实现自己的RPi.GPIO(一)-Python C Extension
树莓派有个RPi.GPIO的Python模块,import之后就可以直接用Python操作ARM芯片的GPIO硬件模块。觉得这个很有意思,于是查资料想在自己画的DM8148平台上面也实现这样的一个模块。
DM8148是TI推出的一款达芬奇系列数字图像处理芯片,比DM8168性能略差,但是功耗更低。之前公司的很多图像处理都是用的DM8168,但是散热和功耗问题一直很让人头疼,于是就让我预研更低功耗的DM8148。DM8148可以理解为ARM+DSP的异构核心,我们要用到的就是它的一颗Cortex A8的ARM核心。
我们公司没有使用TI的EZSDK,而是购买了DVR-RDK。DVR-RDK4.0提供的编译器arm-arago-linux-gnueabi-gcc目录中已经包含了Python2.6,我自己也交叉编译了Python2.7,但是很多库有问题,就直接使用自带的Python2.6。
Python并不能直接操作硬件,直接操作硬件只能用C去实现,然后通过Python的Extensions功能调用C。下面是Python的Extensions功能的一个Demo,从某Python tutorial上拷贝的:
1 #include <python2.6/Python.h> 2 static PyObject *helloworld(PyObject *self) 3 { 4 return Py_BuildValue("s", "Hello, Python extensions!!"); 5 } 6 static char helloworld_docs[] = "helloworld():Any message you want to put hele! 7 "; 8 static PyMethodDef helloworld_funcs[] = { 9 {"helloworld", (PyCFunction)helloworld, METH_NOARGS, helloworld_docs}, 10 {NULL} 11 }; 12 void inithelloworld(void) 13 { 14 Py_InitModule3("helloworld", helloworld_funcs, "Extension module example!"); 15 }
交叉编译:
arm-arago-linux-gnueabi-gcc hello.c -g -I/home/jugg/CodeSourcery/cgt_a8/arago/linux-devkit/arm-arago-linux-gnueabi/usr/include/python2.6 -shared -L/home/jugg/CodeSourcery/cgt_a8/arago/linux-devkit/arm-arago-linux-gnueabi/usr/lib/python2.6 -o helloworld.so
然后将得到的helloworld.so拷贝到Python的库路径中:
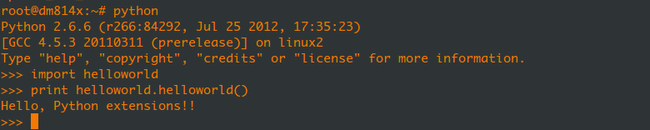
cp ./helloworld.so /home/jugg/working_space/nfs/rfs_814x/usr/lib/python2.6/lib-dynload
在DM8148板卡上测试: