DynaSLAM源码笔记-检测动态物体部分梳理
按照main函数向下细分的顺序大概记录一下rgbd情况下,动态物体去除(inpaint的部分本篇不涉及)的源码的写法,并对应一下论文, 关于ORB-SLAM2本身的部分不会太涉及到。
安装方法见:关于运行DynaSLAM源码这档子事(OpenCV3.x版)
论文笔记见:论文笔记-DynaSLAM: Tracking, Mapping and Inpainting in Dynamic Scenes
如果有什么不同的理解或者本文存在什么错误,欢迎评论交流讨论!
一. rgbd_tum.cc
新增了一个命名空间和类来进行关于MaskRCNN的处理,先进行这个对象的初始化,把相关参数和网络都弄好。
// Initialize Mask R-CNN
DynaSLAM::SegmentDynObject *MaskNet;
if (argc==6 || argc==7)
{
cout << "Loading Mask R-CNN. This could take a while..." << endl;
MaskNet = new DynaSLAM::SegmentDynObject();
cout << "Mask R-CNN loaded!" << endl;
}
下方代码中,执行MaskNet->GetSegmentation()函数,得到每一帧图片对应的分割结果。分割结果(变量maskRCNN)中,1表示先验的动态物体,0表示其他部分。注意,这里还对MaskRCNN分割的结果多进行了一次Dilate处理,也就是说要扣去的人的范围比神经网络的结果再大一点。
关于Dilate,个人觉得如果不想混淆这个概念,最重要的就是清楚它的本质:取邻域的最大值(是和像素值有关的)

// Segment out the images 在这里使用MAskRCNN找到mask
cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::ones(480,640,CV_8U);
if (argc == 6 || argc == 7)
{
cv::Mat maskRCNN;
// 这里的maskRCNN数值在0-1之间, 动态物体的mask对应像素值1
maskRCNN = MaskNet->GetSegmentation(imRGB,string(argv[5]),vstrImageFilenamesRGB[ni].replace(0,4,""));
//vstrImageFilenamesRGB[ni]的结果类似于rgb/1341846647.802247.png, replace是把前面四个字符去掉
cv::Mat maskRCNNdil = maskRCNN.clone();
//这里做了一个形态学的处理,扩大maskRCNN上动态物体轮廓的范围
cv::dilate(maskRCNN,maskRCNNdil, kernel);
mask = mask - maskRCNNdil; //求了个差,1表示静态物体
}
// Pass the image to the SLAM system
// 把Mask的Mat传进系统中
// 如果argc==7,说明需要的6个参数都在终端给了,要进行inpaint就执行if成立后的步骤,其他情况都执行else后的内容
if (argc == 7){SLAM.TrackRGBD(imRGB,imD,mask,tframe,imRGBOut,imDOut,maskOut);}
else {SLAM.TrackRGBD(imRGB,imD,mask,tframe);}
之后的求差,使得最终得到的变量mask,他的像素值范围也是0和1,但1表示rgb图片中要保留的部分(静态部分)。mask变量乘以255之后,就是下图所示:

接着,生成的mask就通过SLAM.TrackRGBD()函数进入了SLAM系统,这个往后就会有更多的细节。
二. Tracking::GrabImageRGBD()
这里先放上论文中的流程图,方便对照:
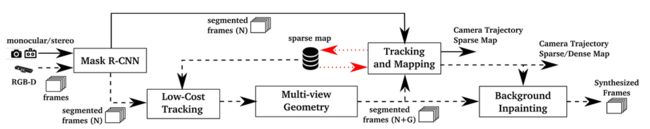
从rgbd_tum.cc就可以顺藤摸瓜到System::TrackRGBD(),这个函数中,有修改的就是Tracking::GrabImageRGBD(), 在获得了有效的灰度图和深度图之后,就开始了与动态检测相关的工作,变化的代码如下:
//删除了落在mask边界上的ORB特征
mCurrentFrame = Frame(mImGray,imDepth,imMask,timestamp,mpORBextractorLeft,mpORBVocabulary,mK,mDistCoef,mbf,mThDepth);
//对应于低成本Tracking的模块
LightTrack();
//对应多视图几何模块,为此作者写了一个Geometry类,来实现论文中识别动态物体的功能
mGeometry.GeometricModelCorrection(mCurrentFrame,mImGray,imMask);
//使用修改后的特征点构造当前帧
mCurrentFrame = Frame(mImGray,imDepth,imMask,timestamp,mpORBextractorLeft,mpORBVocabulary,mK,mDistCoef,mbf,mThDepth);
//原ORB-SLAM2的跟踪
Track();
//更新几何模型的数据库
mGeometry.GeometricModelUpdateDB(mCurrentFrame);
return mCurrentFrame.mTcw.clone();
1. 构造当前帧mCurrentFrame
......
// ORB extraction
ExtractORB(0,imGray);
// Delete those ORB points that fall in Mask borders (Included by Berta)
// 传进来的mask:此时1表示保留的部分,0表示要删除的先验动态物体(稍微多删了一点边界处的部分)
// 下面这几行代码感觉变量命名不是很好,容易引起误解。这里只进行了一次erode操作,相当于把对于人的区域进一步扩大。
cv::Mat Mask_dil = imMask.clone();
int dilation_size = 15;
cv::Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_ELLIPSE,
cv::Size( 2*dilation_size + 1, 2*dilation_size+1 ),
cv::Point( dilation_size, dilation_size ) );
cv::erode(imMask, Mask_dil, kernel);
if(mvKeys.empty())
return;
std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> _mvKeys;
cv::Mat _mDescriptors;
//对于已经提取出来的ORB特征点,如果它的像素位置对应于mask位置上的1,那么这个特征点就是落在了静态物体上,就是有效的
for (size_t i(0); i < mvKeys.size(); ++i)
{
int val = (int)Mask_dil.at<uchar>(mvKeys[i].pt.y,mvKeys[i].pt.x);
if (val == 1)
{
_mvKeys.push_back(mvKeys[i]);
_mDescriptors.push_back(mDescriptors.row(i));
}
}
......
2. Tracking::LightTrack()函数
这个函数就是原来ORB-SLAM2中,Tracking::Track()函数的简化。对于函数LightTrack()来说,它的目的就是为了先用[去除先验动态物体区域后留下的特征点]做一次快速的追踪(这里都没有去和局部地图去匹配),由于留下的特征点中可能还有动态的点,所以这只是得到一个很粗略的结果,并不会让当前这些点去参与局部建图等后续的过程中。所以,这部分代码,其实主要就是Localization模式下的内容。
void Tracking::LightTrack()
{
// Get Map Mutex -> Map cannot be changed
unique_lock<mutex> lock(mpMap->mMutexMapUpdate);
bool useMotionModel = true; //set true
if(mState==NOT_INITIALIZED || mState==NO_IMAGES_YET)
{
cout << "Light Tracking not working because Tracking is not initialized..." << endl;
return;
}
else
{
// System is initialized. Track Frame.
// 系统已经完成系统初始化,下面进行追踪
bool bOK;
{
// Localization Mode:
// 只进行跟踪,局部建图不工作
if(mState==LOST)
{
// 如果跟丢了,使用重定位(这里进行了函数重载)
bOK = Relocalization(1);
}
else
{
//mbVO是对于定位模式才有的变量
//mbVO=true表示当前帧跟地图点的匹配点少于10个。(不好)
//mbVO=false表示当前帧跟地图点的匹配点较多,跟踪能正常工作。
if(!mbVO)
{
// In last frame we tracked enough MapPoints in the map
if(!mVelocity.empty() && useMotionModel)
{
//使用运动模型追踪
bool _bOK = false;
bOK = LightTrackWithMotionModel(_bOK);// TODO: check out!!!
}
else
{
//使用参考关键帧定位
bOK = TrackReferenceKeyFrame();
}
}
else
{
//没有足够的匹配点,所以进入VO模式,既做跟踪又做重定位
// In last frame we tracked mainly "visual odometry" points.
// We compute two camera poses, one from motion model and one doing relocalization.
// If relocalization is sucessfull we choose that solution, otherwise we retain
// the "visual odometry" solution.
//通过运动模型进行跟踪的结果
bool bOKMM = false;
//通过重定位模型进行跟踪的结果
bool bOKReloc = false;
//运动模型中构造的地图点
vector<MapPoint*> vpMPsMM;
//在跟踪运动模型后发现的外点
vector<bool> vbOutMM;
//运动模型得到的位姿
cv::Mat TcwMM;
bool lightTracking = false;
bool bVO = false;
//当运动模型有效时,使用运动模型计算位姿
if(!mVelocity.empty() && useMotionModel)
{
lightTracking = true;
bOKMM = LightTrackWithMotionModel(bVO); // TODO: check out!!
//暂时保存恒速模型跟踪结果,后面重定位的时候会改变这些量
vpMPsMM = mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints;
vbOutMM = mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier;
TcwMM = mCurrentFrame.mTcw.clone();
}
//用重定位的方法来得到当前帧的位姿
bOKReloc = Relocalization(1);
//据前面匀速运动模型、重定位结果来更新状态,谁成功就用谁的
if(bOKMM && !bOKReloc)
{
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(TcwMM);
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints = vpMPsMM;
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier = vbOutMM;
//如果当前帧匹配的3D点很少,增加当前可视地图点的被观测次数
if((lightTracking && bVO) || (!lightTracking && mbVO))
{
for(int i =0; i<mCurrentFrame.N; i++)
{
//如果这个特征点形成了地图点,并且也不是外点的时候
if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i] && !mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i])
{
//增加能观测到该地图点的帧数
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->IncreaseFound();
}
}
}
}
//只要有一种成功就行
bOK = bOKReloc || bOKMM;
}
}
}
//把最新的关键帧当做当前帧的参考关键帧
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
if(!bOK)
{
if(mpMap->KeyFramesInMap()<=5)
{
cout << "Light Tracking not working..." << endl;
return;
}
}
if(!mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF)
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
}
}
三. Geometry类实现动态物体检测
这一节专门讨论一下Tracking::GrabImageRGBD()中的下面两个函数。Geometry类主要是用几何方法去除先验知识以外的动态物体,该类下还有两个类:DataBase类和DynKeyPoint类。
下面代码的第二个函数比较简单,mGeometry.GeometricModelUpdateDB(mCurrentFrame) 的作用是把当前帧加入到Geometry类下的DataBase类变量mDB中,相当于维护一个局部地图(代码默认是20帧),如果变量Geometry::mDB已经存满了20帧数据,那么新来的帧会从最早存入DB的帧开始覆盖,从而实现更新。
//Tracking::GrabImageRGBD()中
mGeometry.GeometricModelCorrection(mCurrentFrame,mImGray,imMask);
mGeometry.GeometricModelUpdateDB(mCurrentFrame);
1. Geometry::GeometricModelCorrection()
首先,先来回顾一下这个模块的实现方法:
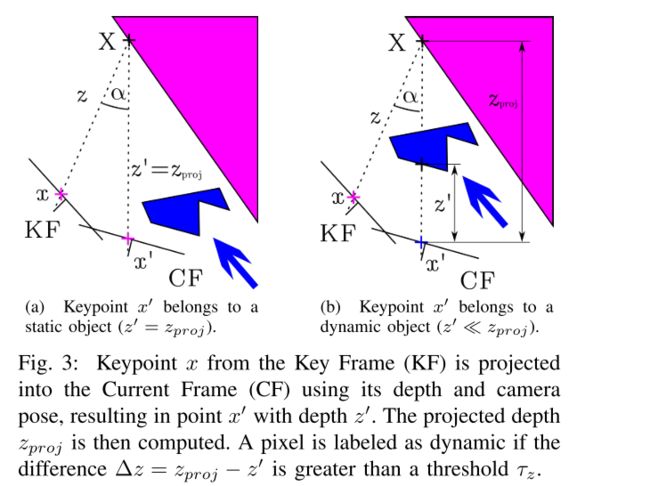
- 对于每一个输入帧,选择之前的和输入帧有最高重合度的多个关键帧(论文设置为5个),这个重合度是通过考虑新的一帧和每个关键帧之间的距离和旋转来决定的。
- 把之前关键帧中的每个关键点 x x x都投影到当前帧,得到关键点 x ′ x' x′和它们的投影深度 z p r o j z_{proj} zproj
对每个关键点,它对应的3D点是 X X X。然后,计算 x x x和 x ′ x' x′反投影之间的夹角,即视差角 α \alpha α。如果角度大于30度,这个点就有可能是静态点出现遮挡情况,之后就会被忽略。- 计算出关于深度的重投影误差: Δ z = z p r o j − z ′ \Delta z = z_{proj} - z' Δz=zproj−z′, z ′ z' z′是是当前帧中还有的关键点的深度(测量值)。如果视差角小于30度且 Δ z > τ z \Delta z > \tau_z Δz>τz,关键点 x ′ x' x′就会被视为动态物体。为了有一个好的精度和召回率,通过最大化 0.7 ∗ P r e s i o n + 0.3 ∗ R e c a l l 0.7*Presion + 0.3*Recall 0.7∗Presion+0.3∗Recall,将 τ z \tau_z τz定为0.4m。
- 有一些被标记为动态的关键点位于移动物体的边界上,这可能会引起问题。为了避免这种情况,可以使用深度图像所提供的信息。如果一个关键点被设定为动态,但在深度图中它周围的区域有很大的方差,我们就把标签改为静态。
- 为了找到动态物体的所有像素点,在深度图的动态点周围进行区域增长算法。
void Geometry::GeometricModelCorrection(const ORB_SLAM2::Frame ¤tFrame,
cv::Mat &imDepth, cv::Mat &mask){
//如果不知道当前帧的位姿,就没办法把之前关键帧中的每个关键点都投影到当前帧
if(currentFrame.mTcw.empty()){
std::cout << "Geometry not working." << std::endl;
}
//如果Geometry的数据库存储的帧超过了5个(能够组成有效的局部地图了)
//那么就可以继续进行后面的步骤
else if (mDB.mNumElem >= ELEM_INITIAL_MAP){
//这里就从和当前帧相关的关键帧中
//选出离当前帧的位姿和旋转最近的5个帧作为参考帧(函数内部进行了距离的计算)
vector<ORB_SLAM2::Frame> vRefFrames = GetRefFrames(currentFrame);
//见第3点
vector<DynKeyPoint> vDynPoints = ExtractDynPoints(vRefFrames,currentFrame);
//以检测到的动态点为中心,对深度图进行区域增长,从而找到动态点所落在的动态物体上,
//在后续的过程中,整个动态物体都会被去除
mask = DepthRegionGrowing(vDynPoints,imDepth);
//把通过深度学习和几何方法得到Mask取并集(函数写的麻烦一点,但就是这个意思)
CombineMasks(currentFrame,mask);
}
}
2. Geometry::GetRefFrames()
函数中展示了怎么取出与输入帧有最高重合度的多个关键帧,和论文中的第一点对应:
- 对于每一个输入帧,选择之前的和输入帧有最高重合度的多个关键帧(论文设置为5个),这个重合度是通过考虑新的一帧和每个关键帧之间的距离和旋转来决定的。
vector<ORB_SLAM2::Frame> Geometry::GetRefFrames(const ORB_SLAM2::Frame ¤tFrame){
cv::Mat rot1 = currentFrame.mTcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3);
cv::Mat eul1 = rotm2euler(rot1); //旋转矩阵转欧拉角
cv::Mat trans1 = currentFrame.mTcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3);
cv::Mat vDist;
cv::Mat vRot;
for (int i(0); i < mDB.mNumElem; i++){
//遍历所有在数据库中的帧,求它到当前帧位姿欧拉角的模长并存储(计算旋转上的距离)
cv::Mat rot2 = mDB.mvDataBase[i].mTcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3);
cv::Mat eul2 = rotm2euler(rot2);
double distRot = cv::norm(eul2,eul1,cv::NORM_L2);
vRot.push_back(distRot);
//计算两帧之间位移上的距离
cv::Mat trans2 = mDB.mvDataBase[i].mTcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3);
double dist = cv::norm(trans2,trans1,cv::NORM_L2);
vDist.push_back(dist); //这里是对cv::Mat进行了push_back操作!
}
//每一次都会更新当前距离在最大距离所占的比例 0-1
double minvDist, maxvDist;
cv::minMaxLoc(vDist, &minvDist, &maxvDist);
vDist /= maxvDist;
double minvRot, maxvRot;
cv::minMaxLoc(vRot, &minvRot, &maxvRot);
vRot /= maxvRot;
//算出来的针对当前帧的一个距离阈值
vDist = 0.7*vDist + 0.3*vRot;
cv::Mat vIndex;
//返回对应原矩阵的索引, 进行对列的降序排列
cv::sortIdx(vDist,vIndex,CV_SORT_EVERY_COLUMN + CV_SORT_DESCENDING);
cout<< "**sortIdx TEST" << vIndex.at<int>(0,1) << vIndex.at<int>(0,2) << vIndex.at<int>(0,3) << endl;
cout << "**OUTPUT Dist:" << vDist.at<double>(vIndex.at<int>(0,1),0) << vDist.at<double>(vIndex.at<int>(0,2),0) <<
vDist.at<double>(vIndex.at<int>(0,3),0) << endl;
// TODO: 这样岂不是选了距离最远的??重合度反而最小????
//因为之前的ELEM_INITIAL_MAP和MAX_REF_FRAMES都是5,其实这里就相当于一定是取5个参考帧
mnRefFrames = std::min(MAX_REF_FRAMES,vDist.rows);
vector<ORB_SLAM2::Frame> vRefFrames;
for (int i(0); i < mnRefFrames; i++)
{
int ind = vIndex.at<int>(0,i);
vRefFrames.push_back(mDB.mvDataBase[ind]);
}
return(vRefFrames);
}
两处思考※
1)这里感觉要去重叠度最大的5帧,应该要用Dist最小的5个,所以源码中的排序应该按照从小到大,即ASCENDING?
2)按照顺序修改后,再运行程序却得到了这个报错(没改时,有时候也会报这个错):
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'cv::Exception'
what(): OpenCV(3.4.5) /.../opencv/modules/core/src/matmul.cpp:1575: error: (-215:Assertion failed) a_size.width == len in function 'gemm'
Aborted (core dumped)
通过Debug发现是没有对Geometry::ExtractDynPoints()中的k值和h值进行检验,导致初始化了size为0的Mat矩阵,增加的代码见下一点。
3. Geometry::ExtractDynPoints()
这一部分就是利用几何方法寻找动态点的核心部分。
vector<Geometry::DynKeyPoint> Geometry::ExtractDynPoints(const vector<ORB_SLAM2::Frame> &vRefFrames,
const ORB_SLAM2::Frame ¤tFrame){
cv::Mat K = cv::Mat::eye(3,3,CV_32F);
K.at<float>(0,0) = currentFrame.fx;
K.at<float>(1,1) = currentFrame.fy;
K.at<float>(0,2) = currentFrame.cx;
K.at<float>(1,2) = currentFrame.cy;
cv::Mat vAllMPw; //存放所有的世界坐标系下地图点
cv::Mat vAllMatRefFrame; //存放参考帧中,关键点的u,v,1
cv::Mat vAllLabels;
cv::Mat vAllDepthRefFrame;
//遍历每一个参考帧
for (int i(0); i < mnRefFrames; i++)
{
ORB_SLAM2::Frame refFrame = vRefFrames[i];
// Fill matrix with points
// 这里是用来存储单独一个参考帧的信息 坐标u,v,1
cv::Mat matRefFrame(refFrame.N,3,CV_32F);
cv::Mat matDepthRefFrame(refFrame.N,1,CV_32F);
cv::Mat matInvDepthRefFrame(refFrame.N,1,CV_32F);
//参考帧中的有效关键点有k个,vLabels.at(k,0)表示第k个有效关键点对应着原来该参考帧中第i个关键点
cv::Mat vLabels(refFrame.N,1,CV_32F);
int k(0);
//遍历这一参考帧的所有关键点
for(int j(0); j < refFrame.N; j++){
const cv::KeyPoint &kp = refFrame.mvKeys[j];
const float &v = kp.pt.y;
const float &u = kp.pt.x;
const float d = refFrame.mImDepth.at<float>(v,u);
//这里的深度单位应该是m
///STEP1: 对参考帧的点的深度进行筛选
if (d > 0 && d < 6){
matRefFrame.at<float>(k,0) = refFrame.mvKeysUn[j].pt.x;
matRefFrame.at<float>(k,1) = refFrame.mvKeysUn[j].pt.y;
matRefFrame.at<float>(k,2) = 1.;
matInvDepthRefFrame.at<float>(k,0) = 1./d;
matDepthRefFrame.at<float>(k,0) = d;
vLabels.at<float>(k,0) = i;
k++;
}
}
if(k==0){
continue; //add!
}
//matRefFrame是一个k*3维度的矩阵,存的是参考帧关键点的像素坐标 u,v,1
matRefFrame = matRefFrame.rowRange(0,k);
matInvDepthRefFrame = matInvDepthRefFrame.rowRange(0,k);
matDepthRefFrame = matDepthRefFrame.rowRange(0,k);
vLabels = vLabels.rowRange(0,k); //一个k*1维的mat
//参考帧的关键点在相机坐标系的坐标 维度3*k 得到归一化坐标 X/Z, Y/Z, 1
cv::Mat vMPRefFrame = K.inv()*matRefFrame.t();
cout <<"vMPRefFrame size " <<vMPRefFrame.size() <<endl;
//把两个vMPRefFrame和matInvDepthRefFrame拼合在一起 变成 X/Z, Y/Z, 1, 1/Z
cv::vconcat(vMPRefFrame,matInvDepthRefFrame.t(),vMPRefFrame); //维度变为 4*k
cv::Mat vMPw = refFrame.mTcw.inv() * vMPRefFrame; //关键点在世界坐标系的归一化坐标 4*k
cv::Mat _vMPw = cv::Mat(4,vMPw.cols,CV_32F);
cv::Mat _vLabels = cv::Mat(vLabels.rows,1,CV_32F);
cv::Mat _matRefFrame = cv::Mat(matRefFrame.rows,3,CV_32F);
cv::Mat _matDepthRefFrame = cv::Mat(matDepthRefFrame.rows,1,CV_32F);
int h(0);
mParallaxThreshold = 30; //视差角
//STEP2: 根据地图点和两帧上的投影点的夹角(视差角)大小进行筛选
for (int j(0); j < k; j++)
{
cv::Mat mp = cv::Mat(3,1,CV_32F);
//这里又从归一化坐标变为了X,Y,Z
mp.at<float>(0,0) = vMPw.at<float>(0,j)/matInvDepthRefFrame.at<float>(0,j);
mp.at<float>(1,0) = vMPw.at<float>(1,j)/matInvDepthRefFrame.at<float>(0,j);
mp.at<float>(2,0) = vMPw.at<float>(2,j)/matInvDepthRefFrame.at<float>(0,j);
cv::Mat tRefFrame = refFrame.mTcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3); //参考帧相机在世界坐标系下的位置
cv::Mat tCurrentFrame = currentFrame.mTcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3); //当前帧相机在世界坐标系下的位置
//对应图中的 X-KF
cv::Mat nMPRefFrame = mp - tRefFrame;
//对应图中的 X-CF
cv::Mat nMPCurrentFrame = mp - tCurrentFrame;
double dotProduct = nMPRefFrame.dot(nMPCurrentFrame);
double normMPRefFrame = cv::norm(nMPRefFrame,cv::NORM_L2);
double normMPCurrentFrame = cv::norm(nMPCurrentFrame,cv::NORM_L2);
//X-KF和X-CF进行点乘然后单位化,求的就是视差角的cos值
double angle = acos(dotProduct/(normMPRefFrame*normMPCurrentFrame))*180/M_PI;
//cout << "parallax angle= " << angle <
//小于30度才保存地图点,参考帧的点; 大于30度的点在论文中被认为是“有遮挡情况的静态点”,如果不筛除,后续就会被错误归为动态点
if (angle < mParallaxThreshold)
{
//j表示满足前面深度要求的地图点的遍历序号,h表示后续还能满足视差角条件的地图点的遍历序号
_vMPw.at<float>(0,h) = vMPw.at<float>(0,j); //X
_vMPw.at<float>(1,h) = vMPw.at<float>(1,j); //Y
_vMPw.at<float>(2,h) = vMPw.at<float>(2,j); //Z
_vMPw.at<float>(3,h) = vMPw.at<float>(3,j); // 1/Z
_vLabels.at<float>(h,0) = vLabels.at<float>(j,0);
_matRefFrame.at<float>(h,0) = matRefFrame.at<float>(j,0); //u
_matRefFrame.at<float>(h,1) = matRefFrame.at<float>(j,1); //v
_matRefFrame.at<float>(h,2) = matRefFrame.at<float>(j,2); //1
_matDepthRefFrame.at<float>(h,0) = matDepthRefFrame.at<float>(j,0);
h++; //对于当前帧和参考帧,有h个有效的地图点满足视差角
}
}
if(h==0){
continue; // add!
}
vMPw = _vMPw.colRange(0,h);
vLabels = _vLabels.rowRange(0,h);
matRefFrame = _matRefFrame.rowRange(0,h);
matDepthRefFrame = _matDepthRefFrame.rowRange(0,h);
//把单帧计算的地图点结果放进All-系列变量中
if (vAllMPw.empty())
{
vAllMPw = vMPw;
vAllMatRefFrame = matRefFrame;
vAllLabels = vLabels;
vAllDepthRefFrame = matDepthRefFrame;
}
else
{
if (!vMPw.empty())
{
hconcat(vAllMPw,vMPw,vAllMPw);
vconcat(vAllMatRefFrame,matRefFrame,vAllMatRefFrame);
vconcat(vAllLabels,vLabels,vAllLabels);
vconcat(vAllDepthRefFrame,matDepthRefFrame,vAllDepthRefFrame);
}
}
}
cv::Mat vLabels = vAllLabels;
//STEP3: 将筛选后参考帧的所有地图点投影到当前帧,如果这些地图点的深度不超过7m才保留
if (!vAllMPw.empty())
{
//把筛选后的所有参考帧在世界坐标系下的地图点投影到当前帧相机坐标系下 /有4行
//世界坐标系下三维点[X/Z,Y/Z,Z/Z,1/Z]-> 得到当前帧坐标系下的归一化坐标
cv::Mat vMPCurrentFrame = currentFrame.mTcw * vAllMPw;
// Divide by last column
for (int i(0); i < vMPCurrentFrame.cols; i++)
{
//vMPCurrentFrame 存的是 [X, Y, Z, 1](由参考帧投过来的)
vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(0,i) /= vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(3,i);
vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(1,i) /= vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(3,i);
vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(2,i) /= vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(3,i);
vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(3,i) /= vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(3,i);
}
cv::Mat matProjDepth = vMPCurrentFrame.row(2);
cv::Mat _vMPCurrentFrame = cv::Mat(vMPCurrentFrame.size(),CV_32F);
cv::Mat _vAllMatRefFrame = cv::Mat(vAllMatRefFrame.size(),CV_32F);
cv::Mat _vLabels = cv::Mat(vLabels.size(),CV_32F);
cv::Mat __vAllDepthRefFrame = cv::Mat(vAllDepthRefFrame.size(),CV_32F);
int h(0);
cv::Mat __matProjDepth = cv::Mat(matProjDepth.size(),CV_32F);
for (int i(0); i < matProjDepth.cols; i++)
{
//只保留计算(投影)得到的当前帧中距离不超过7m的地图点和对应的像素点
if (matProjDepth.at<float>(0,i) < 7)
{
__matProjDepth.at<float>(0,h) = matProjDepth.at<float>(0,i);
_vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(0,h) = vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(0,i); //X
_vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(1,h) = vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(1,i); //Y
_vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(2,h) = vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(2,i); //Z
_vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(3,h) = vMPCurrentFrame.at<float>(3,i); //1
_vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(h,0) = vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(i,0); //u
_vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(h,1) = vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(i,1); //v
_vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(h,2) = vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(i,2); //1
_vLabels.at<float>(h,0) = vLabels.at<float>(i,0);
__vAllDepthRefFrame.at<float>(h,0) = vAllDepthRefFrame.at<float>(i,0);
h++;
}
}
matProjDepth = __matProjDepth.colRange(0,h);
vMPCurrentFrame = _vMPCurrentFrame.colRange(0,h); //一共有h个关键点入选,
vAllMatRefFrame = _vAllMatRefFrame.rowRange(0,h);
vLabels = _vLabels.rowRange(0,h);
vAllDepthRefFrame = __vAllDepthRefFrame.rowRange(0,h);
cv::Mat aux;
//维度是3*4的矩阵
cv::hconcat(cv::Mat::eye(3,3,CV_32F),cv::Mat::zeros(3,1,CV_32F),aux);
//vMPCurrentFrame 存的是 [X, Y, Z, 1]
cv::Mat matCurrentFrame = K*aux*vMPCurrentFrame; //转换到像素坐标 z*(u,v,1)
cv::Mat mat2CurrentFrame(matCurrentFrame.cols,2,CV_32F);
cv::Mat v2AllMatRefFrame(matCurrentFrame.cols,3,CV_32F);
cv::Mat mat2ProjDepth(matCurrentFrame.cols,1,CV_32F);
cv::Mat v2Labels(matCurrentFrame.cols,1,CV_32F);
cv::Mat _vAllDepthRefFrame(matCurrentFrame.cols,1,CV_32F);
//STEP4: 如果把“由多个参考帧的地图点投影到当前帧”的信息换算成一个深度图,投影得到的深度要比测量深度大
int j = 0;
for (int i(0); i < matCurrentFrame.cols; i++)
{
//这个是由参考帧算出来的 u,v值
float x = ceil(matCurrentFrame.at<float>(0,i)/matCurrentFrame.at<float>(2,i));
float y = ceil(matCurrentFrame.at<float>(1,i)/matCurrentFrame.at<float>(2,i));
//如果这个像素坐标在当前帧深度图的特定范围内(这里把深度图的最外20pixel除去了,和后面使用的滑窗有关)
if (IsInFrame(x,y,currentFrame))
{
//当前帧实际测量出的深度值d
const float d = currentFrame.mImDepth.at<float>(y,x);
if (d > 0)
{
//TODO: 如果这里参考帧的投影有重复的,即有相同的u,v坐标,但深度不同。这里没有对重复的筛选?
mat2CurrentFrame.at<float>(j,0) = x;
mat2CurrentFrame.at<float>(j,1) = y;
// 存入所有有效的像素坐标 u,v,1; depth
v2AllMatRefFrame.at<float>(j,0) = vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(i,0);
v2AllMatRefFrame.at<float>(j,1) = vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(i,1);
v2AllMatRefFrame.at<float>(j,2) = vAllMatRefFrame.at<float>(i,2); // =1
//投影得到的当前帧对应点的深度
float d1 = matProjDepth.at<float>(0,i);
mat2ProjDepth.at<float>(j,0) = d1; //深度的投影值
v2Labels.at<float>(j,0) = vLabels.at<float>(i,0);
j++;
}
}
}
vAllDepthRefFrame = _vAllDepthRefFrame.rowRange(0,j);
vAllMatRefFrame = v2AllMatRefFrame.rowRange(0,j);
matProjDepth = mat2ProjDepth.rowRange(0,j);
matCurrentFrame = mat2CurrentFrame.rowRange(0,j);
vLabels = v2Labels.rowRange(0,j);
//在IsInFrame函数中 mDmax初始化为20,所以这里新建了一个维度为[41*41, 2]大小的矩阵
//这个小矩阵u1, 每一行存放着能遍历一个41*41矩阵的坐标id: i,j
// [-20,-20] [-20,-19] ..... [-20,20]
// [-19,-20] [-19,-19] ..... [-19,20]
// .....
cv::Mat u1((2*mDmax+1)*(2*mDmax+1),2,CV_32F);
int m(0);
for (int i(-mDmax); i <= mDmax; i++){
for (int j(-mDmax); j <= mDmax; j++){
u1.at<float>(m,0) = i;
u1.at<float>(m,1) = j;
m++;
}
}
cv::Mat matDepthCurrentFrame(matCurrentFrame.rows,1,CV_32F);
cv::Mat _matProjDepth(matCurrentFrame.rows,1,CV_32F);
cv::Mat _matCurrentFrame(matCurrentFrame.rows,2,CV_32F);
int _s(0);
for (int i(0); i < matCurrentFrame.rows; i++)
{
int s(0);
cv::Mat _matDiffDepth(u1.rows,1,CV_32F);
cv::Mat _matDepth(u1.rows,1,CV_32F);
//这里是按照一个patch一个patch来计算的,patch之间会有重叠的地方,有重复的计算
//这样是为了后面计算一个patch内的深度Diff阈值和标准差
for (int j(0); j < u1.rows; j++)
{
int x = (int)matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,0) + (int)u1.at<float>(j,0);
int y = (int)matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,1) + (int)u1.at<float>(j,1);
float _d = currentFrame.mImDepth.at<float>(y,x); //实际测量值
//如果实际测量值大于0并且小于投影的深度 TODO ///
if ((_d > 0) && (_d < matProjDepth.at<float>(i,0)))
{
_matDepth.at<float>(s,0) = _d;
_matDiffDepth.at<float>(s,0) = matProjDepth.at<float>(i,0) - _d;
s++; //记录计算的DiffDepth的个数,即对多少个像素点,有投影深度>实际深度,这些像素点对应潜在动态点
}
}
//潜在动态点个数大于0时
if (s > 0)
{
_matDepth = _matDepth.rowRange(0,s);
_matDiffDepth = _matDiffDepth.rowRange(0,s);
double minVal, maxVal;
cv::Point minIdx, maxIdx;
//存储DiffDepth的最大最小值以及对应的index
cv::minMaxLoc(_matDiffDepth,&minVal,&maxVal,&minIdx,&maxIdx);
int xIndex = minIdx.x;
int yIndex = minIdx.y;
matDepthCurrentFrame.at<float>(_s,0) = _matDepth.at<float>(yIndex,0); //实际深度
_matProjDepth.at<float>(_s,0) = matProjDepth.at<float>(i,0); //对应的投影深度
//对应的像素点坐标
_matCurrentFrame.at<float>(_s,0) = matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,0);
_matCurrentFrame.at<float>(_s,1) = matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,1);
_s++;
}
}
matDepthCurrentFrame = matDepthCurrentFrame.rowRange(0,_s);
matProjDepth = _matProjDepth.rowRange(0,_s);
matCurrentFrame = _matCurrentFrame.rowRange(0,_s);
mDepthThreshold = 0.6;
cv::Mat matDepthDifference = matProjDepth - matDepthCurrentFrame;
mVarThreshold = 0.001; //0.040;
//STEP5: 根据距离差值的阈值,筛选出最终的动态点
vector<Geometry::DynKeyPoint> vDynPoints;
for (int i(0); i < matCurrentFrame.rows; i++)
{
//深度的差值要大于阈值
if (matDepthDifference.at<float>(i,0) > mDepthThreshold)
{
int xIni = (int)matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,0) - mDmax;
int yIni = (int)matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,1) - mDmax;
int xEnd = (int)matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,0) + mDmax + 1;
int yEnd = (int)matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,1) + mDmax + 1;
cv::Mat patch = currentFrame.mImDepth.rowRange(yIni,yEnd).colRange(xIni,xEnd);
cv::Mat mean, stddev;
cv::meanStdDev(patch,mean,stddev);
double _stddev = stddev.at<double>(0,0);
double var = _stddev*_stddev;
//这个patch内当前帧测量深度的方差(深度值的变化幅度小)要小于一个阈值,理解是这一块不能本身就有很复杂的遮挡关系
if (var < mVarThreshold)
{
DynKeyPoint dynPoint;
dynPoint.mPoint.x = matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,0);
dynPoint.mPoint.y = matCurrentFrame.at<float>(i,1);
dynPoint.mRefFrameLabel = vLabels.at<float>(i,0); //对应着原来的某个关键点
vDynPoints.push_back(dynPoint);
}
}
}
return vDynPoints;
}
else
{
//如果参考帧中没有能满足大于30度视差角的地图点:
vector<Geometry::DynKeyPoint> vDynPoints;
return vDynPoints;
}
}
以上就是对DynaSLAM源码这一部分的笔记内容,完结,撒花~