osgEarth示例分析——osgearth_eci
前言
osgearth_eci示例,展示了J2000的天体坐标系和ECEF地固系的转换,绘制坐标系,以及读取卫星参数绘制卫星的功能。绘制卫星轨迹,添加差值效果和未添加差值的效果。
关于卫星两行根数的数据文件下载路径:CelesTrak: Historical NORAD Two-Line Element Sets
关于卫星两行根数的解释:CelesTrak: NORAD Two-Line Element Set Format
执行命令
// J2000ECI坐标系下绘制, --tessellate 开启差值功能。最好不要开启
osgearth_ecid.exe earth_image\world.earth --tle F:\osgData\Data\space\gps1-01.txt --tessellate
// 还可以通过 --maxpoints 1000 控制添加跟踪卫星的数量
osgearth_ecid.exe earth_image\world.earth --tle F:\osgData\Data\space\gps1-01.txt --maxpoints 1000 --tessellate
// ECEF地固系下 绘制,--tle 加载的文件,一定要写全路径,否则无法找到文件,即使放入系统环境变量也没用。
osgearth_ecid.exe earth_image\world.earth --tle F:\osgData\Data\space\gps1-01.txt --ecef --tessellate效果
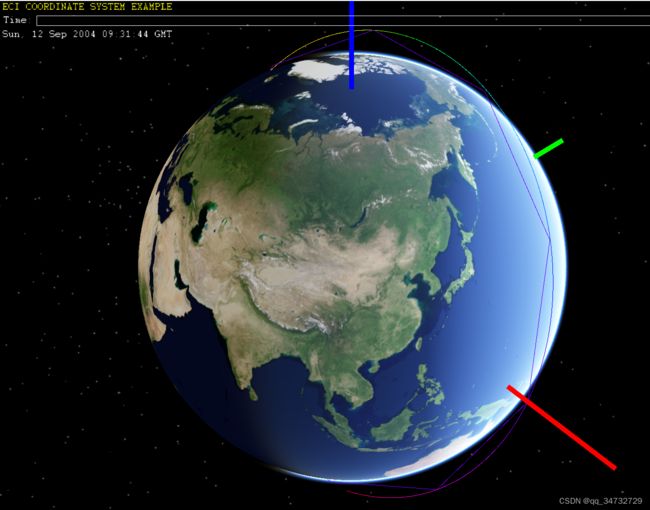
默认J2000ECI坐标系下绘制,此时设置时间为最终时间。共读取了4076条数据。
在ECEF地固坐标系下绘制,此时设置时间为最终时间。共读取了4076条数据。如果代码中app.trackDrawable->load(app.true);参数设置为true,就会出现这种效果。
在ECEF地固坐标系下绘制,此时设置时间为最终时间。共读取了4076条数据。限制绘制100条的情况。如果代码中app.trackDrawable->load(app.true);参数设置为true,就会出现这种效果。
代码分析
1、J2000ECI坐标系:本例中,以地球为中心,Z轴指向北天极,X轴指向2000年1月1日中午12点的春分点,Y轴与Z、X成右手直角坐标系。所以定义J2000ECI坐标系时,需要定义时间。这个坐标系,是不会随着地球自转的。
2、ECEF地固坐标系:以地球质心为中心,Z轴指向北天极,X轴指向格林尼治天文台零度子午面与协议地球极赤道的交点,Y轴与Z、X成右手直角坐标系。这个坐标系是会随着地球自转而自转的。所以两个坐标系转换,需要乘以地球自转的旋转角矩阵,来实现转换。
3、卫星两行根数:跟据两行根数的各个内容,就可以计算出,卫星什么时候在什么坐标下,且速度、加速度等参数,都会有。
/**
* Experiment with using a J2000/ECI reference frame as the root of the scene,
* with the MapNode under an ECI-to-ECEF transform.
* 尝试使用J2000/ECI参考帧作为场景的根,并在ECI到ECEF变换下使用MapNode。
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define LC "[eci] "
using namespace osgEarth;
using namespace osgEarth::Util;
using namespace osgEarth::Symbology;
using namespace osgEarth::Annotation;
namespace ui = osgEarth::Util::Controls;
int
usage(const char* name, const char* msg)
{
OE_NOTICE
<< "\nUsage: " << name << " [file.earth]\n"
<< " --tle : Load a NORAD TLE file\n" // 加载tle文件
<< " --maxpoints : Limit the track size to points\n" // 限制要绘制卫星的个数
<< " --ecef : View the track in ECEF space instead of ECI\n" // 在ECEF空间而不是ECI中查看轨迹。
<< " --tessellate : Add interpolated points to the track data\n" // 向轨迹数据添加插值点
<< "\nDownload NORAD TLE files from https://www.celestrak.com/NORAD/archives\n\n" // 下载 NORAD TLE 文件地址
<< msg << std::endl;
return 0;
}
// Reference time for the J2000 ECI coordinate frame
// J2000 ECI坐标系的参考时间。起始时间为2000年1月1日中午12点整
static DateTime J2000Epoch(2000, 1, 1, 12.00);
// Transform that takes us from a J2000 ECI reference frame
// to an ECEF reference frame (i.e. MapNode)
// 定义 从J2000ECI坐标系转到ECEF坐标系(地固系)的 转换矩阵
class J2000ToECEFTransform : public osg::MatrixTransform
{
public:
void setDateTime(const DateTime& dt)
{
osg::Matrix matrix = createMatrix(dt);
setMatrix(matrix);// 设置给父类
}
// 根据传入UTC时间,定义当前矩阵
static osg::Matrix createMatrix(const DateTime& dt)
{
// Earth's rotation rate: International Astronomical Union (IAU) GRS 67
// 地球自转率,即角速度
const double IAU_EARTH_ANGULAR_VELOCITY = 7292115.1467e-11; // (rad/sec)
// 都转化为儒略日时间,double类型
double secondsElapsed = (double)(dt.asTimeStamp() - J2000Epoch.asTimeStamp());
const double rotation = IAU_EARTH_ANGULAR_VELOCITY * secondsElapsed;// 时间*角速度,得到旋转角度
osg::Matrix matrix;
matrix.makeRotate(rotation, 0, 0, 1);
return matrix;
}
};
// Code to read TLE track data files from https://celestrak.com/NORAD
// 从TLE文件读取跟踪数据的代码
struct ECILocation
{
DateTime timestamp; // point time 运行在某个点的时间
Angle incl; // inclination 倾角
Angle raan; // right ascencion of ascending node 上升节点的右上升
Distance alt; // altitude 高度
osg::Vec3d eci; // ECI coordinate ECI坐标系下的点位置
osg::Vec3d ecef; // ECEF coordinate ECEF坐标系下的点位置
void computeECIAndECEF()// 分别计算两个坐标系
{
// 根据从文件中获取的 raan incl alt ,计算eci
eci =
osg::Quat(raan.as(Units::RADIANS), osg::Vec3d(0, 0, 1)) *
osg::Quat(incl.as(Units::RADIANS), osg::Vec3d(1, 0, 0)) *
osg::Vec3d(alt.as(Units::METERS), 0, 0);
// 根据时间获取转换矩阵
osg::Matrix eci2ecef = J2000ToECEFTransform::createMatrix(timestamp);
ecef = eci * eci2ecef;// 计算出ecef下坐标点
}
};
// ECI跟踪
struct ECITrack : public std::vector
{
// interpolate points for a smoother track
// 差值,使得点连线更圆滑.此算法有问题!!!绘制效果特别差!!!
void tessellate()
{
// 声明一个对象
ECITrack newTrack;
for(unsigned k=0; k(line1.substr(18, 2), 99);
int year = year2digit > 50? 1900+year2digit : 2000+year2digit;
double dayOfYear = osgEarth::as(line1.substr(20, 12), 0);
loc.timestamp = DateTime(year, dayOfYear);
// read ra/decl
loc.incl.set(osgEarth::as(line2.substr(8,8),0), Units::DEGREES);
loc.raan.set(osgEarth::as(line2.substr(17,8),0), Units::DEGREES);
loc.alt.set(6371 + 715, Units::KILOMETERS);
loc.computeECIAndECEF();
}
std::cout << "共解析数据条数:" << i << std::endl;
OE_INFO << "Read " << track.size() << " track points" << std::endl;
return true;
}
};
// If the "global" coordinate system is ECI, you can put this transform
// under the MapNode (in ECEF space) to "revert" to that global ECI frame.
// Useful if you want to put ECI-space data under the MapNode.
// 如果“全局”坐标系是ECI,则可以将ECI坐标系变换放在MapNode(在ECEF空间中)下,
// 然后再“还原”到该全局ECI坐标系。
// 如果要将ECI空间数据放在MapNode下,则非常有用。
class ECIReferenceFrame : public osg::Group
{
public:
ECIReferenceFrame()
{
// 关闭光照
Lighting::set(getOrCreateStateSet(), osg::StateAttribute::OFF);
}
// 遍历
void traverse(osg::NodeVisitor& nv)
{
osgUtil::CullVisitor* cv = Culling::asCullVisitor(nv);
if (cv)
{
const osg::Camera* cam = cv->getRenderStage()->getCamera();
// 添加模型视口矩阵
cv->pushModelViewMatrix(new osg::RefMatrix(cam->getViewMatrix()), osg::Transform::ABSOLUTE_RF);
osg::Group::traverse(nv);
cv->popModelViewMatrix();// 再移除该矩阵
}
else osg::Group::traverse(nv);
}
};
// Loads up an ECITrack for display as a series of points.
// 加载ECITrack以显示为一系列线/点。对LineDrawble类不太熟悉
class ECITrackDrawable : public LineDrawable //public PointDrawable
{
public:
ECITrackDrawable() : LineDrawable(GL_LINE_STRIP)
{
Lighting::set(getOrCreateStateSet(), 0);
//setPointSmooth(true);
//setPointSize(4.0f);
}
// 通过 滑块 设置时间
void setDateTime(const DateTime& dt)
{
// getVertexAttribArray(); 属于爷爷类的方法
// 获取到当前顶点的时间
osg::FloatArray* times = dynamic_cast(getVertexAttribArray(6));
unsigned i;
for (i = 0; i < getNumVerts(); ++i)
{
if (dt.asTimeStamp() < getVertexAttrib(times, i))// getVertexAttrib() 父类方法
break;
}
setCount(i);
}
// 加载 track 列表的所有数据
void load(const ECITrack& track, bool drawECEF)
{
osg::FloatArray* times = new osg::FloatArray();
times->setBinding(osg::Array::BIND_PER_VERTEX);
setVertexAttribArray(6, times);// 调用爷爷类的方法
osg::Vec4f HSLA;// 颜色变量
Color color;
// 循环处理每一个卫星
for(unsigned i=0; iallocate(6);
// X轴
d->setVertex(0, osg::Vec3(0,0,0));
d->setColor(0, osg::Vec4(1,0,0,1));
d->setVertex(1, osg::Vec3(R,0,0));
d->setColor(1, osg::Vec4(1,0,0,1));
// Y轴
d->setVertex(2, osg::Vec3(0,0,0));
d->setColor(2, osg::Vec4(0,1,0,1));
d->setVertex(3, osg::Vec3(0,R,0));
d->setColor(3, osg::Vec4(0,1,0,1));
// Z轴
d->setVertex(4, osg::Vec3(0,0,0));
d->setColor(4, osg::Vec4(0,0,1,1));
d->setVertex(5, osg::Vec3(0,0,R));
d->setColor(5, osg::Vec4(0,0,1,1));
// 坐标轴宽度
d->setLineWidth(10);
return d;
}
// Application-wide data and control structure
// 应用程序范围的数据和控制结构
struct App
{
DateTime start, end; // 时间
HSliderControl* time; // 时间滑块
LabelControl* timeLabel;// 时间标签
SkyNode* sky; // 深空节点
J2000ToECEFTransform* ecef; // 坐标系转换矩阵
osg::Group* eci;
ECITrackDrawable* trackDrawable;// ECI跟踪绘制
ECITrack track; // J2000坐标系下卫星数据列表
App()
{
trackDrawable = 0L;
start = J2000Epoch;// 设置为J2000坐标系的开始时间
end = start + 24.0; // 初始设置时,必须保证start和end保持间距,且start < end
}
// 通过滑块设置时间
void setTime()
{
// 获取最新时间
DateTime newTime(time->getValue());
if (sky)
sky->setDateTime(newTime);
// 如果是地固系,则需要根据时间旋转坐标系
if (ecef)
ecef->setDateTime(newTime);
if (trackDrawable)
trackDrawable->setDateTime(newTime);
// 设置时间的显示
timeLabel->setText(newTime.asRFC1123());
}
};
// 将app.setTime 设置到这个宏定义中,之前其他例子有涉及到此宏定义的用法
OE_UI_HANDLER(setTime);
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
osg::ArgumentParser arguments(&argc,argv);
if ( arguments.read("--help") )
return usage(argv[0], "");
// 声明app变量
App app;
// Read in an optiona TLE track data file
// 读取TLE文件获取数据
std::string tlefile;
if (arguments.read("--tle", tlefile))
{
// 读取并解析卫星数据,到app.track列表中
TLEReader().read(tlefile, app.track);
if (!app.track.empty())
{
int maxPoints;
if (arguments.read("--maxpoints", maxPoints) && app.track.size() > maxPoints)
app.track.resize(maxPoints);// 是否需要调整vector空间大小
if (arguments.read("--tessellate")) {// 是否开启差值功能。最好不要开启,算法有点问题
app.track.tessellate();
std::cout << "开启差值功能 tessellate" << std::endl;
}
app.start = app.track.front().timestamp;// 设置开始时间
app.end = app.track.back().timestamp; // 设置结束时间
}
}
osgViewer::Viewer viewer(arguments);
viewer.setCameraManipulator( new EarthManipulator(arguments) );
bool drawECEF = arguments.read("--ecef");
ui::VBox* container = new ui::VBox();
container->setChildSpacing(3);
// 根据是否为ECI坐标系,更改标题
if (drawECEF) {
container->addControl(new ui::LabelControl("ECEF COORDINATE SYSTEM EXAMPLE", Color::Red));
}
else {
container->addControl(new ui::LabelControl("ECI COORDINATE SYSTEM EXAMPLE", Color::Yellow));
}
// UI control to modify the time of day.
ui::HBox* h = container->addControl(new ui::HBox());
h->addControl(new ui::LabelControl("Time:"));
app.time = h->addControl(new HSliderControl(
app.start.asTimeStamp(), app.end.asTimeStamp(), app.end.asTimeStamp(),
new setTime(app)));
app.time->setWidth(500);// 500宽度太大了,修改小一些,也没有起作用,注释带此行,也没啥变化。
app.timeLabel = container->addControl(new LabelControl());
// Load an earth file
osg::Node* earth = MapNodeHelper().load(arguments, &viewer, container);
if (earth)
{
// New scene graph root
osg::Group* root = new osg::Group();
// First create a Sky which we will place in the (default) ECI frame.
SkyOptions skyOptions;
if (drawECEF) {
// 不太确定这里的 skyOptions.coordinateSystem() 设置为 COORDSYS_ECEF,是否正确,但运行效果没问题。
skyOptions.coordinateSystem() = SkyOptions::COORDSYS_ECEF;// 地固坐标系
std::cout << "ecef 坐标系" << std::endl;
}
else {
skyOptions.coordinateSystem() = SkyOptions::COORDSYS_ECI;// 深空坐标系
std::cout << "eci 坐标系" << std::endl;
}
app.sky = SkyNode::create(MapNode::get(earth));// 创建深空节点
app.sky->attach(&viewer);
app.sky->getSunLight()->setAmbient(osg::Vec4(0.5,0.5,0.5,1.0));// 环境光
root->addChild(app.sky);
// A special transform takes us from the ECI into an ECEF frame
// based on the current date and time.
// The earth (MapNode) lives here since it is ECEF.
app.ecef = new J2000ToECEFTransform();// 坐标系转换
app.sky->addChild(app.ecef);
app.ecef->addChild(earth);// 将地球节点加入到坐标转换矩阵中
// This group holds data in the ECI frame.
app.eci = new ECIReferenceFrame();
app.eci->addChild(createECIAxes());// 添加坐标轴
MapNode::get(earth)->addChild(app.eci);
// Track data
if (!app.track.empty())
{
app.trackDrawable = new ECITrackDrawable();
if (drawECEF)// 地固系,绘制连线
{
app.trackDrawable->load(app.track, false);// 如果设置为true,则会出现很多杂乱的线
MapNode::get(earth)->addChild(app.trackDrawable);
std::cout << "ecef 坐标系" << std::endl;
}
else // J2000坐标系,不绘制连线
{
app.trackDrawable->load(app.track, false);// 如果设置为true,则会出现很多杂乱的线
app.eci->addChild(app.trackDrawable);
std::cout << "eci 坐标系" << std::endl;
}
}
viewer.realize();
app.time->setWidth(viewer.getCamera()->getViewport()->width()-40);
app.setTime();
viewer.setSceneData(root);
viewer.run();
}
else
{
return usage(argv[0], "Bad earth file");
}
return 0;
}