models.py YOLOv3 中 darknet 模型构建过程
文章目录
-
- 说明:
- 模型构建如下:
-
- 1. 模型构建过程
-
- 1. 第一步:理解 模型配置文件 yolov3.cfg
- 2. 第二步:解析 config_path 配置文件,生成 module_defs 列表
- 3. 第三步:根据 module_defs 列表,创建 module_list 模型列表
- 3.1 构建 module_list 模型列表 的主要代码如下:
- 3.2 模型中需要重点理解的地方:
-
- 3.2.1 定义一个 yolo层 需要的三个参数
- 3.2.2 yolo层对数据的处理过程, 计算过程
- 2. yolo 层中loss 的计算
- 完
说明:
- 代码来源:PyTorch-YOLOv3:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/PyTorch-YOLOv3
- 模型是通过论文作者的 .cfg 配置文件自动生成的。
模型构建如下:
1. 模型构建过程
1. 第一步:理解 模型配置文件 yolov3.cfg
YOLO 模型根据一个.cfg 配置文件生成的。配置文件路径:opt.model_def 的默认地址是 “config/yolov3.cfg”
“yolov3.cfg” 文件的部分内容如下:
[net]
# Testing
#batch=1
#subdivisions=1
# Training
batch=16
subdivisions=1
width=416
........
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=32
size=3
.......
[shortcut]
from=-3
activation=linear
......
[yolo]
mask = 6,7,8
anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326
classes=80
num=9
jitter=.3
ignore_thresh = .7
truth_thresh = 1
random=1
[route]
layers = -4
......
[upsample]
stride=2
......
2. 第二步:解析 config_path 配置文件,生成 module_defs 列表
self.module_defs = parse_model_config(config_path) # model.py 文件中解析
parse_model_config 函数:解析 “config/yolov3.cfg” 文件内容成字典,
parse_model_config(config_path) 解析后的结果 self.module_defs(字典)如下:
module_defs 列表 内容如下:
[{'type': 'net', 'batch': '16', 'subdivisions': '1', 'width': '416', 'height': '416', 'channels': '3', 'momentum': '0.9', 'decay': '0.0005', 'angle': '0', 'saturation': '1.5', 'exposure': '1.5', 'hue': '.1', 'learning_rate': '0.001', 'burn_in': '1000', 'max_batches': '500200', 'policy': 'steps', 'steps': '400000,450000', 'scales': '.1,.1'},
{'type': 'convolutional', 'batch_normalize': '1', 'filters': '32', 'size': '3', 'stride': '1', 'pad': '1', 'activation': 'leaky'},
{'type': 'convolutional', 'batch_normalize': '1', 'filters': '64', 'size': '3', 'stride': '2', 'pad': '1', 'activation': 'leaky'},
{'type': 'convolutional', 'batch_normalize': '1', 'filters': '32', 'size': '1', 'stride': '1', 'pad': '1', 'activation': 'leaky'},
{'type': 'convolutional', 'batch_normalize': '1', 'filters': '64', .....
......
}
3. 第三步:根据 module_defs 列表,创建 module_list 模型列表
- module_list 模型列表,即一个
nn.ModuleList()列表, 将网路的各个层nn.Sequential()依次添加在其中。(如 conv、maxpool、upsample、route、shortcut、yolo 层) - 构建模型列表是为了给 model.forward() 函数使用的。
self.hyperparams, self.module_list = create_modules(self.module_defs)
print(len(self.module_defs)) # 107
print(len(self.module_list)) # 107
self.hyperparams 的内容(由 module_defs 列表中第一个字典的内容 构造的)如下:
{'type': 'net', 'batch': '16', 'subdivisions': '1',
'width': '416', 'height': '416', 'channels': '3',
'momentum': '0.9', 'decay': '0.0005', 'angle': '0',
'saturation': '1.5', 'exposure': '1.5', 'hue': '.1',
'learning_rate': '0.001', 'burn_in': '1000',
'max_batches': '500200', 'policy': 'steps',
'steps': '400000,450000', 'scales': '.1,.1'}
self.module_list 的内容(由 module_defs 列表中除了第一个字典的其他内容 构造的)如下:
module_list 内容如下:
ModuleList(
(0): Sequential(
(conv_0): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(batch_norm_0): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(leaky_0): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
)
(1): Sequential(
(conv_1): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(batch_norm_1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(leaky_1): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
)
......
(4): Sequential(
(shortcut_4): EmptyLayer()
)
......
(11): Sequential(
(shortcut_11): EmptyLayer()
)
(12): Sequential(
(conv_12): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(batch_norm_12): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(leaky_12): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
)
.......
(81): Sequential(
(conv_81): Conv2d(1024, 255, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(82): Sequential(
(yolo_82): YOLOLayer(
(mse_loss): MSELoss()
(bce_loss): BCELoss()
)
)
(83): Sequential(
(route_83): EmptyLayer()
)
(84): Sequential(
(conv_84): Conv2d(512, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(batch_norm_84): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(leaky_84): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
)
(85): Sequential(
(upsample_85): Upsample()
)
(86): Sequential(
(route_86): EmptyLayer()
)
(87): Sequential(
(conv_87): Conv2d(768, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(batch_norm_87): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(leaky_87): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
)
......
(104): Sequential(
(conv_104): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(batch_norm_104): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(leaky_104): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
)
(105): Sequential(
(conv_105): Conv2d(256, 255, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(106): Sequential(
(yolo_106): YOLOLayer(
(mse_loss): MSELoss()
(bce_loss): BCELoss()
)
)
)
3.1 构建 module_list 模型列表 的主要代码如下:
- module_list 是根据 module_defs(列表)构建的。
- module_list 是模型列表,列表中的 107 个Sequential()之间是相互独立的,但有先后关系的,可以通过 for … in … 来遍历其中的每一个 Sequential()。
主要涉及的函数如下:
import torch.nn as nn
def create_modules(module_defs):
hyperparams = module_defs.pop(0) # 弹出列表中得第一元素(第一个字典,第一个保存的是net的一些设置)
output_filters = [int(hyperparams["channels"])] # 用于记录 图片的通道数目的变化 3
module_list = nn.ModuleList() # 用于 依次存放每一个网络结构层
for module_i, module_def in enumerate(module_defs): # 遍历列表中的每一个字典(每一层网络)
modules = nn.Sequential() # 构架一个 小模块
if module_def["type"] == "convolutional": # 卷积层
.....
filters = int(module_def["filters"])
modules.add_module( # 模型添加 卷积层
f"conv_{module_i}",
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels= output_filters[-1]
out_channels=
kernel_size=
stride=
padding=
bias=not bn,
),
)
if bn: # 模型添加 BN 层
moudle.add_moudule(f"batch_norm_{module_i}", nn.BatchNorm2d(filters, momentum=0.9, eps=1e-5))
if module_def["activation"] == "leaky": # 模型添加 relu 层
modules.add_module(f"leaky_{module_i}", nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)) # x < 0时, y = 0.1 * X
elif module_def["type"] == "maxpool": # 池化层
modules.add_module(f"_debug_padding_{module_i}", nn.ZeroPad2d((0, 1, 0, 1))) # 模型添加 pad 处理
modules.add_module(f"maxpool_{module_i}", maxpool) # 模型添加 最大池化层
elif module_def["type"] == "upsample": # 上采样 参数设置
modules.add_module(f"upsample_{module_i}", upsample)
elif module_def["type"] == "route":
filters = ...
modules.add_module(f"route_{module_i}", EmptyLayer())
elif module_def["type"] == "shortcut":
filters = ...
modules.add_module(f"shortcut_{module_i}", EmptyLayer())
elif module_def["type"] == "yolo":
modules.add_module(f"yolo_{module_i}", yolo_layer)
module_list.append(modules) # modules 是模型中一个 Sequential() # module_list 是所有的 Sequential(),即整个模型
output_filters.append(filters) # filters 数量
return hyperparams, module_list
3.2 模型中需要重点理解的地方:
3.2.1 定义一个 yolo层 需要的三个参数
yolo_layer = YOLOLayer(anchors, num_classes, img_size)
anchors # 一共有 9 组。每一个yolo检测层只使用其中的三组,如:[(116, 90), (156, 198), (373, 326)]
num_classes # 80
img_size # 图片的大小 416
3.2.2 yolo层对数据的处理过程, 计算过程
-
需要的参数:
grid_size # 网格的个数 13
stride # 每个网格的步幅宽度 416 / 13 = 32
scaled_anchors # 缩放anchors: [(116, 90), (156, 198), (373, 326)] / 32
grid_x # tensor([[[
[0, 1, 2 … 12],
[0, 1, 2 … 12],
[0, 1, 2 … 12]]]])
grid_y # tensor([[[
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2]
…
[12, 12, 12]]]])
scaled_anchors # tensor([
[ 3.6250, 2.8125],
[ 4.8750, 6.1875],
[11.6562, 10.1875]], device=‘cuda:0’)
anchor_w # 当前三个anchor 的宽度 3.6 4.8 11.6
anchor_h # 当前三个anchor 的高度 2.8 6.1 10.1 -
输入yolo层的数据是 x :
三个yolo层(网路一共有三个yolo层)中的输入数据x的shape 分别是:
torch.Size([1, 255, 13, 13])
torch.Size([1, 255, 26, 26])
torch.Size([1, 255, 52, 52])
这里的255是不能改变的 255 = 3 *(5 + 80) (255 的原因:每张图片会被分成 13 * 13 个格子,每个格子使用 3 个anchor 进行预测, 每个 anchor 需要预测 4 个坐标的概率 + 1个box框的概率 + 80 个类别的概率。)
prediction时,需要将255才开成 3 * 85,方便后续处理:
torch.Size([1, 3, 13, 13, 85])
torch.Size([1, 3, 26, 26, 85])
torch.Size([1, 3, 52, 52, 85]) -
输出 yolo 层的数据是 output
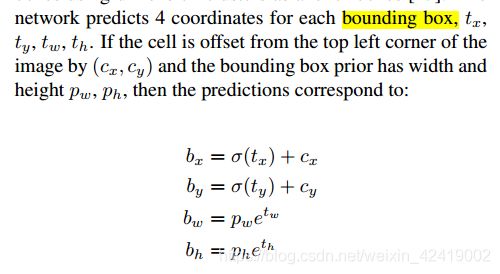
在 yolo 层中,不是对数据进行卷积、池化之类的操作,而是对数据进行sigmod或exp之类的处理。4个坐标数据需要经过论文中计算, 将相对于 grid cell 的坐标转化成相对于整幅图片的坐标。
output 也是由 1 * 13 * 13 * (4 + 1 + 80) 组成,只是其中的 4 +1 + 80 个数据经过 “类似”sigmod操作后的 output。
程序中的计算代码如下:
# 4个坐标的 sigmod 处理过程:
x = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 0]) # Center x # 预测到的一个目标框的 x 值
y = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 1]) # Center y
pred_boxes[..., 0] = x.data + self.grid_x # 给每一个预测的box 添加片偏置量, 作为最后的预测结果
pred_boxes[..., 1] = y.data + self.grid_y
pred_boxes[..., 2] = self.anchor_w * torch.exp(w.data)
pred_boxes[..., 3] = self.anchor_h * torch.exp(h.data)
# 1个 边框置信度 和 80个类别信息也是经过 sigmod 处理后得到的。
pred_conf = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 4]) # Conf 预测到的一个目标框的 置信度 值
pred_cls = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 5:]) # Cls pred. 预测到的一个目标框的 80个类别 的概率
2. yolo 层中loss 的计算
重点理解
- yolo 层中 计算 loss时, 输入的坐标数据不是相对于原始图片标签坐标,而是相对于特征图的坐标信息,所以计算 loss 时,需要将相对于原图的标签转化成相对于特征图的标签坐标信息。
- mse_loss:均方损失函数, 计算坐标 x y w h 时使用
- bce_loss:二分类用的交叉熵损失函数,计算 1 + 80 个数据时使用
- 最后总的 loss 就是前面这些 loss 的简单相加即可。
# Loss : Mask outputs to ignore non-existing objects (except with conf. loss)
loss_x = self.mse_loss(x[obj_mask], tx[obj_mask]) # mse 均方误差
loss_y = self.mse_loss(y[obj_mask], ty[obj_mask])
loss_w = self.mse_loss(w[obj_mask], tw[obj_mask])
loss_h = self.mse_loss(h[obj_mask], th[obj_mask])
loss_conf_obj = self.bce_loss(pred_conf[obj_mask], tconf[obj_mask]) # 二分类用的交叉熵损失函数
loss_conf_noobj = self.bce_loss(pred_conf[noobj_mask], tconf[noobj_mask]) # 如何理解两个类别?????
loss_conf = self.obj_scale * loss_conf_obj + self.noobj_scale * loss_conf_noobj # 判断有误边框。有目标:没目标 是 1:100的权重
loss_cls = self.bce_loss(pred_cls[obj_mask], tcls[obj_mask]) # 80个类别的
total_loss = loss_x + loss_y + loss_w + loss_h + loss_conf + loss_cls # 总的loss