Thread-Process-AppDomain
Thread
1、为什么我设置了多线程的优先级,可是线程的输出并不是按优先级的高低输出啊?
看如下代码:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace _05线程的优先级 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Thread[]t = new Thread[5]; t[0] =new Thread( new ThreadStart(Tell)); t[0].Name = "Lowest"; t[0].Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest; t[1] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Tell)); t[1].Name = "BelowNormal"; t[1].Priority = ThreadPriority.BelowNormal; t[2] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Tell)); t[2].Name = "Normal"; t[3] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Tell)); t[3].Name = "AboveNormal"; t[3].Priority = ThreadPriority.AboveNormal; t[4] = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Tell)); t[4].Name = "Highest"; t[4].Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest; foreach (Thread itemt in t) { itemt.Start(); } Console.ReadLine(); } public static void Tell() { Console.WriteLine("当前线程为:{0},线程级别是{1}",Thread.CurrentThread.Name,Thread.CurrentThread.Priority); } } }
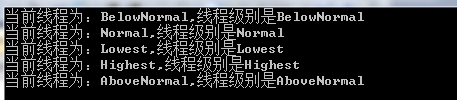
运行结果之一:
首先,解释一下线程的优先级:
线程的优先级并不是你想象的先执行哪个后执行哪个
而是所有的线程不论优先级高低都会执行,
优先级越高表示CPU分配给该线程的时间片越多,执行时间就多
优先级越低表示CPU分配给该线程的时间片越少,执行时间就少
就这个问题我们可以做一些测试,看如下代码:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace _05线程的优先级_测试线程优先级发生概率 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Thread th1 = new Thread(delegate() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { Console.Write("H"); } }); // th1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest; Thread th2 = new Thread(delegate() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { Console.Write("A"); } } ); // th2.Priority = ThreadPriority.AboveNormal; Thread th3 = new Thread(delegate() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { Console.Write("N"); } } ); // th3.Priority = ThreadPriority.Normal; Thread th4 = new Thread(delegate() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { Console.Write("B"); } } ); // th4.Priority = ThreadPriority.BelowNormal; Thread th5 = new Thread(delegate() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { Console.Write("L"); } } ); // th5.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest; th1.Start(); th2.Start(); th3.Start(); th4.Start(); th5.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
运行结果之一:
将注释代码取消注释,运行结果之一:
总结一句话就是:我们给线程分配优先级增加或减少的是该线程被优先执行的概率:
ThreadPool
static void Main(string[] args) { //打印当前线程ID Console.WriteLine("Main threading"+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); //调用线程池中的线程,将方法插入队列 for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { //线程池线程执行的回调方法 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(new Program().Show), "OK"); } Console.ReadKey(); } public void Show(object s) { Console.WriteLine("ThreadPool's thread,number is"+s.ToString()+" "+Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); }
当我们想绝对控制一个线程时单独创建线程,一般就用线程池交于系统分配
ObjectPool
namespace 对象池_线程池技术 { class Program { /// <summary> /// 模拟一个生产者消费者的对象池 /// 具体情景:池子的容量是100,生产者向池子里生产产品,当产品个数小于0或者大于100时继续生产但是不添加到 /// 池子里面去;当池子中有产品时,消费者开始消费产品,消费者消费是从底端开始的;采用锁机制是因为当消费 /// 正在消费完第8个产品时,生产者生产完第9个产品,该产品应放在原来第8号产品的位置,但此时index没有被更 /// 新,所以对对象锁定 /// </summary> /// <param name="args"></param> static void Main(string[] args) { //1、首先定义一个对象池 MyPool[]myPools=new MyPool[100]; //2、定义一个游标 int index = 0; //3、声明一个对象 Program program = new Program(); //4、定义生产者线程 #region 生产者线程 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { Thread threadProducer = new Thread( () => { while (true) { lock (program) { //声明对象 MyPool myPool = new MyPool(); //进行判断 if (index >= 100 || index < 0) { continue;//继续生产 } //将生产的对象添加到对象池中 myPools[index] = myPool; //对象索引增加 index++; //打印当前生产的产品的所在线程 Console.WriteLine("生产者生产一个产品,该产品所在线程是:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } //生产一次休息1秒-1秒之类生产者可能生产了好几个,设置的时间不同产生的效果也就不一样 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } } ); //设置为后台线程 threadProducer.IsBackground = true; //启动该线程 threadProducer.Start(); } #endregion for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) { //声明消费者线程 Thread threadConsumer = new Thread( () => { while (true) { lock (program) { if (index <= 0) { continue;//继续消费 } //当生产者线程执行一次之后index++,此时该index++的产品还未生产出来,消费者执行时index已经加了1,所以对应的应该减1 myPools[index - 1] = null; index--; //打印消线程费 Console.WriteLine("消费者消费掉了一个产品,该消费者线程是:{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } //消费一个产品休息1秒钟 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } } ); //后台线程 threadConsumer.IsBackground = true; //开始执行消费者线程 threadConsumer.Start(); } Console.ReadKey(); } } public class MyPool { public string Name { get; set; }//名字 } }
其中用到了lock锁,锁住的是同一个对象,不然不是同一个锁,需要提醒一下的是lock锁定的是引用类型对象,当然你也可以锁定值类型,不过需要装箱转换成object类型,装箱后再分配内存地址,有时候会想能否锁定字符串,当然可以锁定,但是会出问题,字符串是全局变量,比如说锁定了lock("a"),那么你能保证这个字符串不会再出现在你程序的其他地方吗?
Process
1、Start a process
static void Main(string[] args) { //开启一个新的进程 Process process = Process.Start("iexplore.exe","http://www.baidu.com"); //打印该进程的标识符Id Console.WriteLine(process.Id); Console.ReadKey(); }
2、Foreach all processes
#region Foreach processes //获取当前计算机的线程 Process[] allProcess = Process.GetProcesses(); //遍历所有线程 foreach (var process in allProcess) { //打印线程的ID和Name Console.WriteLine(process.Id + " : " + process.ProcessName); } Console.ReadKey(); #endregion
3、Kill CurrentProcess
//kill掉当前线程 Process.GetCurrentProcess().Kill();
在操作office的时候会弹出excel、word等进程,这时候就需要考虑将其kill掉
private void KillExcel() { try { System.Diagnostics.Process[] processes = System.Diagnostics.Process.GetProcesses(); foreach (System.Diagnostics.Process process in processes) { if (process.ProcessName.ToLower().Equals("excel")) { process.Kill(); } } } catch (Exception exception) { exception.Message.ToString(); } }
一个进程中含有好几个应用程序域=》每个应用程序域中可以执行多个线程=》对于另外开辟的线程,同一时间只能在一个应用程序域中执行,如下是传智播客教程截图,该很容易懂吧