6.filters滤波
在点云处理流程中滤波处理作为预处理的第一步,对后续的影响比较大,只有在滤波预处理中将噪声点 ,离群点,孔洞,数据压缩等按照后续处理定制,才能够更好的进行配准,特征提取,曲面重建,可视化等后续应用处理,PCL中点云滤波模块提供了很多灵活实用的滤波处理算法,例如:双边滤波,高斯滤波,条件滤波,直通滤波,基于随机采样一致性滤波。
PCL中总结了几种需要进行点云滤波处理情况,这几种情况分别如下:
(1) 点云数据密度不规则需要平滑
(2) 因为遮挡等问题造成离群点需要去除
(3) 大量数据需要下采样
(4) 噪声数据需要去除
对应的方案如下:
(1)按照给定的规则限制过滤去除点
(2) 通过常用滤波算法修改点的部分属性
(3)对数据进行下采样
PCL点云格式分为有序点云和无序点云
- 一般深度相机采集到的点云的数据是有序点云,针对有序点云提供了双边滤波、高斯滤波、中值滤波等
- 而我们激光雷达采集的点云的数据是无序的点云,针对无序点云提供了体素栅格、随机采样等
头文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include 1.直通滤波
将点云中Z坐标在(0,400)范围外的点过滤掉
void filters_passthrough()
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
//load cloud
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("do1.pcd", *cloud);
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->size(); ++i)
{
std::cout << (*cloud).points[i].x << " "
<< (*cloud).points[i].y << " "
<< (*cloud).points[i].z << " " << std::endl;
}
//设置滤波器对象
pcl::PassThrough pass;
pass.setInputCloud(cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass.setFilterLimits(0.0, 400.0);//保留0-400内,符合条件的
//pass.setFilterLimitsNegative (true); //设置保留范围内还是过滤范围内 true 取范围外 false 保留范围内
pass.filter(*cloud_filtered);
std::cout << "---------------------" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < cloud_filtered->size(); ++i)
{
std::cout << (*cloud_filtered).points[i].x << " "
<< (*cloud_filtered).points[i].y << " "
<< (*cloud_filtered).points[i].z << " " << std::endl;
}
return;
}
2.VoxelGrid滤波器下采样
使用体素化网格方法实现下采样,即减少点的数量,并同时保存点云的形状特征,在提高配准,曲面重建,形状识别等算法速度中非常实用,VoxelGrid类通过输入的点云数据创建一个三维体素栅格,容纳后每个体素内用体素中所有点的重心来近似显示体素中其他点,这样该体素内所有点都用一个重心点最终表示,对于所有体素处理后得到的过滤后的点云,这种方法比用体素中心逼近的方法更慢,但是对于采样点对应曲面的表示更为准确。
VoxelGrid滤波器是使用体素化网格的方法实现下采样,并保持点云的形状特征;
具体:voxelGrid类通过在点云数据中创建三维体素栅格,然后用每个体素的重心来近似表达体素中的其它点。
这种方法比用体素中心来逼近的方法更慢,但它对采样点对应曲面的表示更为准确
void filters_voxel_gird()//体素化网格方法 下采样
{
pcl::PCLPointCloud2::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PCLPointCloud2());
pcl::PCLPointCloud2::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PCLPointCloud2());
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("do1.pcd", *cloud);
//点云对象读取
pcl::PCDReader reader;
reader.read("do1.pcd", *cloud);
pcl::VoxelGrid gird;
gird.setInputCloud(cloud);
gird.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);//设置滤波时创建的体素体积为1cm的立方体
gird.filter(*cloud_filtered);
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write("do1_downsampled.pcd", *cloud_filtered);
return;
} 3.statisticalOutlierRemoval滤波器移除离群点
使用统计分析技术,从一个点云数据中集中移除测量噪声点(也就是离群点)比如:激光扫描通常会产生密度不均匀的点云数据集,另外测量中的误差也会产生稀疏的离群点,使效果不好,估计局部点云特征(例如采样点处法向量或曲率变化率)的运算复杂,这会导致错误的数值,反过来就会导致点云配准等后期的处理失败。
具体操作:
每个点的邻域进行一个统计分析,并修剪掉一些不符合一定标准的点,稀疏离群点移除方法基于在输入数据中对点到临近点的距离分布的计算,对每一个点,计算它到它的所有临近点的平均距离,,假设得到的结果是一个高斯分布,其形状是由均值和标准差决定,平均距离在标准范围之外的点,可以被定义为离群点并可从数据中去除。
void filters_statictical_outlier_removal()
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PCDReader reader;
reader.read("do1.pcd", *cloud);
//创建滤波器 对每个点分析的临近点的个数设置为50 ,将标准差倍数设置为1
//意味着如果一个点的距离超出了平均距离一个标准差以上,则该点被标记为离散点,并将它移除并保存
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval sor;
sor.setInputCloud(cloud);
sor.setMeanK(50);
sor.setStddevMulThresh(1.0);
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write("do1_statistical_inliers", *cloud_filtered, false);
sor.setNegative(true);
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
writer.write("do1_statistical_outliers", *cloud_filtered, false);
} 4.参数化模型投影点云
ProjectInliers使用PointCloud的模型和一组inlier索引将它们投影到单独的PointCloud中。
void filers_project_inliers()//平面投影滤波
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_project(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("do1.pcd", *cloud);
//填充ModelCoefficients的值,使用ax+by+cz+d=0平面模型,其a=b=d=0,c=1,即
//x--y平面,定义模型数据对象,并填充对应的数据
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients());
coefficients->values.resize(4);
coefficients->values[0] = 0;
coefficients->values[1] = coefficients->values[3] = 0;
coefficients->values[2] = 1.0f;
//创建Project_Inliers对象,使用Modelcoefficient作为投影对象的模型参数
pcl::ProjectInliersproj;//创建投影滤波对象
proj.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);//设置对象对应的滤波模型
proj.setInputCloud(cloud);
proj.setModelCoefficients(coefficients);//设置模型对应系数
proj.filter(*cloud_project);
pcl::io::savePCDFile("do1_proj", *cloud_project);
return;
} 5.用ConditionalRemoval或RadiusOutlinerRemoval移除离群点
如何在滤波模块使用几种不同的方法移除离群点
- ConditionalRemoval滤波器,可以一次删除满足对输入的点云设定的一个或多个条件指标的所有的数据
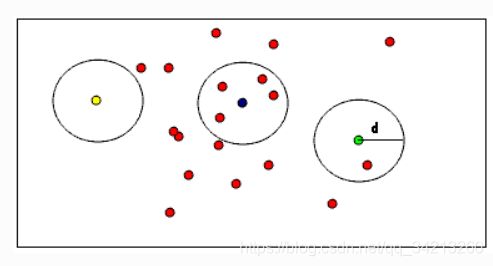
- RadiusOutlinerRemoval滤波器,它可以删除在输入点云一定范围内没有达到足够多近邻的所有数据点。关于RadiusOutlinerRemoval的理解,在点云数据中,设定每个点一定范围内周围至少有足够多的近邻,不满足就会被删除
- 在点云数据中,用户指定每个点的一定范围内周围至少要有足够多的近邻。例如,如果指定至少要有1个邻居,只有黄色的点会被删除,如果指定至少要有2个邻居,黄色和绿色的点都将被删除。
void filters_condition_Radius_outliers(int selection)//条件,半径剔除离散点
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("do1.pcd", *cloud);
if (selection >= 0)//use radius
{
pcl::RadiusOutlierRemoval radius_sor;
radius_sor.setInputCloud(cloud);
radius_sor.setRadiusSearch(0.8);//设置半径0.8的范围内找临近点
radius_sor.setMinNeighborsInRadius(2);//设置查询点邻域点集数小于2 的删除
radius_sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);//条件滤波:在半径为0.8邻域内查找点集且有两个邻居点,才保存
}
else//use condition
{
pcl::ConditionAnd::Ptr cond_range(new pcl::ConditionAnd());
//GT > EQ= LT< GE:>or= LE:addComparison(pcl::FieldComparison::ConstPtr
(new pcl::FieldComparison("z", pcl::ComparisonOps::GT, 0.0)));//添加z字段上>0的比较算子
cond_range->addComparison(pcl::FieldComparison::ConstPtr
(new pcl::FieldComparison("z", pcl::ComparisonOps::LT, 0.8)));//添加z字段上<0.8的比较算子
//创建滤波器并用条件定义对象初始化
pcl::ConditionalRemoval cond_cor;
cond_cor.setCondition(cond_range);
cond_cor.setInputCloud(cloud);
//设置保持点云结构,
//设置是否保留滤波后删除的点,以保持点云的有序性,
//通过setuserFilterValue设置的值填充点云;或从点云删除滤波后的点,从而改变其组织结构
//如果设置为TRUE且不设置setfiltervalue的值,则用nan填充点云
cond_cor.setKeepOrganized(true);
cond_cor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
}
pcl::io::savePCDFile("do1_condORradius", *cloud_filtered);
} 6.双边滤波
双边滤波算法,是通过取邻近采样点的加权平均来修正当前采样点的位置,从而达到滤波效果。同时也会有选择地剔除部分与当前采样点“差异”太大的相邻采样点,从而达到保持原特征的目的。
void filters_bilater()//双边滤波
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);//需要pointxyzi
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PCDReader reader;
reader.read("do1.pcd", *cloud);
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree1(new pcl::search::KdTree);
pcl::BilateralFilter sor;
sor.setInputCloud(cloud);
sor.setSearchMethod(tree1);
sor.setStdDev(0.1);
sor.setHalfSize(0.1);
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
return;
} 7.按索引滤波
a.下采样
b.平面分割出索引
c.按索引滤波
void filters_extract_indices()
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud);
//下采样
pcl::VoxelGridsor;
sor.setInputCloud(cloud);
sor.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud),
cloud_p(new pcl::PointCloud);
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
//创建分割对象
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PARALLEL_PLANE);//平面模型
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(1000);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.01);
//创建滤波器对象
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;
int i = 0, nr_points = (int)cloud_filtered->points.size();
while (cloud_filtered->points.size() > 0.3 * nr_points)
{
// 从余下的点云中分割最大平面组成部分
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size() == 0)
{
std::cerr << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl;
break;
}
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers);
extract.setNegative(false);
extract.filter(*cloud_p);
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_p->width * cloud_p->height << " data points." << std::endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "table_scene_lms400_plane_" << i << ".pcd";
i++;
}
} 8.CropHull任意多边形内部点云提取
void filters_cropHull()
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("pig.pcd", *cloud);
//
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr boundingbox_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud);
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(0.1, 0.1, 0));
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(0.1, -0.1, 0));
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(-0.1, 0.1, 0));
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(-0.1, -0.1, 0));
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(0.15, 0.1, 0));
pcl::ConvexHull hull;//创建凸包对象
hull.setInputCloud(boundingbox_ptr);
hull.setDimension(2);//设置凸包维度
//保存凸包顶点
std::vector polygons;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr surface_hull(new pcl::PointCloud);//该点云用来描述凸包形状
hull.reconstruct(*surface_hull, polygons);
//创建crophull对象
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr objects(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::CropHull bb_filter;
bb_filter.setDim(2);
bb_filter.setInputCloud(cloud);
bb_filter.setHullIndices(polygons);
bb_filter.setHullCloud(surface_hull);
bb_filter.filter(*objects);
//可视化
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer (new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255);
int v1(0);
viewer->createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.33, 1, v1);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255, v1);
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud, "cloud", v1);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 255, 0, 0, "cloud");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 3, "cloud");
viewer->addPolygon(surface_hull, 0, 0.69 * 255, 0.2 * 255, "back_hull_polyline1", v1);
int v2(0);
viewer->createViewPort(0.33, 0.0, 0.66, 1, v2);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255, v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(surface_hull, "surface_hull", v2);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 255, 0, 0, "surface_hull");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 8, "surface_hull");
viewer->addPolygon(surface_hull, 0, .069 * 255, 0.2 * 255, "backview_hull_polyline", v2);
int v3(0);
viewer->createViewPort(0.66, 0.0, 1, 1, v3);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255, v3);
viewer->addPointCloud(objects, "objects", v3);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 255, 0, 0, "objects");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 3, "objects");
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce(1000);
}
system("pause");
}