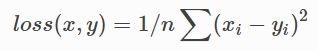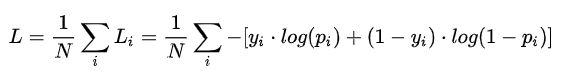CIFAR-10数据集分类实验报告
本篇文章只是一篇CIFAR-10数据集分类简介,是我的一门课程的大作业,从BP网络进行分类到CNN进行分类。
程序贴在最后!!!
1 开发环境
目前主流的神经网络框架有Tensorflow,Pytorch,MXNET,Keras等。本次实验使用Pytroch深度学习框架。PyTorch看作加入了GPU支持的numpy,并且它是一个拥有自动求导功能的强大的深度神经网络。
2 BP神经网络相关知识
2.1 激活函数
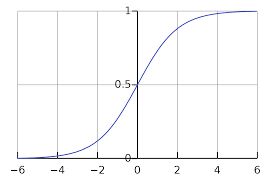
-
上图是sigmoid激活函数。
-
计算量大,反向传播求误差梯度时,求导涉及除法。
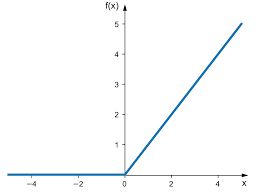
-
上图是ReLU激活函数。
-
ReLU 的收敛速度会比 sigmoid 快很多。
2.2 损失函数
3 CIFAR-10数据集
- 该数据集分为训练集和测试集,一共有10种动物。其中,训练集有50000张图片,测试集有10000张图片,训练集和测试集不重叠,图片大小为32 * 32 * 3。
4 BP网络实验
- SGD(随机梯度下降)优化策略。SGD就是每一次随机抽取一个mini-batch,迭代计算mini-batch的梯度,然后对参数进行更新。weight decay(权重衰减):设置为5e-4,防止过拟合,是放在正则项(regularization)前面的一个系数,正则项一般指示模型的复杂度。momentum(动量):设置为0.9,提高收敛速度。学习率设置为0.01,ReLU实验的学习率为0.005。
- 引入Batchsize,设置为128,通过并行化提高内存的利用率。就是尽量让你的GPU满载运行,提高训练速度;适当Batch Size使得梯度下降方向更加准确。
- 输入是将32 * 32 * 3的图像展平为3072维的图像特征,输出是10维。
- 总共学习100个epochs。
- 从隐藏层神经元个数、激活函数和隐藏层层数三个角度实验,证明对BP网络的影响。
- 实验并没有对学习率有一个很好的调整,只是大范围的确定了学习率,所以训练的精度不代表模型最好精度。
4.1 三层BP网络隐藏层神经元个数
-
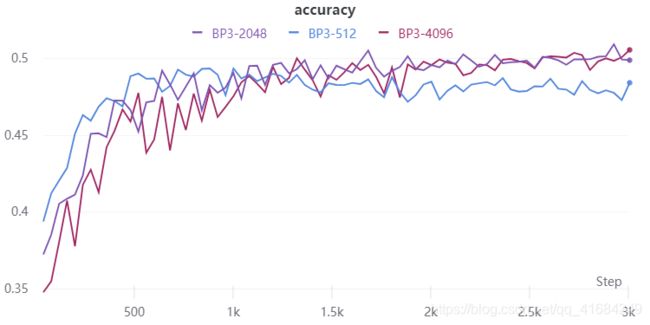
如图,对三层BP网络的隐藏层分别设置为8,2048和10240个神经元。
-
对于隐藏层设置为8个神经元,神经元个数太少会导致网络表达能力太弱,无法对特征进行正确的表达。
-
对于隐藏层设置为10240个神经元,神经元个数太多不一定就能够对特征有正确的表达,而且神经元个数过大容易导致模型泛化能力较差。
-
分别选择512,2048,4096个神经元,可以看到512个神经元相对于2048和4096个神经元稍微差一点,而2048和4096个神经元效果相似。
4.2 激活函数Sigmoid和ReLU
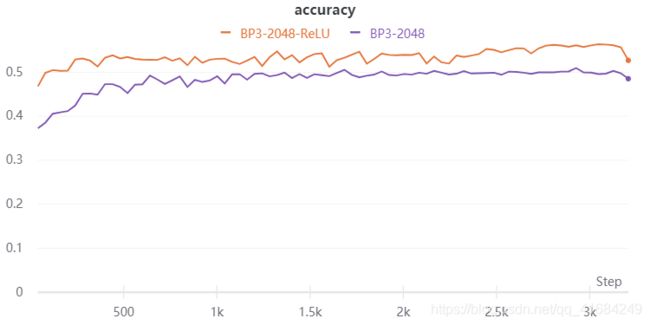
- 使用三层BP网络实验,隐藏层神经元个数为2048,该实验只改变了两个模型的激活函数。
- 可以看到ReLU激活函数明显优于Sigmoid激活函数。
- ReLU收敛速度更快,且能使损失收敛到一个更小的值。
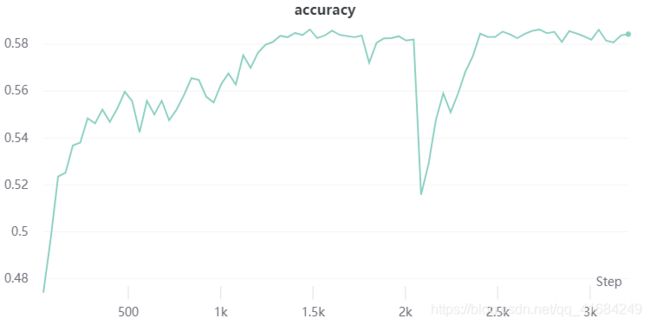
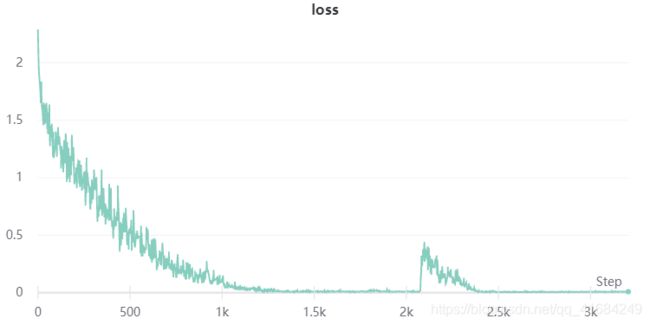
- 注意这里有一个尖峰,损失突然增大,我个人的理解是我只固定了一个学习率,当损失很小的适合应该使用小学习率。
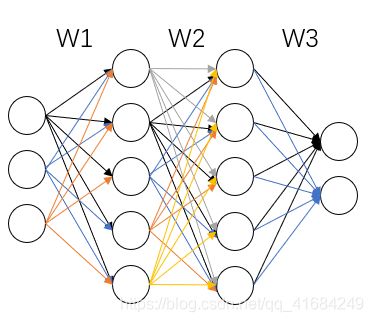
4.3 隐藏层层数
-
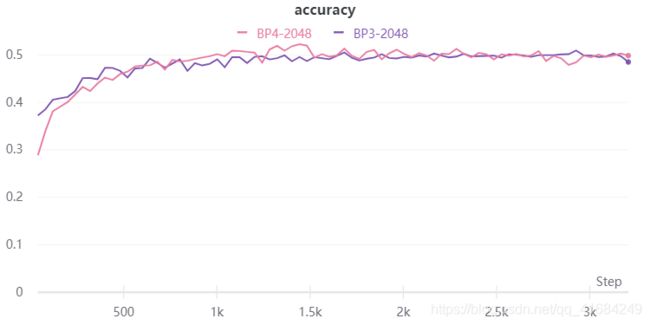
如图所示,粉色和紫色分别表示4层BP网络和3层BP网络,他们使用Sigmoid激活函数。
-
层数的增加反而训练收敛速度变慢,看测试准确率几乎相似,,说明层数增加并没有对特征有个更好的非线性表示,这有可能是我参数没调好,也有可能是Sigmoid激活函数两端梯度为0,梯度不均匀,训练不稳定。


-
在上述实验基础上,将Sigmoid函数改为ReLU函数,可以看到,层数增加,模型的收敛速度更快,精度更高,能更好的表示非线性。
5 卷积神经网络
- BP网络实验我将图片的像素展平为32 * 32 * 3的数组,将该数组作为这张图片的特征。实际上可以将分类问题实际上是特征提取之后加全连接层进行分类,这里提取特征就可以使用效率更高的CNN卷积神经网络。
5.1 LeNet-5
- 首先进行卷积操作,提取图片特征后,将特征展平用全连接层进行分类。

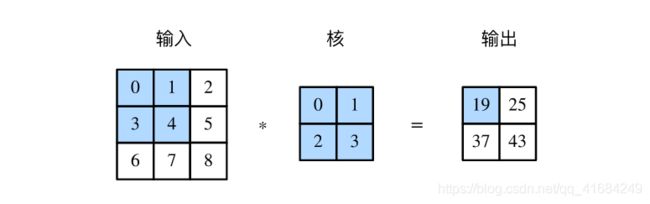
- 网络结构,假设原来图像大小32 * 32 * 3,conv1将其变为16 * 16 * 6,conv2经过第一个Conv卷积核变为12 * 12 * 16,然后经过MaxPool变为6 * 6 * 16,然后输入到全连接层。
5.2 自制CNN
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 8, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(8, 16, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(64 * 2 * 2, 120),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
- 使用大小为3的卷积核
5.3 实验
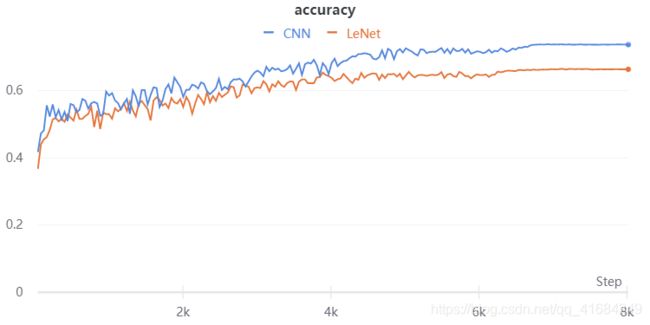
- 如图,使用卷积神经网络效果要远远好于BP网络。
6 代码
import torch
from torch.utils import data
import torch.nn as nn
from tqdm import tqdm
import wandb
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
class BP_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(BP_model, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(32 * 32 * 3, 2048) # 线性层
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(2048, 2048)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(2048, 10)
def forward(self, x):
out = x.view(-1, 32 * 32 * 3) # 展平处理
out = nn.ReLU()(self.fc1(out))
out = nn.ReLU()(self.fc2(out))
out = self.fc3(out)
return out
class LeNet5(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet5, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5, 1, 2), # 卷积核 原来通道数 转换后通道数 卷积核大小 步长 填充
nn.ReLU(), # 激活函数
nn.MaxPool2d(2) # 最大池化层
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5, 1, 0),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(16 * 6 * 6, 120),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(-1, 16 * 6 * 6)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 8, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(8, 16, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(64 * 2 * 2, 120),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = x.view(-1, 64 * 2 * 2)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
wandb.init(project="BP")
wandb.config.dropout = 0.2
wandb.config.hidden_layer_size = 128
# 读取数据,数据预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010))]) # totensor是将0-255转到0-1,normalize是将0-1转换到-1-1
trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True,
download=False, transform=transform) # 读取数据集,数据预处理
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=128,
shuffle=True, num_workers=1, pin_memory=True) # 打乱,包装成batchsize
testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False,
download=False, transform=transform)
testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=128,
shuffle=False, num_workers=1, pin_memory=True)
device = torch.device("cuda:0") # 选择cpu或者GPU
# model = BP_model()
# model = LeNet5() # 用哪个模型,打开哪个,屏蔽另外两个
model = CNN()
model.to(device) # 选择cpu或者gpu
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 交叉熵损失
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD([{'params': model.parameters()}],
lr=0.005, weight_decay=5e-4, momentum=0.9) # 随机梯度优化策略
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=200) # CNN训练使用该学习率优化策略,bp网络也可以使用试试
for epoch in range(80):
# 训练
model.train()
for i, (img, label) in tqdm(enumerate(trainloader)):
img, label = img.to(device, non_blocking=True), label.to(device, non_blocking=True).long() # 加载数据
output = model(img) # 计算结果
loss = criterion(output, label) # 计算损失
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 优化器更新
iters = epoch * len(trainloader) + i
if iters % 10 == 0:
wandb.log({'loss': loss}) # 可视化
# 测试
accuracy = 0
model.eval()
for i, (img, label) in enumerate(testloader):
img, label = img.to(device), label.to(device).long()
output = model(img)
output = output.max(dim=1)[1] # 预测是哪一类
accuracy += (output==label).sum().item() # 准确率计算
accuracy = accuracy / 10000 # 准确率计算
print(accuracy)
wandb.log({'accuracy': accuracy}) # 可视化
scheduler.step() # 学习率更新