【深度学习常见问题——NMS】
深度学习常见问题——NMS
- 用途
- NMS
-
- 具体步骤
- 实现代码
- 缺点
- Soft-NMS
-
- 具体步骤
- 实现代码
- Softer-NMS
-
- 大体思路
- 参考资料
用途
目标检测网络中,不论one-stage还是two-stage,都会产生超量的目标检测框,很多都指向了同一个目标,因此需要通过极大值抑制(Non Maximum Suppression)算法来筛选掉多余的检测框,找到每个目标最优的检测框
NMS
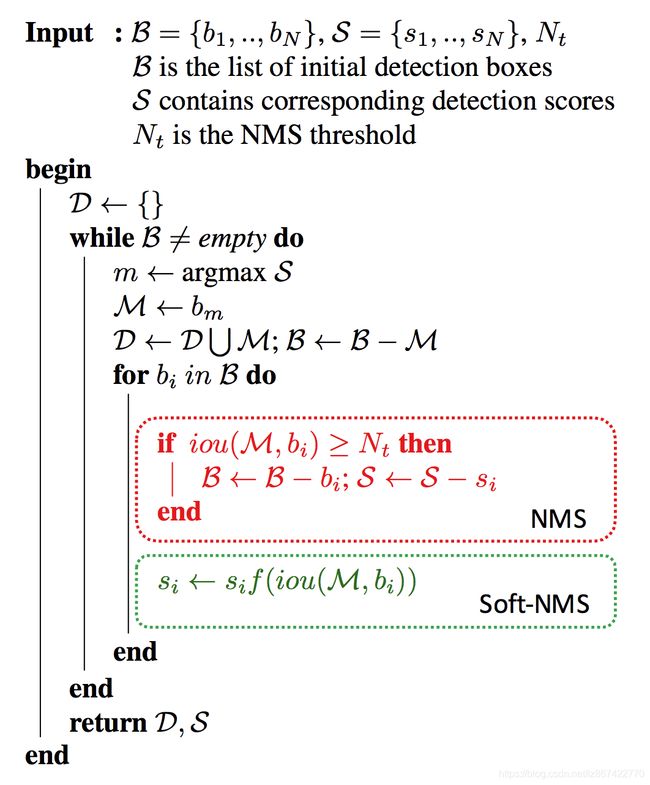
具体步骤
- 设置一个IOU阈值,通常为0.5
- 按照置信度将候选框进行降序排列
- 将候选框中置信度最高的框A移除,并添加到输出结果列表中
- 将候选框中与A的IOU超过阈值的框都删掉不考虑
- 重复3,4两步,直到候选框列表为空
实现代码
def nms(bboxes, iou_thr):
"""
Steps:
1. 按照score排序bbox
2. 选择最大score的bbox,放入predict_bboxes中
3. 将bboxes中IOU>iou_thr的bbox删掉
Args:
bboxes(list): (n, x1,y1,x2,y2,conf)-[n, left, top, right, bottom, score]
iou_thr(int): step3中筛选IOU的标准
Returns:
predict_bboxes(list): (m, x1, y1, x2, y2, conf)筛选后的bbox
"""
if len(bboxes) == 0:
return []
predict_bboxes = []
bboxes = np.array(bboxes)
# 计算bbox各自的面积
x1 = bboxes[:, 0]
y1 = bboxes[:, 1]
x2 = bboxes[:, 2]
y2 = bboxes[:, 3]
scores = bboxes[:, 4]
areas = (x2-x1+1) * (y2-y1+1)
# Step1 按照score排序bbox
order = np.argsort(scores) #np.argsort默认从小到大
while order.size > 0:
# Step2 选择当前置信度最高的bbox
index = order[-1]
predict_bboxes.append(bboxes[index])
# Step3 计算选中的bbox与其他bbox的IOU,进行筛选
# 计算IOU
x11 = np.maximum(x1[index], x1[order[:-1]])
y11 = np.maximum(y1[index], y1[order[:-1]])
x22 = np.minimum(x2[index], x2[order[:-1]])
y22 = np.minimum(y2[index], y2[order[:-1]])
inter_w = np.maximum(0.0, x22-x11+1)
inter_h = np.maximum(0.0, y22-y11+1)
inters = inter_w * inter_h
ious = inters / (areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]] - inters)
# 筛选
left = np.where(ious < iou_thr)
order = order[left]
return predict_bboxes
缺点
如果两个目标是交叠的,甚至是包含关系的,那NMS会把其中一个目标的bbox筛掉而导致漏检测。
Soft-NMS
针对于两目标交叠的情况做出了改进,在IOU大于阈值时不是直接将框删除,而是通过衰减其置信度的方式让其优先级靠后,但是保留了其被输出的可能性。
具体步骤
- 设置一个IOU阈值,通常为0.5
- 按照置信度将候选框进行降序排列
- 将候选框中置信度最高的框A移除,并添加到输出结果列表中
- 将候选框中与A的IOU超过阈值的框都
删掉不考虑进行置信度衰减,衰减方式为:
s i = s i ( 1 − I O U ( A , b i ) ) , i o u ( A , b i ) < t h r e s h o l d s_i = s_i(1-IOU(A, b_i)), iou(A, b_i)< threshold si=si(1−IOU(A,bi)),iou(A,bi)<threshold - 重复3,4两步,直到候选框列表为空
于原版NMS方法的比对伪代码如下:
实现代码
def soft_nms(bboxes, Nt=0.3, sigma2=0.5, score_thresh=0.3, method=2):
# 在 bboxes 之后添加对于的下标[0, 1, 2...], 最终 bboxes 的 shape 为 [n, 5], 前四个为坐标, 后一个为下标
res_bboxes = deepcopy(bboxes)
N = bboxes.shape[0] # 总的 box 的数量
indexes = np.array([np.arange(N)]) # 下标: 0, 1, 2, ..., n-1
bboxes = np.concatenate((bboxes, indexes.T), axis=1) # concatenate 之后, bboxes 的操作不会对外部变量产生影响
# 计算每个 box 的面积
x1 = bboxes[:, 0]
y1 = bboxes[:, 1]
x2 = bboxes[:, 2]
y2 = bboxes[:, 3]
scores = bboxes[:, 4]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
for i in range(N):
# 找出 i 后面的最大 score 及其下标
pos = i + 1
if i != N - 1:
maxscore = np.max(scores[pos:], axis=0)
maxpos = np.argmax(scores[pos:], axis=0)
else:
maxscore = scores[-1]
maxpos = 0
# 如果当前 i 的得分小于后面的最大 score, 则与之交换, 确保 i 上的 score 最大
if scores[i] < maxscore:
bboxes[[i, maxpos + i + 1]] = bboxes[[maxpos + i + 1, i]]
scores[[i, maxpos + i + 1]] = scores[[maxpos + i + 1, i]]
areas[[i, maxpos + i + 1]] = areas[[maxpos + i + 1, i]]
# IoU calculate
xx1 = np.maximum(bboxes[i, 0], bboxes[pos:, 0])
yy1 = np.maximum(bboxes[i, 1], bboxes[pos:, 1])
xx2 = np.minimum(bboxes[i, 2], bboxes[pos:, 2])
yy2 = np.minimum(bboxes[i, 3], bboxes[pos:, 3])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
intersection = w * h
iou = intersection / (areas[i] + areas[pos:] - intersection)
# Three methods: 1.linear 2.gaussian 3.original NMS
if method == 1: # linear
weight = np.ones(iou.shape)
weight[iou > Nt] = weight[iou > Nt] - iou[iou > Nt]
elif method == 2: # gaussian
weight = np.exp(-(iou * iou) / sigma2)
else: # original NMS
weight = np.ones(iou.shape)
weight[iou > Nt] = 0
scores[pos:] = weight * scores[pos:]
# select the boxes and keep the corresponding indexes
inds = bboxes[:, 5][scores > score_thresh]
keep = inds.astype(int)
return res_bboxes[keep]
Softer-NMS
大体思路
NMS和Soft-NMS的默认前提都是:置信度最高的bbox就是最精确的,但是实际上可能不成立。本文关注两个问题:
- 所有bbox都足够精确,无法确定哪一个
- 具有高置信度的bbox不够精确
参考资料
1.非极大值抑制(nms)算法详解[python_CSDN_智能血压计的博客]