一、类的继承
文章目录
-
-
-
- 一、类的继承
-
- 1.继承类的定义
-
- 2.三种类继承的方式以及成员声明的方式+多个类的继承
-
1.继承类的定义
#include
using namespace std;
class Student {
protected:
const char* name;
int num;
public:
Student(const char* name, int num) :name(name), num(num) {};
void display(void);
};
void Student::display(void) {
cout << "name:" << name << "num:" << num << endl;
}
class Pri_Student:public Student {
private:
int height;
int weight;
public:
Pri_Student(const char* name, int num, int h, int w) :Student(name, num) { height = h; weight = w; };
//不仅需要对派生类增加的数据成员的初始化,也要考虑基类的数据成员的初始化(直接调用基类的初始化函数)
//格式:派生类的构造函数(全部成员参数):基类的构造函数(基类的成员参数){派生类参数的初始化}
//实现形式非常类似与参数初始化列表
//也可以用参数初始化列表一并进行参数初始化
//Pri_Student(char name[], int num, int h, int w) :Student(name, num) ,height(h),weight(w){};
void display1(void);
void display(void); //在子类中也可以定义与基类相同名字的函数,其定义会覆盖基类的函数定义
};
void Pri_Student::display(void) {
cout << "display" << endl;
}
void Pri_Student::display1(void) {
cout << "name: " << name << "num: " << num << "height: " << height << "weight: " << weight << endl;
}
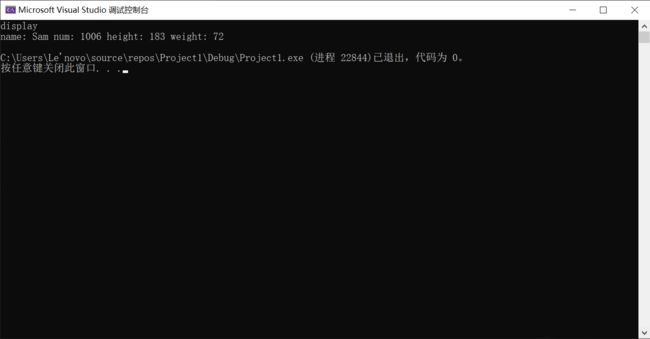
int main(void) {
Pri_Student S1("Sam", 1006, 183, 72);
S1.display();
S1.display1();
return 0;
}
运行结果1:
2.三种类继承的方式以及成员声明的方式+多个类的继承
# private:私有(最少用)
# protected:保护(派生类可以访问)
# public: 公用(所有人都可以访问)
* 友元函数与派生类的区分:
# 友元函数需要在基类中声明,可以直接访问基类的成员数据(私有成员也可以直接访问)
# 派生类只能访问基类中的公用变量以及保护变量,不可以直接访问基类中的私有变量
#include
using namespace std;
class Student {
//成员访问权限限定符:private,public,protected
private:
int score;
protected:
string name;
public:
Student(int num, int score, string name) :num(num), name(name) ,score(score) {};
int num;
};
//继承方式限定符:public,protected,private
//公用继承public:基类公用成员+保护成员在派生类中保持原有访问权限,基类私有成员仍为基类私有
class Mid_Student_pub : public Student
{
public:
Mid_Student_pub(int num, int score, string name, int math) :Student(num, score, name) { Math = math; };
//void Display(void){printf("%d",score);}非法访问基类的私有变量,会报错
void Display_pub(void);
protected:
int Math;
};
void Mid_Student_pub::Display_pub(void) {
cout << name << " : " << num << " , " << Math << endl;
}
//基类的私有成员不可以被派生类访问,只能借助基类的函数间接引用基类的私有成员(很好用private和private继承)
//私有继承private:公用成员+保护成员在派生类中变成了私有成员,基类的私有成员仍为基类私有
class Mid_Student_pri : private Student
{
public:
Mid_Student_pri(int num, int score, string name, int english) :Student(num, score, name) { English = english; };
void Display_pri(void);
protected:
int English;
};
void Mid_Student_pri::Display_pri(void) {
cout << name << " : " << num << " , " << English << endl;
}
//受保护的继承protected:公用成员+保护成员在派生类中变成了保护成员,基类的私有成员仍为基类私有
class Mid_Student_pro : protected Student
{
public:
Mid_Student_pro(int num, int score, string name, int chinese) :Student(num, score, name) { Chinese = chinese; };
void Display_pro(void);
protected:
int Chinese;
};
void Mid_Student_pro :: Display_pro(void) {
cout << name << " : " << num << " , " << Chinese << endl;
}
class Score {
protected:
int Chinese;
int Math;
int English;
public:
Score(int math, int chinese, int english) :Math(math), Chinese(chinese), English(english) {};
};
class Student_sum : public Student,public Score
{
public:
Student_sum(int num, int score, string name, int math, int english, int chinese) :Student(num, score, name), Score(math,chinese,english) {};
void Display_sum(void);
};
void Student_sum::Display_sum(void) {
cout << name << " : " << num << " , " << "Chinese: " << Chinese << " English: " << English << " Math: " << Math << endl;
}
//如果类作为对外的借口,用public->不改变基类成员的权限
//如果不希望派生类被外部访问,则用protected
int main(void)
{
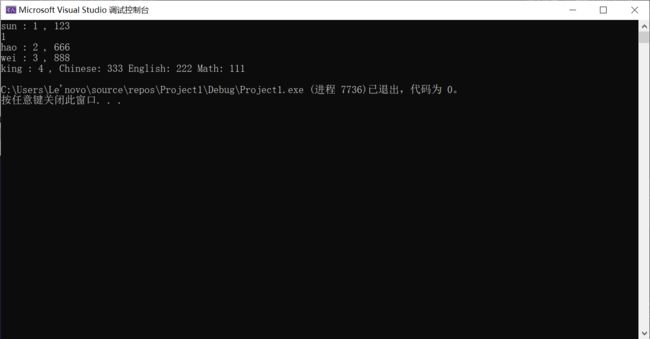
Mid_Student_pub S1(1,12,"sun", 123);
S1.Display_pub();
cout << S1.num << endl; //可以正常输出!
Mid_Student_pri S2(2, 13, "hao", 666);
S2.Display_pri();
//cout << S1.num << endl;不可以正常输出,num已经变成私有的了
Mid_Student_pro S3(3, 14, "wei", 888);
S3.Display_pro();
//cout << S1.num << endl;不可以正常输出,num已经变成保护成员protected了
Student_sum S4(4, 15, "king", 111, 222, 333);
S4.Display_sum();
return 0;
}
//多级继承都使用公用继承,否则如果父亲使用了私有继承,那么爷爷的公用和保护成员在父亲处成为了私有成员
//无法被儿子访问(隔代无法正常访问的问题)
运行结果2: