=true将导致整个分类变得缓慢;当数据集较小,且树的深度有限制,presort=true才会加速分类。
二、方法
(1)训练(拟合):fit(X, y[, sample_weight])——fit(train_x, train_y)
(2)预测:predict(X)返回标签、predict_log_proba(X)、predict_proba(X)返回概率,每个点的概率和为1,一般取predict_proba(X)[:, 1]
(3)评分(返回平均准确度):score(X, y[, sample_weight])——score(test_x, test_y)。等效于准确率accuracy_score
(4)参数类:获取分类器的参数get_params([deep])、设置分类器的参数set_params(**params)。——print(clf.get_params()) ,clf.set_params(***)
DecisionTreeClassifier的其他方法:
apply(X[, check_input])
Returns the index of the leaf that each sample is predicted as.
返回每个样本被预测为叶子的索引。
decision_path(X[, check_input]) Return the decision path in the tree 返回树的决策路径
get_depth() Returns the depth of the decision tree. 获取决策树的深度
get_n_leaves() Returns the number of leaves of the decision tree. 获取决策树的叶子节点数
模型调参注意事项:
1、当样本少数量但是样本特征非常多的时候,决策树很容易过拟合,一般来说,样本数比特征数多一些会比较容易建立健壮的模型
2、如果样本数量少但是样本特征非常多,在拟合决策树模型前,推荐先做维度规约,比如主成分分析(PCA),特征选择(Losso)或者独立成分分析(ICA)。这样特征的维度会大大减小。再来拟合决策树模型效果会好。
3、推荐多用决策树的可视化,同时先限制决策树的深度(比如最多3层),这样可以先观察下生成的决策树里数据的初步拟合情况,然后再决定是否要增加深度。
4、在训练模型先,注意观察样本的类别情况(主要指分类树),如果类别分布非常不均匀,就要考虑用class_weight来限制模型过于偏向样本多的类别。
5、决策树的数组使用的是numpy的float32类型,如果训练数据不是这样的格式,算法会先做copy再运行。
6、如果输入的样本矩阵是稀疏的,推荐在拟合前调用csc_matrix稀疏化,在预测前调用csr_matrix稀疏化。
其他:
如果使用默认DecisionTreeClassifier的参数,得到的AUC较低,很可能是因为出现过拟合,需调整默认参数,避免过拟合