如何利用OpenMesh实现不同格式的3D文件间的转换
可以进行的转化如下
(出处链接见文末参考文档)
本文示例将文本格式(ASCII)的stl文件转化为二进制格式(Binary)。
目录
step 1 配置openmesh环境
step2 代码实现
step3 设置命令参数
step 4 运行程序得到输出文件
参考文档
step 1 配置openmesh环境
可以参考
环境配置 | VS2017配置OpenMesh源码和环境
step2 代码实现
注:debug下跑得同,release下不行,也没搞清原因
#include
#include
// -------------------- OpenMesh
#include
#include
#include
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
using namespace OpenMesh;
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
typedef TriMesh_ArrayKernelT<> MyMesh;
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define CHKROPT( Option ) \
std::cout << " provides " << #Option \
<< (ropt.check(IO::Options:: Option)?": yes\n":": no\n")
#define CHKWOPT( Option ) \
std::cout << " write " << #Option \
<< (wopt.check(IO::Options:: Option)?": yes\n":": no\n")
#define MESHOPT( msg, tf ) \
std::cout << " " << msg << ": " << ((tf)?"yes\n":"no\n")
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void parse_commandline(int _argc, char **_argv, MyMesh& _mesh,
IO::Options &ropt, IO::Options &wopt);
void usage_and_exit(int xcode);
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
MyMesh mesh;
IO::Options ropt, wopt;
// -------------------- evaluate commandline
parse_commandline(argc, argv, mesh, ropt, wopt);
// -------------------- read mesh
if (!IO::read_mesh(mesh, argv[optind], ropt))
{
std::cerr << "Error loading mesh from file " << argv[optind] << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// -------------------- show options
std::cout << "File " << argv[optind] << std::endl;
std::cout << " is binary: "
<< (ropt.check(IO::Options::Binary) ? " yes\n" : " no\n");
std::cout << " byte order: ";
if (ropt.check(IO::Options::Swap))
std::cout << "swapped\n";
else if (ropt.check(IO::Options::LSB))
std::cout << "little endian\n";
else if (ropt.check(IO::Options::MSB))
std::cout << "big endian\n";
else
std::cout << "don't care\n";
std::cout << " provides VertexNormal"
<< ( // strange layout for doxygen
ropt.check(IO::Options::VertexNormal)
? ": yes\n" : ": no\n");
CHKROPT(VertexColor);
CHKROPT(VertexTexCoord);
CHKROPT(FaceNormal);
CHKROPT(FaceColor);
// -------------------- mesh stats
std::cout << "# Vertices: " << mesh.n_vertices() << std::endl;
std::cout << "# Edges : " << mesh.n_faces() << std::endl;
std::cout << "# Faces : " << mesh.n_faces() << std::endl;
// -------------------- show write options
std::cout << "Selected write options:\n";
std::cout << " use binary: "
<< (wopt.check(IO::Options::Binary) ? " yes\n" : " no\n");
std::cout << " byte order: ";
if (wopt.check(IO::Options::Swap))
std::cout << "swapped\n";
else if (wopt.check(IO::Options::LSB))
std::cout << "little endian\n";
else if (wopt.check(IO::Options::MSB))
std::cout << "big endian\n";
else
std::cout << "don't care\n";
std::cout << " write VertexNormal"
<< (wopt.check(IO::Options::VertexNormal) ? ": yes\n" : ": no\n");
CHKWOPT(VertexColor);
CHKWOPT(VertexTexCoord);
CHKWOPT(FaceNormal);
CHKWOPT(FaceColor);
// -------------------- show mesh capabilities
std::cout << "Mesh supports\n";
MESHOPT("vertex normals", mesh.has_vertex_normals());
MESHOPT("vertex colors", mesh.has_vertex_colors());
MESHOPT("texcoords", mesh.has_vertex_texcoords2D());
MESHOPT("face normals", mesh.has_face_normals());
MESHOPT("face colors", mesh.has_face_colors());
// -------------------- write mesh
std::cout << "Write mesh to " << argv[optind + 1] << "..";
if (!IO::write_mesh(mesh, argv[optind + 1], wopt))
{
std::cerr << "Error" << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Possible reasons:\n";
std::cerr << "1. Chosen format cannot handle an option!\n";
std::cerr << "2. Mesh does not provide necessary information!\n";
std::cerr << "3. Or simply cannot open file for writing!\n";
return 1;
}
else
std::cout << "Ok.\n";
return 0;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void parse_commandline(int _argc, char **_argv, MyMesh& _mesh,
IO::Options &ropt, IO::Options &wopt)
{
int c;
while ((c = getopt(_argc, _argv, "bhsBF:LMSV:X:")) != -1)
{
switch (c)
{
// -------------------- read options
// force binary input
case 'b':
ropt += IO::Options::Binary;
break;
// force swapping the byte order, when reading a binary file
case 's':
ropt += IO::Options::Swap;
break;
// -------------------- write options
// Write binary variant of format if possible
case 'B':
wopt += IO::Options::Binary;
break;
//
case 'F':
for (size_t i = 0; optarg[i]; ++i)
switch (optarg[i]) {
case 'n': wopt += IO::Options::FaceNormal; break;
case 'c': wopt += IO::Options::FaceColor; break;
}
break;
// Use little endian when writing binary data
case 'L':
wopt += IO::Options::LSB;
break;
// Use big endian when writing binary data
case 'M':
wopt += IO::Options::MSB;
break;
// Swap byte order when writing binary data
case 'S':
wopt += IO::Options::Swap;
break;
//
case 'V':
{
for (size_t i = 0; optarg[i]; ++i)
switch (optarg[i]) {
case 'n': // dont't change layout!!
wopt += IO::Options::VertexNormal;
break;
case 't': wopt += IO::Options::VertexTexCoord; break;
case 'c': wopt += IO::Options::VertexColor; break;
}
break;
}
// -------------------- request mesh' standard properties
case 'X':
{
char entity = '\0';
for (size_t i = 0; optarg[i]; ++i)
switch (optarg[i]) {
case 'v':
case 'f': entity = optarg[i]; break;
case 'n':
switch (entity) {
case 'v': _mesh.request_vertex_normals(); break;
case 'f': _mesh.request_face_normals(); break;
}
break;
case 'c':
switch (entity) {
case 'v': _mesh.request_vertex_colors(); break;
case 'f': _mesh.request_face_colors(); break;
}
break;
case 't':
switch (entity) {
case 'v': _mesh.request_vertex_texcoords2D(); break;
}
break;
}
break;
}
// -------------------- help
case 'h':
usage_and_exit(0);
default:
usage_and_exit(1);
}
}
if (_argc - optind != 2)
usage_and_exit(1);
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void usage_and_exit(int xcode)
{
std::ostream &os = xcode ? std::cerr : std::cout;
os << "Usage: io_options [Options] step3 设置命令参数
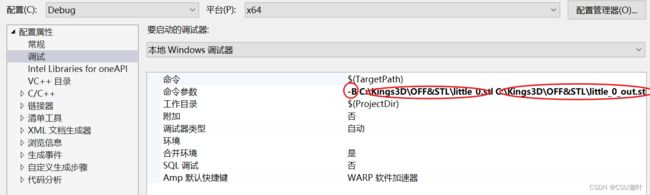
命令参数之间用空格而不是分号隔开
这里我设置了3个参数
-B 表示输出文件为二进制
C:\Kings3D\OFF&STL\little_0.stl 输入文件
C:\Kings3D\OFF&STL\little_0_out.stl 输出文件
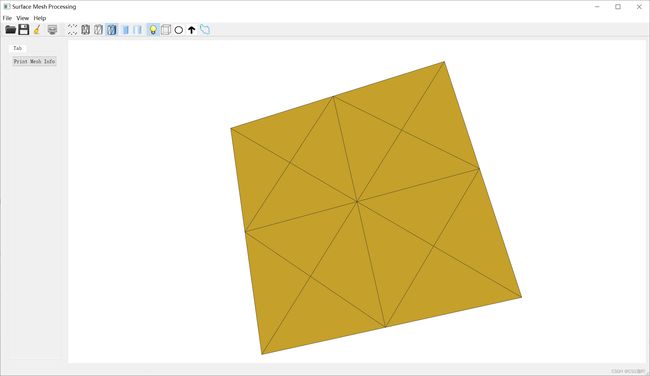
step 4 运行程序得到输出文件
用一个可视化程序打开转化后的二进制stl,验证无误
参考文档
OpenMesh: Using IO::Options