Matlab 数字图像处理的基本函数和运算
目录
目录
目录
图像类别
基本函数
读写显示函数
数据清空命令
取整函数
图像转换
获取图片大小
图像运算
图像的代数运算
图像的逻辑运算
图像几何运算
平移
镜像
旋转
缩放
图像类别
二值图像、亮度图像、索引图像、RGB图像
数据类型:int、double
基本函数
读写显示函数
imread() %读
imwrite() %写
imtool() %显示
imshow() %显示
subplot() %分图double型的图像显示:imshow(I,[]);把图像拉长显示
数据清空命令
clear all; %清楚工作空间所有变量
close all; %关闭所有窗口
clc; %清空命令行取整函数
round(); %对浮点数取整,四舍五入
fix(); %对浮点数直接取整数位
floor(); %向下取整
ceil(); %向上取整图像转换
rgb2ind(x,N); %rgb到索引,N可以为64,0.2,colorcube(),jet(M)等
im2bw(I,0.4); %0.4为阈值 将图像转化为二值图像
%基本上图像转换都是 'x1'2'x2' ,'x1''x2'都是图像的英文前几个字母获取图片大小
[m,n]=size(I); %获取I的行列
m=size(I,1); %获取I的行,同理,列就是2
图像运算
图像的代数运算
imadd(X,Y); %加法,图像有叠加效果
imsubtract(); %减法
imabsdiff(); %也是减法,可以避免有负值导致该点数值为0
immultiply(); %乘法,最好先将图像转换为double型,im2double()
imdivide(A,B); %除法
imcompletent(); %求补图像的逻辑运算
&:与
|:或
~:非
xor(A,B):异或
图像几何运算
平移
向下平移
clear all;
close all;
clc;
I=imread('coins.png');
[m,n]=size(I);
J=zeros(m,n);
d1=50;
for i=1:m-d1
for j=1:n
J(i+d1,j)=I(i,j); %向下移
end
end
subplot(121),imshow(I);
subplot(122),imshow(J,[]); %J为double型
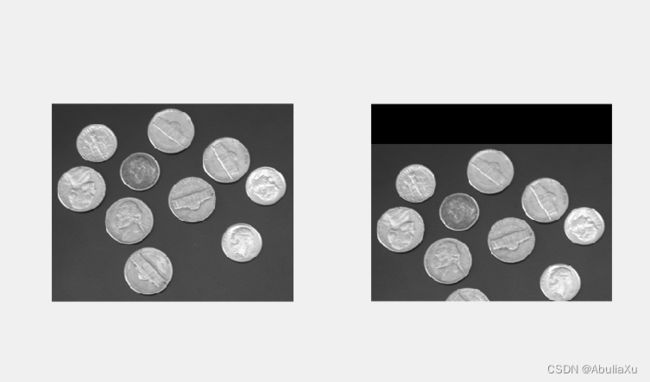
相右平移
clear all;
close all;
clc;
I=imread('coins.png');
[m,n]=size(I);
J=zeros(m,n);
d1=50;
for i=1:m
for j=1:n-d1
J(i,j+d1)=I(i,j);
end
end
subplot(121),imshow(I);
subplot(122),imshow(J,[]);
镜像
水平镜像
clear all;
close all;
clc;
I=imread('cameraman.tif');
[m,n]=size(I);
J=zeros(m,n);
for i=1:m
for j=1:n
J(i,j)=I(i,n-j+1);
end
end
subplot(121),imshow(I);
subplot(122),imshow(J,[]);竖直镜像就是y保持不变,x坐标处变化。
旋转
clear all;
close all;
clc;
I=imread('cameraman.tif');
[m,n]=size(I);
J=imrotate(I,30,'bicubic','crop'); %填充
K=imrotate(I,30,'bicubic','loose'); %不填充
%其中'bicubic'是插值方法,还有'nearest':最近邻插值算法,'bilinear':双线性插值算法,
%'bicubic':双三次插值算法
subplot(131),imshow(I);
subplot(132),imshow(J);
subplot(133),imshow(K);缩放
clear all;
close all;
clc;
I=imread('cameraman.tif');
[m,n]=size(I);
J=imresize(I,5);
K=imresize(I,0.3);
subplot(131),imshow(I);
subplot(132),imshow(J);
subplot(133),imshow(K);从上图可以看出,imresize默认是等比缩放,数值<1:缩小,数值>1:放大。