使用腾讯云盲水印服务进行图片水印添加和提取的一个Python Demo
目录
- 前言
- 起因(可略过)
- 代码
-
- addWatermark.py
- extractWatermark.py
- 运行效果
-
- 加水印
- 提取水印
- 最后
前言
首先,本文写于 2021-5-17,也许在未来的某个时间点,腾讯云盲水印服务的 Python SDK 文档已经写的比较好了,然后你读到了这篇文章,那么可以考虑略过。
起因(可略过)
腾讯云盲水印服务的 Python SDK 文档 确实已经存在,但问题是,对于一个想快速上手此服务的开发者来说,这份SDK文档并不是一个适合抄作业的良好示例。
以下是 2021-5-17 腾讯云盲水印服务 Python SDK 文档的截图
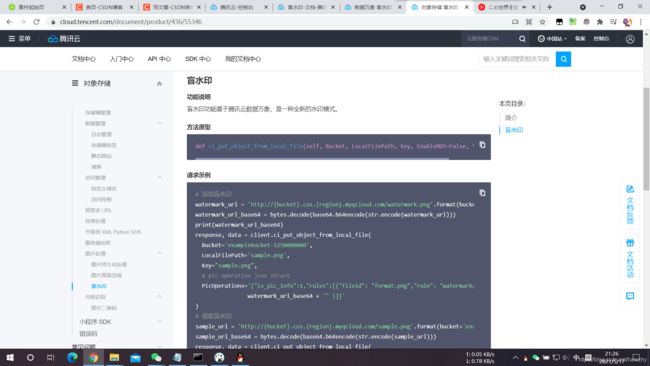
其文档定义了一个叫ci_put_object_from_local_file()的方法原型,然后又给出了调用了这个方法的一个代码片段。经过实际运行,问题有二。
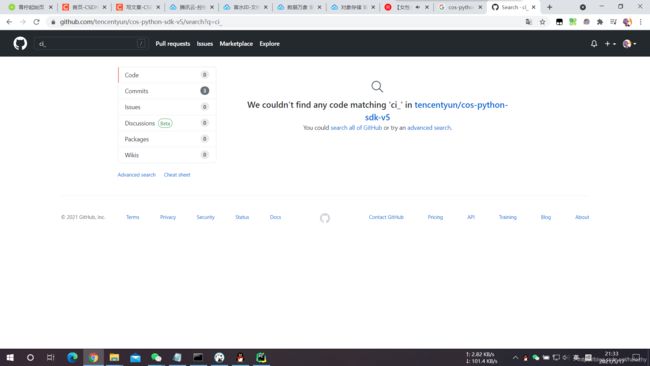
- 此方法在
cos-python-sdk-v5==1.9.4的pip库中根本不存在,以下为 2021-5-17 GitHub 仓库搜索截图,使用的关键词为ci_,可见,连个影子都没有。
不过,这个方法可以使用put_object_from_local_file()方法代替,各项参数均不需改变。 - 上传时添加盲水印的接口,腾讯云在 盲水印的API文档 里提到了 “图片上传时添加盲水印的请求包与 PUT Object 接口一致”,顺着链接找到 PUT Object 接口文档,在“响应 - 响应体”部分,腾讯云的文档明明白白地写着 “此接口响应体为空。” ,而此处 python 示例代码,却使用了两个变量接住
put_object_from_local_file()的返回值。
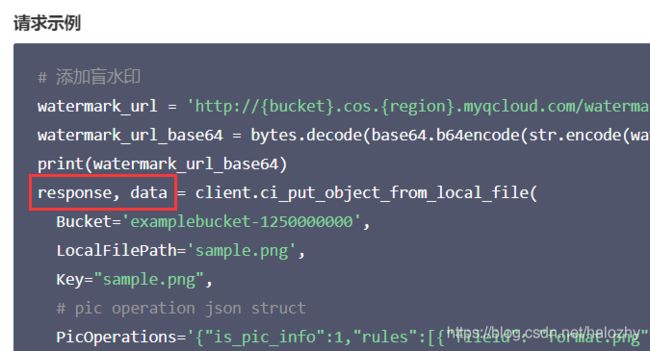
这样会直接导致 python 报出ValueError: too many values to unpack的异常,删去一个变量之后恢复正常。
这两个问题导致了我在使用此服务时产生了很多疑惑,走了不少弯路,但愿在你看到本文章的时候,已经不存在这两个问题了。
代码
- 使用之前确保开通了腾讯云的 对象存储服务(COS) 以及 数据万象服务,下面代码的
bucketName和region参数需要填你自己在 COS 中开的桶的参数 - 下面的 Demo 是假设你在某个 bucket 里面的根目录已经上传了一张叫
watermark.png的水印图,并且访问控制设为了公有读(反正就是不通过特别的鉴权就能访问到 COS 里面存的水印图),并且watermark.png水印图在程序目录下也有一份 - 此 Demo 中的盲水印模式为 type2
addWatermark.py
添加盲水印
# -*- coding=utf-8
import sys
from qcloud_cos import CosConfig
from qcloud_cos import CosS3Client
from PIL import Image
import base64
secret_id = '用户的secret_id' # 替换为用户的secret_id
secret_key = '用户的secret_key' # 替换为用户的secret_key
region = '用户的region' # 替换为用户的region
token = None # 使用临时密钥需要传入Token,默认为空,可不填
proxies = {
'http': '127.0.0.1:7890', # 替换为用户的 HTTP 代理地址
'https': '127.0.0.1:7890' # 替换为用户的 HTTPS 代理地址
}
# config = CosConfig(Region=region, SecretId=secret_id, SecretKey=secret_key, Token=token) # 获取配置对象,无Proxies
config = CosConfig(Region=region, SecretId=secret_id, SecretKey=secret_key, Token=token, Proxies=proxies) # 获取配置对象
client = CosS3Client(config) # 获取client对象
# 我只开了一个桶,直接全局变量了
bucketName = '用户的bucketName'
# 设定盲水印在COS中的url以及base64
watermark_url = 'http://{bucket}.cos.{region}.myqcloud.com/watermark.png'.format(bucket=bucketName,
region=region)
watermark_url_base64 = bytes.decode(base64.b64encode(str.encode(watermark_url)))
def mark(file_path):
split = src_file_path.split('\\')
file_name = split[len(split) - 1]
split_name = file_name.split('.')
# 设定加了盲水印之后图片的文件名
tgt_file_name = ''
for i in range(len(split_name)):
if i == len(split_name) - 2:
tgt_file_name = tgt_file_name + split_name[i] + '_format' + '.'
elif i == len(split_name) - 1:
tgt_file_name = tgt_file_name + split_name[i]
else:
tgt_file_name = tgt_file_name + split_name[i] + '.'
# 设定加了盲水印之后图片的文件完整路径
tgt_file_path = ''
for i in range(len(split)):
if i == len(split) - 1:
tgt_file_path = tgt_file_path + tgt_file_name
else:
tgt_file_path = tgt_file_path + split[i] + '\\'
# 上传时加盲水印,type为2
print('put src image')
response = client.put_object_from_local_file(
Bucket=bucketName,
LocalFilePath=file_path,
Key='sample.png', # 上传到桶里面,在桶里面名字叫sample.png,之后加了盲水印的图叫做format.png,这个图也会被保存在桶里面
PicOperations='{"is_pic_info":1,"rules":[{"fileid": "format.png","rule": "watermark/3/type/2/image/' +
watermark_url_base64 + '" }]}',
)
# 下载加了水印的图片
print('get formatted image')
res = client.get_object(
Bucket=bucketName,
Key='format.png' # 从桶里面把名字叫format.png的图下回来
)
res['Body'].get_stream_to_file(tgt_file_path)
print('all finished')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 程序运行的时候需要加一个参数,为要加盲水印的文件路径,
# 例:python addWatermark.py sample.png
src_file_path = sys.argv[1]
# 水印图的长宽必须小于要处理的图的1/8,详见https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/436/46781
im_src = Image.open(src_file_path)
safe_wm_width = im_src.size[0] // 8
safe_wm_height = im_src.size[1] // 8
im_wm = Image.open('watermark.png')
if im_wm.size[0] < safe_wm_width and im_wm.size[1] < safe_wm_height:
# 一切正常,那就直接处理
print('safe pic size')
mark(src_file_path)
else:
'''
WARNING!
如果程序进入了这个分支,说明要加水印的图像素不够多,或者水印图不够小,不满足水印图的长宽必须小于要处理的图的1/8这个条件
'''
print('fail, pic size is too small')
extractWatermark.py
提取盲水印
# -*- coding=utf-8
import sys
from qcloud_cos import CosConfig
from qcloud_cos import CosS3Client
from PIL import Image
import base64
secret_id = '用户的secret_id' # 替换为用户的secret_id
secret_key = '用户的secret_key' # 替换为用户的secret_key
region = '用户的region' # 替换为用户的region
token = None # 使用临时密钥需要传入Token,默认为空,可不填
proxies = {
'http': '127.0.0.1:7890', # 替换为用户的 HTTP 代理地址
'https': '127.0.0.1:7890' # 替换为用户的 HTTPS 代理地址
}
# config = CosConfig(Region=region, SecretId=secret_id, SecretKey=secret_key, Token=token) # 获取配置对象,无Proxies
config = CosConfig(Region=region, SecretId=secret_id, SecretKey=secret_key, Token=token, Proxies=proxies) # 获取配置对象
client = CosS3Client(config) # 获取client对象
# 我只开了一个桶,直接全局变量了
bucketName = '用户的bucketName'
# 设定盲水印在COS中的url以及base64
watermark_url = 'http://{bucket}.cos.{region}.myqcloud.com/watermark.png'.format(bucket=bucketName,
region=region)
watermark_url_base64 = bytes.decode(base64.b64encode(str.encode(watermark_url)))
def extract(file_path):
split = src_file_path.split('\\')
file_name = split[len(split) - 1]
split_name = file_name.split('.')
tgt_file_name = ''
for i in range(len(split_name)):
if i == len(split_name) - 2:
tgt_file_name = tgt_file_name + split_name[i] + '_extracted_wm' + '.'
elif i == len(split_name) - 1:
tgt_file_name = tgt_file_name + split_name[i]
else:
tgt_file_name = tgt_file_name + split_name[i] + '.'
tgt_file_path = ''
for i in range(len(split)):
if i == len(split) - 1:
tgt_file_path = tgt_file_path + tgt_file_name
else:
tgt_file_path = tgt_file_path + split[i] + '\\'
print('extract wm')
response = client.put_object_from_local_file(
Bucket=bucketName,
LocalFilePath=src_file_path,
Key='format.png', # 把处理过的图上传到桶里面,在桶里面名字叫format.png,提取出的水印叫format_out.png,也保存至桶里面
PicOperations='{"is_pic_info":1,"rules":[{"fileid": "format_out.png","rule": "watermark/4/type/2/image/' +
watermark_url_base64 + '" }]}',
)
print('get extracted wm')
res = client.get_object(
Bucket=bucketName,
Key='format_out.png' # 从桶里面把名字叫format_out.png的图下回来
)
res['Body'].get_stream_to_file(tgt_file_path)
print('all finished')
if __name__ == '__main__':
src_file_path = sys.argv[1]
extract(src_file_path)
运行效果
我提前放在COS中的水印图,当然,这个水印图在程序目录下也需要放一份
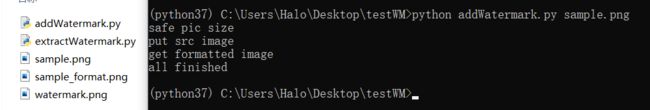
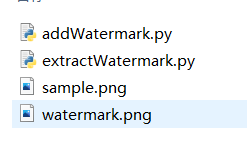
程序目录下的文件,sample.png是待处理的图
加水印
python addWatermark.py sample.png
提取水印
python extractWatermark.py sample_format.png
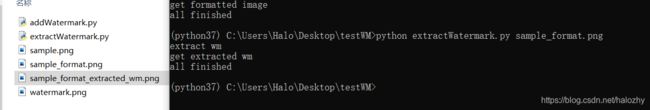
sample_format_extracted_wm.png即为提取出的水印图,效果如下

最后
可能这个 Demo 中的部分代码写的并不是很好,还望轻喷,可以评论反馈