ROS2 humble教程学习笔记
ROS2 humble教程学习笔记
- 一、相关链接
- 二、基础概念
-
- 2.1 理解nodes
-
- ros2 run 命令
- 2.2 理解topics
- 2.3 理解service
- 2.4 理解参数
-
- load parameter file on node startup
- 2.5 理解actions
-
- 背景
- 使用actions
- ros2的action接口
- 2.6 使用rqt_console查看日志
- 2.7 启动节点
- 2.8 记录并回放数据
- 2.9 总结
- 三、客户端库
-
- 3.1 使用`colcon`构建包
-
- 创建自己的package
- 3.2 创建工作空间
- 3.3 创建包
- 3.4 Writing a simple publisher and subscribler(C++)
- 3.5 写一个简单的s/c
- 3.6 创建自定义消息和文件
- 3.7 实现自定义接口
一、相关链接
- ubuntu系统下如何安装 ROS2 Humble Hawksbill
- VMware安装ubuntu虚拟机
- Ubantu文件系统和常用命令
- cmake实践笔记
- ubuntu配置opencv
- 官网英文教程
二、基础概念
2.1 理解nodes
ros2 run 命令
ros2 run
,如
ros2 run turtlesim turtlesim_node
Here, the package name is turtlesim and the executable name is turtlesim_node
ros2 run turtlesim turtle_teleop_key
查看nodes名称可以使用ros2 node list。该命令会显示所有正在运行的node,在需要进行节点交互或者跟踪节点时非常有用。如下命令可以用来创建指定名称的turtle节点,
ros2 run turtlesim turtlesim_node --ros-args --remap __node:=myturtle
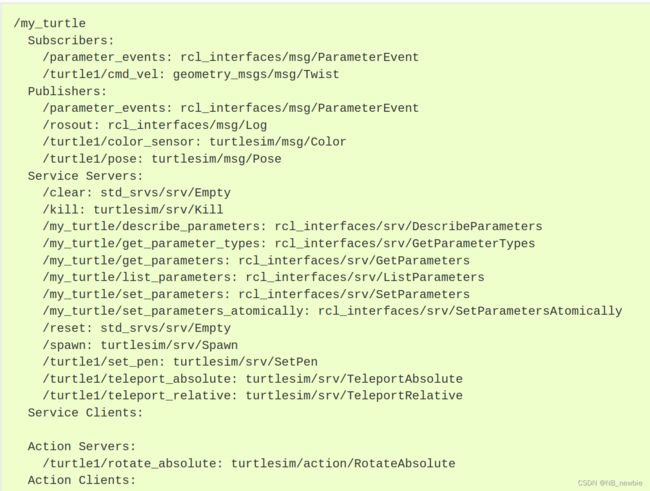
显示node的信息使用如下格式代码:ros2 node info
ros2 node info /my_turtle
2.2 理解topics
rqt_graph可视化节点之间的通信。看在topic上的数据用如下命令:
ros2 topic echo 。
ros2 topic info /turtle1/cmd_vel命令查看topic的publisher数目和subscription数目。
节点(nodes)使用消息(messages)通过主题(topics)发送数据。发布者(publisher)和订阅者(subscription)必须发送和接收相同类型的消息才能进行通信。
查看消息类型的详情使用如下命令:ros2 interface show geometry_msgs/msg/Twist。
知道消息类型后,就可直接通过命令行传递消息了。
ros2 topic pub ''
ros2 topic pub --once /turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/msg/Twist "{linear: {x: 2.0, y: 0.0, z: 0.0}, angular: {x: 0.0, y: 0.0, z: 1.8}}"
--once表示只传递一次消息。如果需要连续传递消息,可以使用如下命令:
ros2 topic pub --rate 1 /turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/msg/Twist "{linear: {x: 2.0, y: 0.0, z: 0.0}, angular: {x: 0.0, y: 0.0, z: 1.8}}"
对于这个过程的最后一次自省,您可以使用以下命令查看数据发布的速率:
ros2 topic hz /turtle1/pose。
2.3 理解service
service是另一种ros节点间通信的方式。服务基于呼叫和响应模型,而不是主题的发布者-订阅者模型。主题允许节点订阅数据流并获得持续更新,但服务仅在客户机专门调用时才提供数据。
service类型用于指定服务的呼叫和响应是如何组织的,其定义和topic类型类似,只是service的类型包含呼叫类型和响应类型两部分,查看service类型的命令如下:
ros2 service type
ros2 service list -t或者ros2 service list –show-types可以在列出services的同时附加每个service的类型。
如果你想要查找某种类型的service,输入如下命令:
ros2 service find
如ros2 service find std_srvs/srv/Empty的返回结果为
/clear
/reset
您可以从命令行调用服务,但首先需要知道输入参数的结构。
ros2 interface show
现在您已经知道了服务类型是什么,如何查找服务类型,以及如何查找该类型参数的结构,您可以使用以下命令调用服务:
ros2 service call
ros2 service call /spawn turtlesim/srv/Spawn "{x: 2, y: 2, theta: 0.2, name: ''}"
2.4 理解参数
understanding parameters
参数是节点的配置值,可以看作是节点的设置。节点可以将参数存储为整数、浮点、布尔、字符串和列表。在ROS2中,每个节点维护自身的参数。
ros2 param list用于显示参数,示例如下:
/teleop_turtle:
qos_overrides./parameter_events.publisher.depth
qos_overrides./parameter_events.publisher.durability
qos_overrides./parameter_events.publisher.history
qos_overrides./parameter_events.publisher.reliability
scale_angular
scale_linear
use_sim_time
/turtlesim:
background_b
background_g
background_r
qos_overrides./parameter_events.publisher.depth
qos_overrides./parameter_events.publisher.durability
qos_overrides./parameter_events.publisher.history
qos_overrides./parameter_events.publisher.reliability
use_sim_time
每个节点都有use_sim_time参数。/turtlesim的参数中含有RGB颜色值,是决定turtlesim窗口背景颜色的。使用ros2 param get确定参数类型,其格式如下:
ros2 param get
示例显示节点/turtlesim的参数background_g的值:
ros2 param get /turtlesim background_g
ros2 param set 在运行中改变参数值。
ros2 param set /turtlesim background_r 150
使用set命令设置参数只会在当前会话中更改,而不会永久更改。但是,您可以保存设置并在下次启动节点时重新加载它们。
ros2 param dump 用于查看节点当当前所有参数值。ros2 param dump /turtlesim > turtlesim.yaml用于将参数值保存在turtlesim.yaml文件中。
ros2 param load 从文件中加载节点的参数值。
注意:只读参数只能在启动时修改,不能在启动后修改,这就是为什么“qos_overrides”参数会出现一些警告的原因。
load parameter file on node startup
使用已保存的参数值来启动同样的节点,使用,
ros2 run 。
注意:此处,正在启动时修改参数,因此指定的只读参数也将生效。
2.5 理解actions
背景
actions是ros2中的通信类型之一,用于长时间运行的任务,由三部分组成:目标、反馈和结果。Actions基于topics和services,它们的功能与服务类似,只是actions可以取消。它们还提供稳定的反馈,而不是service那样返回单个响应。Actions使用客户端-服务器模型,类似于发布者-订阅者模型。“action客户端”节点将目标发送到“action服务器”节点,该节点确认目标并返回反馈流和结果,如图所示。
使用actions
/teleop_turtle节点通过键盘G|B|V|C|D|E|R|T按键控制海龟旋转以及键盘F按键取消旋转的操作就是通过action实现的。操作成功完成后会有如下提示:
[INFO] [turtlesim]: Rotation goal completed successfully
如果在执行中间按下F键,则为用户端取消目标,命令行出现提示:
[INFO] [turtlesim]: Rotation goal canceled
不仅客户端一侧可以停止目标,服务端一侧也可以。当按下E后立即按下C,则得到如下提示:
[WARN] [turtlesim]: Rotation goal received before a previous goal finished. Aborting previous goal
此操作服务器选择中止第一个目标,因为它有一个新目标。它可以选择其他的东西,比如拒绝新目标或在第一个目标完成后执行第二个目标。不要以为每个动作服务器都会在获得新目标时选择放弃当前目标。
ros2 action list将列出运行在ROS graph中的所有actions。动作有类型,类似于主题和服务。要查找/turle1/rotate_ansabsolute的类型,请运行命令:
ros2 action list -t
返回:
/turtle1/rotate_absolute [turtlesim/action/RotateAbsolute]
可见action /turtle1/rotate_absolute的类型为turtlesim/action/RotateAbsolute。当您想从命令行或代码执行操作时,您将需要它。
进一步透视action /turtle1/rotate_absolute,使用如下命令:
ros2 action info /turtle1/rotate_absolute
返回:
Action: /turtle1/rotate_absolute
Action clients: 1
/teleop_turtle
Action servers: 1
/turtlesim
ros2的action接口
在发送或执行行动目标之前,您还需要一条信息,那就是action类型的结构。输入如下命令,查看/turtle1/rotate_absolute的类型turtlesim/action/RotateAbsolute的结构:
ros2 interface show turtlesim/action/RotateAbsolute
返回:
# The desired heading in radians
float32 theta
---
# The angular displacement in radians to the starting position
float32 delta
---
# The remaining rotation in radians
float32 remaining
使用如下语法在命令行中发送action目标:
ros2 action send_goal
其中,
输入:
ros2 action send_goal /turtle1/rotate_absolute turtlesim/action/RotateAbsolute "{theta: 1.57}"
返回:
Waiting for an action server to become available...
Sending goal:
theta: 1.57
Goal accepted with ID: 07335a9e9df14252af6e425efae5f2ed
Result:
delta: 1.5520000457763672
Goal finished with status: SUCCEEDED
要查看此目标的反馈,请将--feedback添加到ros2操作send_goal命令:
ros2 action send_goal /turtle1/rotate_absolute turtlesim/action/RotateAbsolute "{theta: -1.57}" --feedback
现在,您已经涵盖了所有核心ROS 2概念。“用户”集中的最后几篇教程将向您介绍一些工具和技术,这些工具和技术将使您更容易使用ROS2,从使用rqt_console查看日志开始。
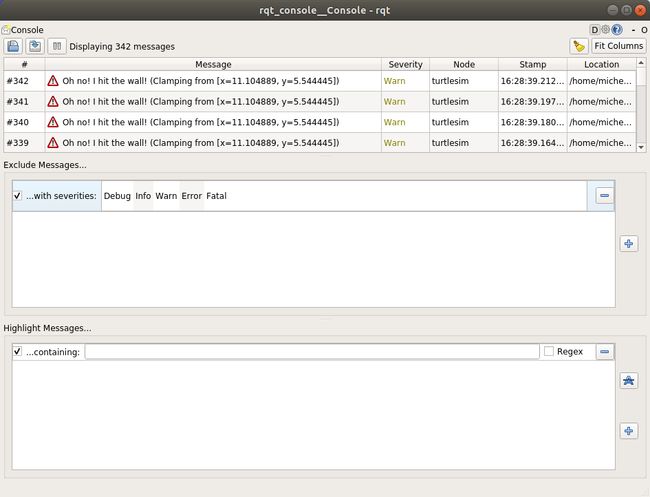
2.6 使用rqt_console查看日志
ros2 topic pub -r 1 /turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/msg/Twist "{linear: {x: 2.0, y: 0.0, z: 0.0}, angular: {x: 0.0,y: 0.0,z: 0.0}}"
以恒定的速率运动。
对于每个级别的指示没有确切的标准,但可以安全地假设:
- 致命消息表明系统将终止以保护自身免受损害。
- 错误消息表示不一定会损坏系统的重大问题,但会阻止系统正常运行。
- 警告消息表示意外的活动或不理想的结果,这可能表示更深层的问题,但不会彻底损害功能。
- 信息消息指示事件和状态更新,用于直观验证系统是否按预期运行。
- 调试消息详细说明了系统执行的整个逐步过程。
通常,只有Debug消息被隐藏,因为它们是唯一比Info低的级别。例如,如果将默认级别设置为Warn,则只能看到严重级别为Warn、Error和Fatal的消息。
设置默认logger level的例子如下:
ros2 run turtlesim turtlesim_node --ros-args --log-level WARN
如果需要仔细检查来自系统的日志消息,rqtconsole会非常有用。您可能会出于各种原因检查日志消息,通常是为了找出哪里出错了,以及导致出错的一系列事件。
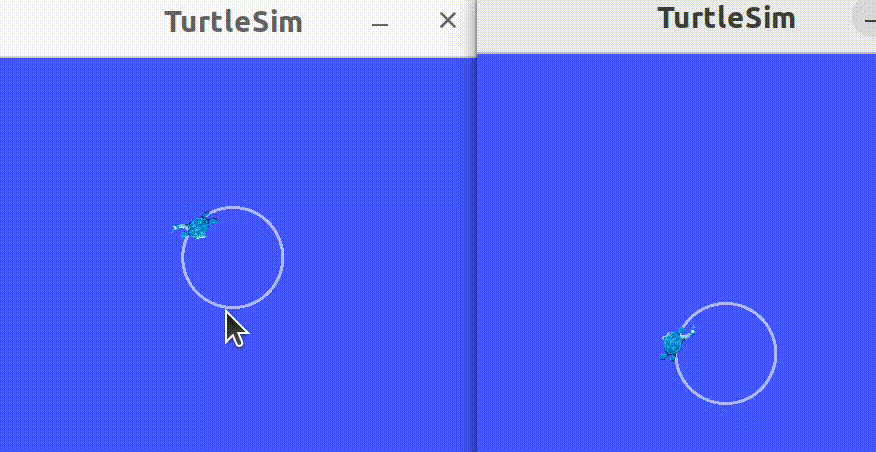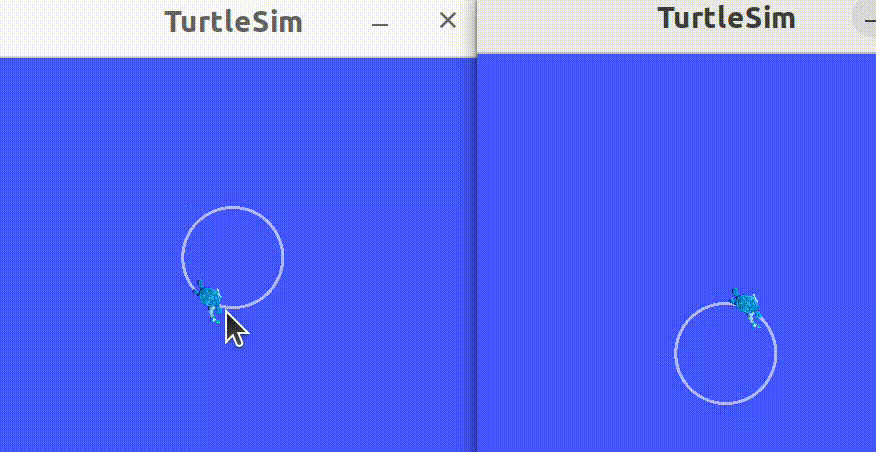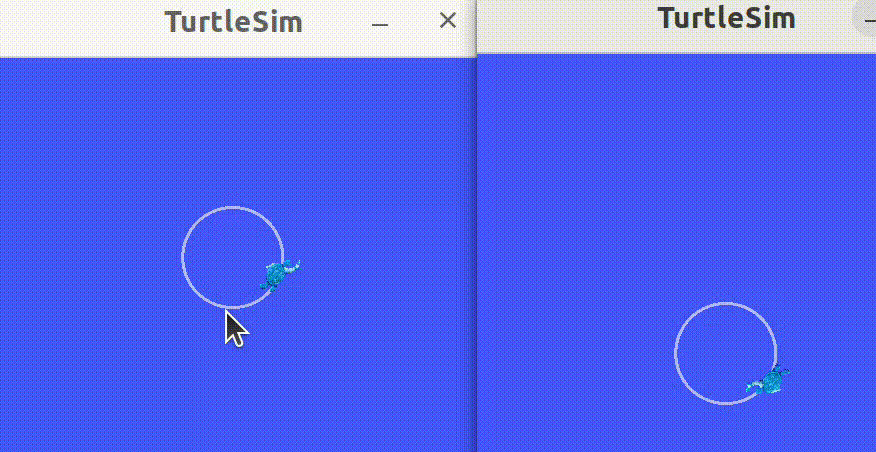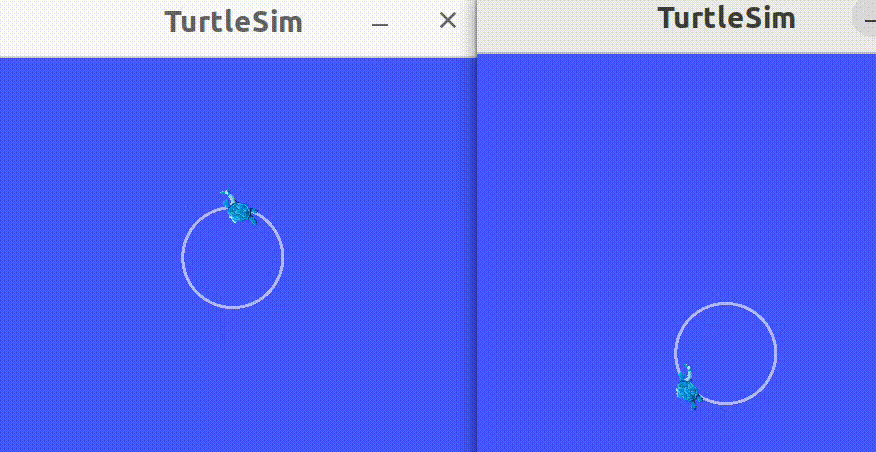
2.7 启动节点
launching nodes
使用命令行工具一次启动多个节点。
打开终端,运行如下命令:
ros2 launch turtlesim multisim.launch.py
这个命令将运行如下的launch file:
# turtlesim/launch/multisim.launch.py
from launch import LaunchDescription
import launch_ros.actions
def generate_launch_description():
return LaunchDescription([
launch_ros.actions.Node(
namespace= "turtlesim1", package='turtlesim', executable='turtlesim_node', output='screen'),
launch_ros.actions.Node(
namespace= "turtlesim2", package='turtlesim', executable='turtlesim_node', output='screen'),
])
The launch file above is written in Python, but you can also use XML and YAML to create launch files. You can see a comparison of these different ROS 2 launch formats in Using Python, XML, and YAML for ROS 2 Launch Files.
以上启动了两个turtlesim——node,开启两个命令窗口,分别运行如下代码,使得海龟分别朝相反的方向运动:
ros2 topic pub /turtlesim1/turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/msg/Twist "{linear: {x: 2.0, y: 0.0, z: 0.0}, angular: {x: 0.0, y: 0.0, z: 1.8}}"
ros2 topic pub /turtlesim2/turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/msg/Twist "{linear: {x: 2.0, y: 0.0, z: 0.0}, angular: {x: 0.0, y: 0.0, z: -1.8}}"
2.8 记录并回放数据
记录topic发布的数据以便随时回放和测试。
ros2 bag积累通过topics的所有数据并以数据库的形式储存,以便我们复现测试或者实验结果,此外还有利与共享工作和重新创造。
如果系统无法识别ros2 bag,运行如下命令重装:
sudo apt-get install ros-humble-ros2bag \
ros-humble-rosbag2-storage-default-plugins
ros2 bag只能记录通过topics传递的数据。
使用如下语法来记录topic发布的数据:
ros2 bag record
记录多个topic以及更改记录文件的名称,使用如下命令
ros2 bag record -o subset /turtle1/cmd_vel /turtle1/pose
-o选项允许您为包文件选择唯一的名称。以下字符串(在本例中subset)是文件名。要一次记录多个topics,只需列出用空格分隔的每个topic。
还有另一个选项可以添加到命令-a中,它记录系统上的所有主题。
ros2 bag info
2.9 总结
ros2 bag:
- record
- play
- info
更多rosbag2详情
三、客户端库
3.1 使用colcon构建包
这是一个实用教程,并不是为了取代核心文档而设计的。关于colcon详细使用文档。
首先安装 colcon,sudo apt install python3-colcon-common-extensions。下载示例到工作目录中,git clone https://github.com/ros2/examples src/examples -b humble。
输入如下命令构建examples:
colcon build --symlink-install
以上构建了一个demo,并通过如下命令运行实现窗口通信。
ros2 run examples_rclcpp_minimal_subscriber subscriber_member_function
ros2 run examples_rclcpp_minimal_publisher publisher_member_function
创建自己的package
这一部分比较抽象。
3.2 创建工作空间
创建一个工作区,并学习如何为开发和测试设置覆盖层(overlay)。
工作区是一个包含ros包的目录。
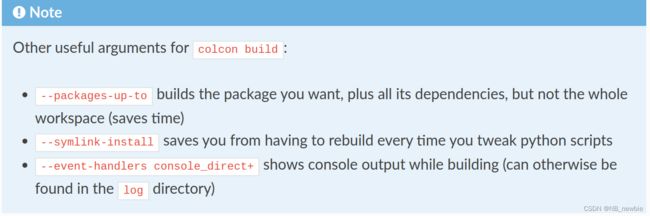
3.3 创建包
命令格式如下:
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_cmake
使用可选参数--node-name可创建一个简单的Hello World类型的执行文件于包内。
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_cmake --node-name my_node my_package
编译指定包命令:
colcon build --packages-select my_package
3.4 Writing a simple publisher and subscribler(C++)
使用C++创建并运行发布者和订阅者节点。
- 创建包,
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_cmake cpp_pubsub; - 编写源码;
- 在package.xml文件中添加依赖;
- 修改CMakeLists.txt文件;
- 在build前检查依赖,
rosdep install -i --from-path src --rosdistro humble -y; - build包,
colcon build --packages-select cpp_pubsub; - 要使用这个包,首先source安装文件,
. install/setup.bash; - 使用包,
ros2 run cpp_pubsub talker,
ros2 run cpp_pubsub listener。
总结:您创建了两个node来publish和subscrible topic上的data。在编译和运行它们之前,您将它们的依赖项和可执行文件添加到包配置文件中。
3.5 写一个简单的s/c
基于c++创建并运行service/client节点。
- 创建包,
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_cmake cpp_srvcli --dependencies rclcpp example_interfaces - 分别编写service和client的源码;
- 修改package.xml和CMakeLists.txt文件;
- 检查依赖项;
- 配置环境
. install/setup.bash - 编译运行。
源码的编写是否需深入学习呢?
3.6 创建自定义消息和文件
定义自定义接口文件(.msg和.srv)并使用。
3.7 实现自定义接口
未完待续……