Thrift基础教程
前言
Thrift是一个RPC框架,大概说一下什么是RPC,想深入理解一点的可以去Google,假如我们现在想实现一个功能,输入2个数,输出这2个值的和,我们一般的做法是自己写一个求和函数,当然我们也可以调用别的项目中写好的求和函数,只要这2个程序可以通讯即可。这个在实际项目中是很有用的,因为业务逻辑别的部门已经都帮你写好了,而这些业务逻辑都很复杂,没必要自己再实现一遍,重复造轮子没必要。你可能会想通过HTTP发送请求,然后解析返回的json之类的也可以实现啊,但这样其实很不方便。RPC框架帮你解决了这个问题,调用别的地方的代码,就像调用本地的代码一样.
使用
定义Thrift文件
Thrift是一个跨语言的RPC框架,怎么用thrift呢?你先得定义一个Thrift文件,以上面的例子为例,我想把对2个数加和然后返回值这个方法服务一个服务暴露出去供别人调用,先定义如下Thrift文件
namespace java com.st.thrift
service SumService{
string getSum(1:i32 num1, 2:i32 num2)
}下载exe文件
然后指定参数运行thrift.exe就能得到你想到的代码了(从官网下载thrift.exe),
LZ下载的是windows版本,只有一个exe文件,LZ重命名为thritf.exe,可以将exe文件所在的路径加入到环境变量中,这样在命令行中直接就可以运行thrift这个命令,LZ没有配置,直接将thrift.exe和thrift文件放在项目中,这样别人就能直接用,LZ写了一个脚本方便使用
@echo off
title gen code by thrift
for /f %%i in ('dir /B *.thrift ') do thrift-0.10.0.exe -v -r --gen java -out ../src/main/java/ %%i
@pause-v 是显示执行的过程(可忽略)
–gen 是指定语言
–out指定生成到哪个文件夹
直接点击这个脚本就能生成代码,传输的部分thrift已经帮你写好了,业务逻辑只要实现接口就行,(下面代码是一部分,建议下载LZ放在Github上的代码)
public class SumService {
public interface Iface {
public java.lang.String getSum(int num1, int num2) throws org.apache.thrift.TException;
}
public interface AsyncIface {
public void getSum(int num1, int num2, org.apache.thrift.async.AsyncMethodCallback resultHandler) throws org.apache.thrift.TException;
}
} 现在实现这个接口,也就是业务逻辑
public class SumServiceImp implements SumService.Iface {
@Override
public int getSum(int num1, int num2) throws TException {
return num1 + num2;
}
}运行Demo
服务器端
public class TestServer1 {
public static final int PORT = 8090;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("服务端开启");
TProcessor tProcessor = new SumService.Processor(new SumServiceImp());
// 简单的单线程服务模型
TServerSocket serverTransport = new TServerSocket(PORT);
TServer.Args tArgs = new TServer.Args(serverTransport);
tArgs.processor(tProcessor);
tArgs.protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocol.Factory());
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(tArgs);
server.serve();
} catch (TTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 客户端
public class TestClient1 {
public static final String SERVER_IP = "127.0.0.1";
public static final int SERVER_PORT = 8090;
public static final int TIMEOUT = 30000;
public static void main(String[] args) {
TTransport transport = null;
try {
transport = new TSocket(SERVER_IP, SERVER_PORT, TIMEOUT);
// 协议要和服务端一致
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
SumService.Iface client = new SumService.Client(protocol);
transport.open();
// 在这里,就像调用本地代码一样,其实实现逻辑在服务器
int sum = client.getSum(10, 20);
System.out.println(sum);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (null != transport) {
transport.close();
}
}
}
}到目前为止,你已经能写一个正确的Thrift服务了
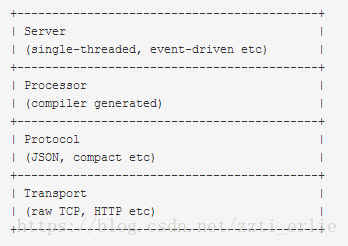
结构
- 最上层是用户自行实现的业务逻辑代码
- 第二层是由thrift编译器自动生成的代码,主要用于结构化数据的解析,发送和接收。TServer主要任务是高效的接受客户端请求,并将请求转发给Processor处理。Processor负责对客户端的请求做出响应,包括RPC请求转发,调用参数解析和用户逻辑调用,返回值写回等处理
- 从TProtocol以下部分是thirft的传输协议和底层I/O通信。TProtocol是用于数据类型解析的,将结构化数据转化为字节流给TTransport进行传输
- TTransport是与底层数据传输密切相关的传输层,负责以字节流方式接收和发送消息体,不关注是什么数据类型。底层IO负责实际的数据传输,包括socket、文件和压缩数据流等。
| 层级 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| Transport (运输) | 网络读取/写入网络 |
| Protocol(协议) | 一个协议规定了数据类型如何使用底层传输来对自身进行编码/解码,如JSON,XML,纯文本,二进制 |
| Processor (处理器) | 处理器封装了从输入流中读取数据并写入输出流的能力 |
| Server (服务器) | 服务器将上述所有功能汇集在一起 |
interface TProcessor {
bool process(TProtocol in, TProtocol out) throws TException
}| 传输协议 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| TBinaryProtocol | 二进制编码格式进行数据传输 |
| TCompactProtocol | 高效率的、密集的二进制编码格式进行数据传输 |
| TJSONProtocol | 使用 JSON 的数据编码协议进行数据传输 |
| TSimpleJSONProtocol | 只提供 JSON 只写的协议,适用于通过脚本语言解析 |
| 服务端类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| TSimpleServer | 单线程服务器端使用标准的阻塞式 I/O |
| TThreadPoolServer | 多线程服务器端使用标准的阻塞式 I/O |
| TNonblockingServer | 多线程服务器端使用非阻塞式 I/O |
例子
源码
https://github.com/erlieStar/study-thrift
参考博客
[1]https://www.cnblogs.com/fingerboy/p/6424248.html
[2]https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-apachethrift/
[3]https://www.cnblogs.com/johnc/archive/2011/06/19/2084508.html
[4]http://www.micmiu.com/soa/rpc/thrift-sample/
Spring Boot集成thrift
[5]https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1050391