深度学习中的attention机制
SE
文章 https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers/Hu_Squeeze-and-Excitation_Networks_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf![]() https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers/Hu_Squeeze-and-Excitation_Networks_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf
https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers/Hu_Squeeze-and-Excitation_Networks_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=4):
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel), )
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
y = torch.clamp(y, 0, 1)
return x * y
class SEBasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None,
*, reduction=16):
super(SEBasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes, 1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.se = SELayer(planes, reduction)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.se(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class SEBottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None,
*, reduction=16):
super(SEBottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * 4)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.se = SELayer(planes * 4, reduction)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out = self.se(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
代码
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
插入位置:
SE模块的插入位置
通过Resnet的基础模块和bottleneck模块 可以看出SE模块插入到,跳连结构add之前,对前面特征提取之后的特征图给与不同的权重,再与shortcut跳连分支相加。
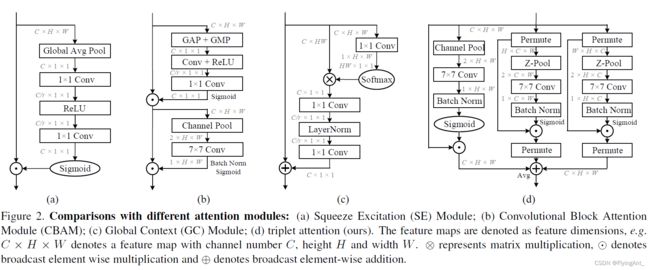
CBAM
文章
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.06521.pdf
github:GitHub - Jongchan/attention-module: Official PyTorch code for "BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module (BMVC2018)" and "CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module (ECCV2018)"
第一步:利用SE同时进行全局最大和全局平均池化,生成1x1xC通道注意力图,不同通道加权;
第二步: 通过channel池化,生成两个HxW的特征图,再卷积成1xHxW,对spatial进行逐点加权。
注意机制(CBAM)理解_Tc.小浩的博客-CSDN博客_cbam注意力机制
分两个注意力,CAM和SAM。
CAM
CAM和SE的不同在于:同时进行了全局平均池化,和全局最大池化。
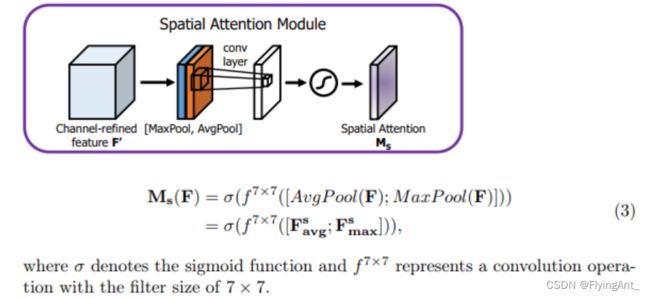
SAM
# (1)通道注意力机制
class channel_attention(nn.Module):
# ratio代表第一个全连接的通道下降倍数
def __init__(self, in_channel, ratio=4):
super().__init__()
# 全局最大池化 [b,c,h,w]==>[b,c,1,1]
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(output_size=1)
# 全局平均池化 [b,c,h,w]==>[b,c,1,1]
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=1)
# 第一个全连接层, 通道数下降4倍(可以换成1x1的卷积,效果相同)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features=in_channel, out_features=in_channel // ratio, bias=False)
# 第二个全连接层, 恢复通道数(可以换成1x1的卷积,效果相同)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features=in_channel // ratio, out_features=in_channel, bias=False)
# relu激活函数
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
# sigmoid激活函数
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
# 前向传播
def forward(self, inputs):
b, c, h, w = inputs.shape
# 输入图像做全局最大池化 [b,c,h,w]==>[b,c,1,1]
max_pool = self.max_pool(inputs)
# 输入图像的全局平均池化 [b,c,h,w]==>[b,c,1,1]
avg_pool = self.avg_pool(inputs)
# 调整池化结果的维度 [b,c,1,1]==>[b,c]
max_pool = max_pool.view([b, c])
avg_pool = avg_pool.view([b, c])
# 第一个全连接层下降通道数 [b,c]==>[b,c//4]
x_maxpool = self.fc1(max_pool)
x_avgpool = self.fc1(avg_pool)
# 激活函数
x_maxpool = self.relu(x_maxpool)
x_avgpool = self.relu(x_avgpool)
# 第二个全连接层恢复通道数 [b,c//4]==>[b,c]
# (可以换成1x1的卷积,效果相同)
x_maxpool = self.fc2(x_maxpool)
x_avgpool = self.fc2(x_avgpool)
# 将这两种池化结果相加 [b,c]==>[b,c]
x = x_maxpool + x_avgpool
# sigmoid函数权值归一化
x = self.sigmoid(x)
# 调整维度 [b,c]==>[b,c,1,1]
x = x.view([b, c, 1, 1])
# 输入特征图和通道权重相乘 [b,c,h,w]
outputs = inputs * x
return outputs
# (2)空间注意力机制
class spatial_attention(nn.Module):
# 卷积核大小为7*7
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super().__init__()
# 为了保持卷积前后的特征图shape相同,卷积时需要padding
padding = kernel_size // 2
# 7*7卷积融合通道信息 [b,2,h,w]==>[b,1,h,w]
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=2, out_channels=1, kernel_size=kernel_size,
padding=padding, bias=False)
# sigmoid函数
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
# 前向传播
def forward(self, inputs):
# 在通道维度上最大池化 [b,1,h,w] keepdim保留原有深度
# 返回值是在某维度的最大值和对应的索引
x_maxpool, _ = torch.max(inputs, dim=1, keepdim=True)
# 在通道维度上平均池化 [b,1,h,w]
x_avgpool = torch.mean(inputs, dim=1, keepdim=True)
# 池化后的结果在通道维度上堆叠 [b,2,h,w]
x = torch.cat([x_maxpool, x_avgpool], dim=1)
# 卷积融合通道信息 [b,2,h,w]==>[b,1,h,w]
x = self.conv(x)
# 空间权重归一化
x = self.sigmoid(x)
# 输入特征图和空间权重相乘
outputs = inputs * x
return outputs
# (3)CBAM注意力机制
class CBAM(nn.Module):
# 初始化,in_channel和ratio=4代表通道注意力机制的输入通道数和第一个全连接下降的通道数
# kernel_size代表空间注意力机制的卷积核大小
def __init__(self, in_channel, ratio=4, kernel_size=7):
super().__init__()
# 实例化通道注意力机制
self.channel_attention = channel_attention(in_channel=in_channel, ratio=ratio)
# 实例化空间注意力机制
self.spatial_attention = spatial_attention(kernel_size=kernel_size)
# 前向传播
def forward(self, inputs):
# 先将输入图像经过通道注意力机制
x = self.channel_attention(inputs)
# 然后经过空间注意力机制
x = self.spatial_attention(x)
return xCA
文章:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2021/papers/Hou_Coordinate_Attention_for_Efficient_Mobile_Network_Design_CVPR_2021_paper.pdf
code: GitHub - houqb/CoordAttention: Code for our CVPR2021 paper coordinate attention
参考文档:
CA(Coordinate attention) 注意力机制 - 知乎
2021CVPR-Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design 坐标注意力机制_小哈蒙德的博客-CSDN博客_坐标注意力机制