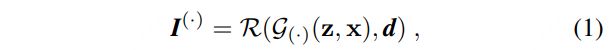【论文解析】NeRFInvertor: High Fidelity NeRF-GAN Inversion for Single-shot Real Image Animation
用于Single-shot 实景动画的高保真NeRF-GAN Inversion
- Overview
-
- What problem is addressed in the paper?
- What is the result?
- Is it a new problem? If so, why does it matter? If not, why does it still matter?
- What is the key to the solution?
- What is the main contribution?
- What can we learn from ablation studies?
- Potential fundamental flaws; how this work can be improved?
- Method
-
- 3.1. Image Space Supervision
- 3.2. Explicit Geometrical Regularization
- 3.3. Implicit Geometrical Regularization
- 3.4. Masked Regularizations
- Experiments
-
- 4.2. Qualitative Evaluation
-
- Comparison with inversion methods.
- Comparison with single-shot NeRF methods.
- Evaluation on multiple NeRF-GANs.
- 4.3. Quantitative Evaluation
- 4.4. Ablation Study
-
- Effectiveness of Regularization.
- Neighborhood Selection.
- Conclusion
Overview
What problem is addressed in the paper?
In this paper, we propose a universal method to surgically fine-tune these NeRF-GAN models in order to achieve high-fidelity animation of real subjects only by a single image. (在本文中,我们提出了一种通用的方法来微调这些NeRF-GAN模型,以便仅通过单个图像实现真实主题的高保真动画)
What is the result?
Our experiments confirm the effectiveness of our method in realistic, highfidelity, and 3D consistent animation of real faces on multiple NeRF-GAN models across different datasets. (我们的实验证实了我们的方法在不同数据集的多个NeRF-GAN模型上真实人脸的逼真、高保真和3D一致动画的有效性。)

- Figure 1. Image animation results of our method.
Is it a new problem? If so, why does it matter? If not, why does it still matter?
No,
In previous works, there remains a notable identity gap between the synthesized results and input images, indicating the inefficiency of single-shot NeRFs for real image inversion. (在以往的工作中,合成结果与输入图像之间存在明显的身份差距,这表明单发nerf对真实图像反演的效率较低)
Due to the insufficient geometry and content information in a single image, single-shot NeRFs without additional supervision (i.e. multi-view images or 3D objects) remain challenging. (由于单幅图像中的几何和内容信息不足,没有额外监督的单幅nerf(即多视图图像或3D对象)仍然具有挑战性。)
What is the key to the solution?
- Given the optimized latent code for an out-of-domain real image, we employ 2D loss functions on the rendered image to reduce the identity gap. (针对域外实景图像的优化潜码,我们在渲染图像上使用二维损失函数来减小身份差距。)
- our method leverages explicit and implicit 3D regularizations using the in-domain neighborhood samples around the optimized latent code to remove geometrical and visual artifacts. (我们的方法利用显式和隐式3D正则化,使用优化的潜在代码周围的域内邻域样本来去除几何和视觉伪影。)
What is the main contribution?
- We proposed a universal method for inverting NeRF-GANs to achieve 3D-consistent, high-fidelity, and identity-preserving animation of real subjects given only a single image.
- We introduce a novel geometric constraint by leveraging density outputs of in-domain samples around the input to provide crucial guidance for the unobserved part in the 2D space
What can we learn from ablation studies?
- the fine-tuned model with just image space losses Limg is prone to generating artifacts in novel-view images and inaccurate 3D geometry; the implicit implicit geometrical regularization Limp helps to eliminate artifacts; the explicit geometrical regularizationLexp improves visual quality and the subject’s 3D geometry; the full model with masked regularizations reduces fogging around the hair, ear, or cheek.
- We empirically find out that the distance between the optimized and neighborhood latent codes affects the ID-preserving ability and geometrical constraints.
Potential fundamental flaws; how this work can be improved?
Method
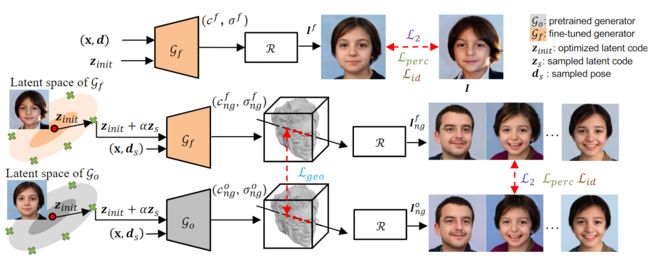
- Figure 3. Framework of NeRFInvertor.
- x ∈ R 3 x \in R^3 x∈R3 是3D location,
- z 是latent code, d ∈ R 3 d \in R^3 d∈R3 是camera pose
- R 表示volume rendering。
优化的latent code z i n i t z_{init} zinit 可以根据如下公式计算:
![]()
- 也就是根据 原始图像I 和生成图像 I o I^o Io之间的两个loss 来优化z
- L p e r c , L p i x L_{perc},L_{pix} Lperc,Lpix分别表示 感知损失和像素级的L2损失。
通常情况下,生成的图像与真实图像之间会有差距,因为在NeRF-GANs中,真实图像大多是域外样本。
为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种具有新颖正则化的fine-tune过程
- we fine-tune the generator with image space loss functions (Sec. 3.1) to reduce
the identity gap. (fine-tune 以减少 identity gap) - We also apply an explicit geometrical constraint (Sec. 3.2) and an implicit geometrical regularization (Sec. 3.3) to maintain the model’s ability to produce highquality and 3D-consistent images. (增加约束以产生高保证和3d一致性的图像)
3.1. Image Space Supervision
在给定优化后的letent code z i n i t z_{init} zinit的情况下,我们来fine-tune generator,通过使生成图像在原始视角d 的情况下来匹配输入图像(重构)。
我们将fine-tune的生成器表示为 g f g_f gf, 它以 letent code z i n i t z_{init} zinit 和x作为输入,输出颜色的体密度。 最后得到的图像表示为 I f I^f If,表示为:
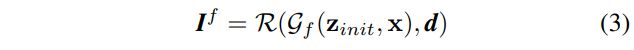
image space supervision:
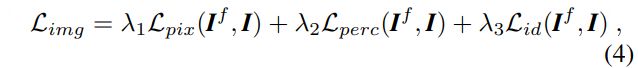
- 其中 L i d L_{id} Lid表示身份损失。
在图像空间监督下,经过微调的模型很好地重构了原始视图中的输入,但容易对输入图像进行过拟合,导致新视图合成图像产生伪影,导致被测对象的三维几何不准确。
3.2. Explicit Geometrical Regularization
为了解决上述问题,我们放松了第3.1节中描述的严格图像空间对齐的假设。
为了正则化模型,我们利用优化的潜在代码周围的邻域样本来增强新视图和表达式合成的几何形状、真实感和保真度。
我们首先随机抽取优化后的潜伏码周围的具有不同姿态和表情的邻居潜伏码 z n g z_{ng} zng。邻域潜码可以通过下面公式获得:
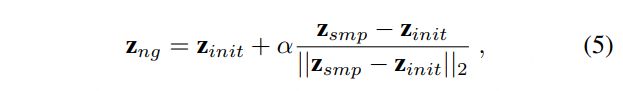
- 其中α为随机采样的zsmp ~ N(0,1)与优化的潜变量zinit之间的插值距离。
为了利用原始生成器Go的高保真质量,我们迫使经过微调的生成器Gf在邻域潜码、视角和表情上执行与Go相同的操作。
几何约束是根据Gf和Go上邻域样本的颜色和密度输出定义的,分别表示为: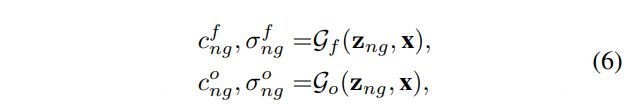
通过将每条射线(即像素)根据其深度重新投影到3D空间,我们定义了两组基于Go和Gf图像的点云So和Sf,我们利用倒角距离(Chamfer distance)比较两个点云的相似度,并定义几何约束如下: 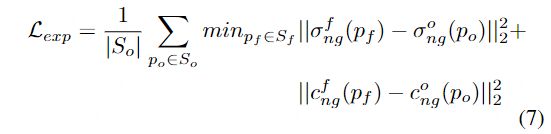
- 其中po和pf分别为点云集合so和Sf中的三维位置。
3.3. Implicit Geometrical Regularization
给定一个新的视图ds, Gf和Go的渲染图像可以表示为:
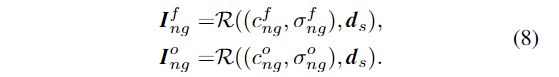
我们使用像素、感知和身份损失最小化Gf生成的图像和Go生成图像之间的距离。因此,总的损失可以表示为
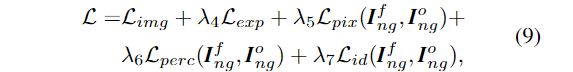
3.4. Masked Regularizations
在上述工作的情况下:我们仍然注意到头发或脸颊周围有一些雾状的部分,如图5所示。

为了去除伪影并获得更精确的几何形状,我们通过一个掩模来增强几何和图像的正则化,这是基于输入图像上的抠图信息。 如图4所示,我们根据红色和绿色所显示的前景和背景区域来预测输入视图图像的掩码。 特别是,如果一个拍摄射线到达输入图像的前景区域,我们将该射线上的所有样本点分类为前景点。类似地,如果一个射击射线到达图像的背景区域,我们将该射线上的所有数据点分类为背景点。 (红色和绿色区域的标识又是怎么来的呢?)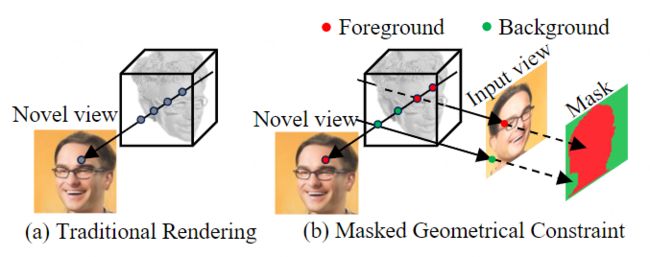
- 图4。蒙面几何约束。(a)展示了新视图图像的传统渲染过程。(b)蒙面几何约束只考虑前景点。为了渲染新颖的视图,只使用红点进行图像渲染。两个绿色的点被忽略了,因为它们肯定来自背景区域。
Experiments
- 图6。真实图像动画的例子在“复仇者联盟”。
- NeRFInvertor使用预先训练的AniFaceGAN合成真实的人脸,并给出一个训练图像,具有可控的姿态和表情序列。
- 可以看出,NeRFInvertor不仅能够保留身份属性,而且能够在不同的姿势和表情下生成高质量且外观一致的图像。
4.2. Qualitative Evaluation
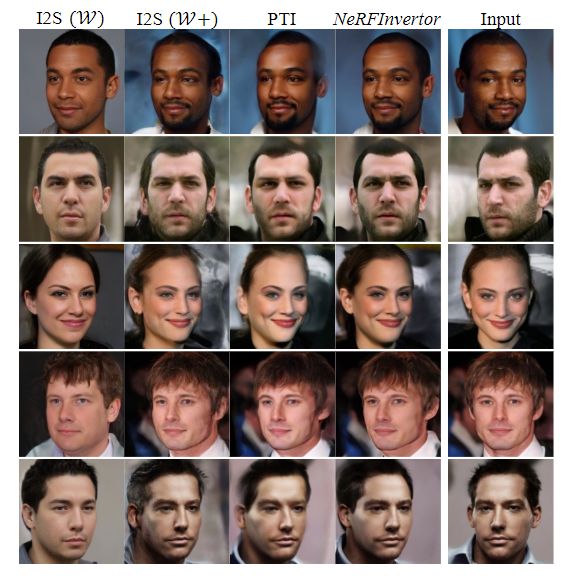
Comparison with inversion methods.
- 图7显示了这些方法在从单个输入图像合成新视图方面的定性比较。
- I2S (W)能够生成具有可接受视觉质量的图像,但与输入图像存在显著的身份差距。
- 相比之下,I2S (W+)保留了身份属性,但在新视图中引入了大量伪影。
- 通过图像空间监督对模型进行微调,PTI表现出比I2S (W)和I2S (W+)更好的性能。然而,由于在三维空间中缺乏显式的约束,它无法生成输入物体的精确几何形状和原始视图中隐藏的内容。
- 所提出的NeRFInvertor在视觉质量和身份保持方面优于这些方法。此外,该方法可以生成与输入图像具有相似纹理的新视图图像。
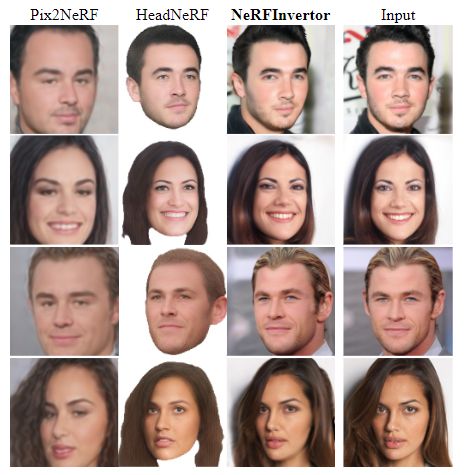
Comparison with single-shot NeRF methods.
- Pix2NeRF[7]提出了一种编码器将图像转换到Pi-GAN[9]潜空间,并联合训练编码器和Pi-GAN生成器。
- HeadNeRF[14]提出了一种基于nerf的参数化头部模型来合成各种姿态的图像。
- 图8中的结果表明,Pix2NeRF不是真实人脸合成的好候选者,因为它不能正确地保留身份。
- HeadNeRF存在生成的图像和输入图像之间明显的身份差距。此外,它还继承了三维参数模型的缺点,产生了一些虚假的视觉效果。
- 与这两种方法相比,NeRFInvertor实现了更高的保真度和更好的身份保持。
Evaluation on multiple NeRF-GANs.
我们在各种NeRF-GANs上验证我们的方法,包括AniFaceGAN [39], GRAM[12]和EG3D[8]。
- 在图9中,我们展示了给定单个输入图像的重建、新视图和表情合成。
- AniFaceGAN使用可变形的NeRF结构,并为动态场景进行了训练。证明了NeRFInvertor可以忠实地将单个图像转换为可变形的NeRF表示,使我们能够以可控的姿态和表情生成逼真的人脸编辑(图6和9)。
- 给定固定的潜代码,GRAM和EG3D为静态场景生成NeRF表示。在这两种方法上验证了所提出方法,表明可以将单幅图像转换为静态场景的传统NeRF表示。
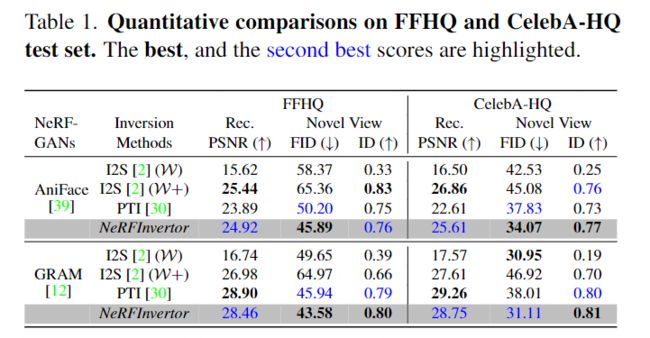
4.3. Quantitative Evaluation
- 对CelebA-HQ测试集和FFHQ数据集的前150个样本进行定量实验。
- I2S (W)不能保持输入图像的身份,ID分数很差。
- I2S (W+)在新视图中引入了伪影,并导致高FID分数。
- 与PTI相比,所提出方法生成了相当的重建,但在视觉质量(即FID分数)和更好的身份保持(即ID分数)方面具有卓越的新视图合成。
- 我们在所有指标上实现了最佳的整体性能。更多的定量结果(如新颖观点和表达评估)可以在补充材料中找到。
4.4. Ablation Study
Effectiveness of Regularization.
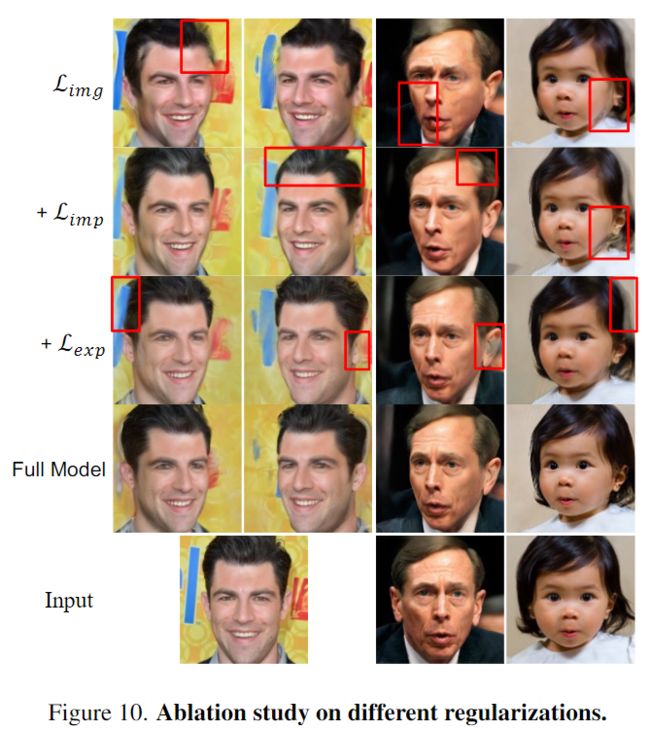
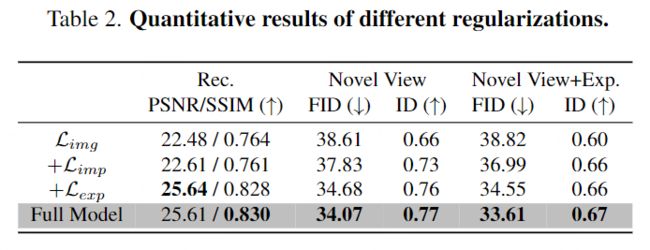

与现有的图像空间损失Limg相比,在图10和表2中显示了所提出的隐几何正则化(Limp)、显式几何正则化(Lexp)和掩码正则化(全模型)的影响。
- 图10中的结果表明,仅具有图像空间损失的微调模型Limg容易在新视角图像中生成伪影和不准确的3D几何;
- 隐式几何正则化Limp有助于消除伪影;
- 显式几何正则化lexp提高了视觉质量和主体的3D几何;
- 带有掩码正则化的完整模型减少了头发、耳朵或脸颊周围的雾气。
- 表2的定量结果与图10的定性结果一致。
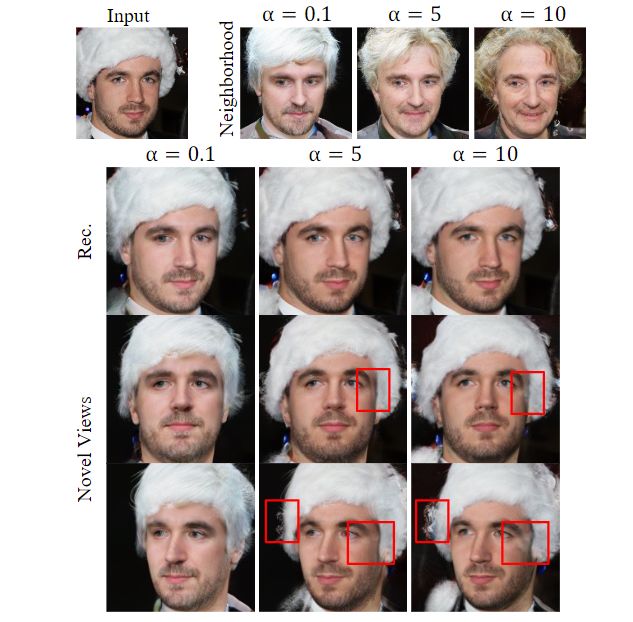
Neighborhood Selection.
- 通过实验发现,优化后的潜代码和邻域潜代码之间的距离会影响id保持能力和几何约束。
- 如图11所示,如果距离过小(即α <= 1),模型表现出更好的几何约束,但同一性保持较差。
- 如果距离过大(即α >= 10),则模型具有更好的保idability,但在新视图中会出现不理想的3D几何形状和视觉伪影。
- 将距离α设置在[1,10]范围内,我们能够很好地平衡图像空间监督和正则化。因此,我们简单地将实验中所有训练样本的距离设置为5。
Conclusion
引入NeRFInvertor作为一种通用方法,用于在静态和动态NeRF-GAN模型上单次反演真实图像。采用图像空间监督来微调NeRF-GANs生成器,以减少身份差距,以及显式和隐式几何约束,以消除新视图和表情中几何和渲染图像中的伪影。实验验证了该方法中每个组件对真实人脸图像的3D一致、id保持和高保真动画的重要性。