【目标检测】kera-yolo3模型计算mAP
这些是GitHub上的源码,下载之后均要修改一下。
keras-yolo v3 源码:https://github.com/qqwweee/keras-yolo3
mAP计算代码:https://github.com/Cartucho/mAP
【目标检测】交并比IoU、准确率precision、查全率recall、mAP
上一篇博客【目标检测】基于YOLOv3的海上船舶目标检测分类(Tensorflow/keras)记录了我训练模型的过程。
计算mAP,直接运行项目中main.py就好了。唯一难点就是要生成符合格式要求的detection-results和ground-truth。
目录
- 一、mAP项目构成
- 二、 批量测试图片
- 三、计算mAP
-
- 3.1 生成detection-results
- 3.2 生成ground-truth
- 3.3 计算mAP
一、mAP项目构成
mAP项目如下:
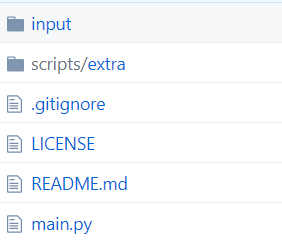
我们所需要了解的就是input文件,input目录下包含:detection-results、ground-truth、images-optional。
| 文件夹 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| detection-results | 模型预测的检测结果 |
| ground-truth | 图片本身的标记信息 |
| images-optional | 原始图片 |
detection-results 格式
每张图片保存在一个txt文件内,文件命名为图片的名称,每一行代表一个检测结果,格式为:class score left top right bottom。

ground-truth 格式
与detection-results 格式基本相同,只是缺少score这一项。
二、 批量测试图片
在keras-yolo3项目内建立新的python文件test_yolo.py(随便起的名,里面的代码是在yolo.py的基础上修改的)。该代码实现了对test.txt内图片的批量测试,并将结果保存在results目录下。

result.txt文件内记录预测的结果。每一行代表一张图片的信息,依次代表图片名称、种类、得分、左、上、右、下。
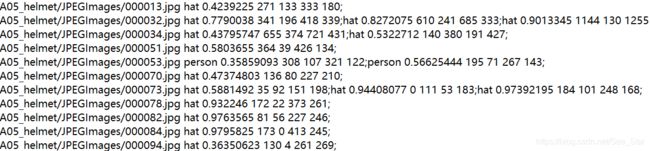
代码同时复制一份原始图片到mAP/input/images-optional目录下。
代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Class definition of YOLO_v3 style detection model on image and video
"""
import colorsys
import os
import time
from timeit import default_timer as timer
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.layers import Input
from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
from yolo3.model import yolo_eval, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body
from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
import os
from keras.utils import multi_gpu_model
# 创建创建一个存储检测结果的dir
result_path = './result'
if not os.path.exists(result_path):
os.makedirs(result_path)
# result如果之前存放的有文件,全部清除
for i in os.listdir(result_path):
path_file = os.path.join(result_path, i)
if os.path.isfile(path_file):
os.remove(path_file)
# 创建一个记录检测结果的文件
txt_path = result_path + '/result.txt'
file = open(txt_path, 'w')
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
"model_path": 'logs/000/trained_weights.h5',
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"classes_path": 'model_data/voc_classes.txt',
"score" : 0.3,
"iou" : 0.45,
"model_image_size" : (416, 416),
"gpu_num" : 1,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults) # set up default values
self.__dict__.update(kwargs) # and update with user overrides
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
def _get_class(self):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def _get_anchors(self):
anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# Load model, or construct model and load weights.
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
is_tiny_version = num_anchors==6 # default setting
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//2, num_classes) \
if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//3, num_classes)
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
num_anchors/len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
np.random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
# Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
if self.gpu_num>=2:
self.yolo_model = multi_gpu_model(self.yolo_model, gpus=self.gpu_num)
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
return boxes, scores, classes
def detect_image(self, image):
start = timer()
if self.model_image_size != (None, None):
assert self.model_image_size[0]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
assert self.model_image_size[1]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)))
else:
new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
image.height - (image.height % 32))
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
print(image_data.shape)
image_data /= 255.
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf',
size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300
# # 保存框检测出的框的个数 (添加)
# file.write('find ' + str(len(out_boxes)) + ' target(s) \n')
for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
predicted_class = self.class_names[c]
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
# # 写入检测位置(添加)
# file.write(
# predicted_class + ' score: ' + str(score) + ' \nlocation: top: ' + str(top) + '、 bottom: ' + str(
# bottom) + '、 left: ' + str(left) + '、 right: ' + str(right) + '\n')
file.write(predicted_class + ' ' + str(score) + ' ' + str(left) + ' ' + str(top) + ' ' + str(right) + ' ' + str(bottom) + ';')
print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
# My kingdom for a good redistributable image drawing library.
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle(
[left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
outline=self.colors[c])
draw.rectangle(
[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
fill=self.colors[c])
draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
del draw
end = timer()
print(end - start)
return image
def close_session(self):
self.sess.close()
def detect_video(yolo, video_path, output_path=""):
import cv2
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
if not vid.isOpened():
raise IOError("Couldn't open webcam or video")
video_FourCC = int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FOURCC)) # 获得视频编码MPEG4/H264
video_fps = vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
video_size = (int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),
int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
isOutput = True if output_path != "" else False
if isOutput:
print("!!! TYPE:", type(output_path), type(video_FourCC), type(video_fps), type(video_size))
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, video_FourCC, video_fps, video_size)
accum_time = 0
curr_fps = 0
fps = "FPS: ??"
prev_time = timer()
while True:
return_value, frame = vid.read()
image = Image.fromarray(frame) # 从array转换成image
image = yolo.detect_image(image)
result = np.asarray(image)
curr_time = timer()
exec_time = curr_time - prev_time
prev_time = curr_time
accum_time = accum_time + exec_time
curr_fps = curr_fps + 1
if accum_time > 1:
accum_time = accum_time - 1
fps = "FPS: " + str(curr_fps)
curr_fps = 0
cv2.putText(result, text=fps, org=(3, 15), fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
fontScale=0.50, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.namedWindow("result", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("result", result)
if isOutput:
out.write(result)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
yolo.close_session()
# 批量处理文件
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 读取test文件
with open("A05_helmet/ImageSets/Main/test.txt", 'r') as f: # 打开文件
test_list = f.readlines() # 读取文件
test_list = [x.strip() for x in test_list if x.strip() != ''] # 去除/n
# print(test_list)
t1 = time.time()
yolo = YOLO()
for filename in test_list:
image_path = 'A05_helmet/JPEGImages/'+filename+'.jpg'
portion = os.path.split(image_path)
# file.write(portion[1]+' detect_result:\n')
file.write(image_path + ' ')
image = Image.open(image_path)
image_mAP_save_path = 'E:/Activities/fwwb2019/code/mAP-master/input/images-optional/'
image.save(image_mAP_save_path + filename + '.jpg')
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
file.write('\n')
#r_image.show() 显示检测结果
image_save_path = './result/result_'+portion[1]
print('detect result save to....:'+image_save_path)
r_image.save(image_save_path)
time_sum = time.time() - t1
# file.write('time sum: '+str(time_sum)+'s')
print('time sum:',time_sum)
file.close()
yolo.close_session()
三、计算mAP
首先在mAP项目中建立名为cal_mAP文件夹,在其中分别建立如下两个python文件。分别用于生成符合detection-result和ground-truth的格式要求的txt文件。

3.1 生成detection-results
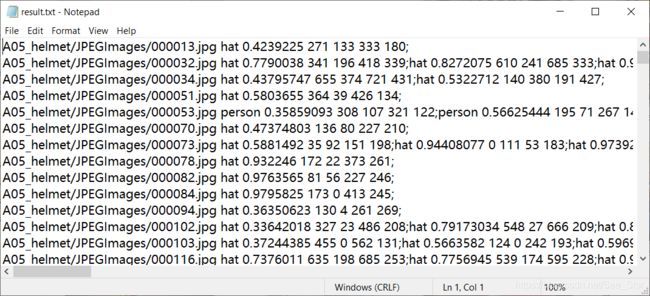
从第二部分介绍的result,我们可以生成符合detection-results文件。下图为result.txt:
通过如下代码:
import re
import os
dir_project = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../..")) # 获取上上级目录
dir_result = '/result/result.txt' # yolo批量处理结果的目录
dir_detection_results = '/mAP/input/detection-results' # detection-results目录
surplus = 'A05_helmet/JPEGImages/' # result.txt文件中图片名称多余的部分
if __name__ == '__main__':
with open(dir_project + dir_result, 'r') as f: # 打开文件
filename = f.readlines() # 读取文件
for i in range(len(filename)):
filename[i] = re.sub(surplus, '', filename[i]) # 去除文件名多余的部分
for i in range(len(filename)): # 中按行存放的检测内容,为列表的形式
r = filename[i].split('.jpg ')
file = open(dir_project + dir_detection_results + '/' + r[0] + '.txt', 'w')
t = r[1].split(';')
# 去除空格和换行
t.remove('\n')
if len(t) == 0: # 如果没有对象
file.write('')
else:
for k in range(len(t)):
file.write(t[k] + '\n')
将其转化为如下txt文件,每一张图片用一个txt文本表示:
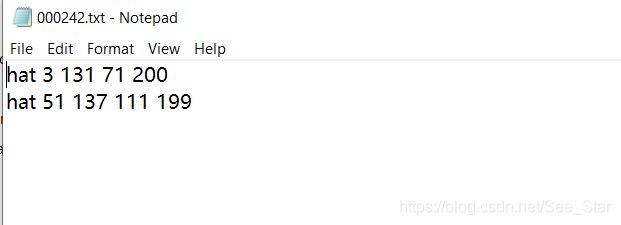
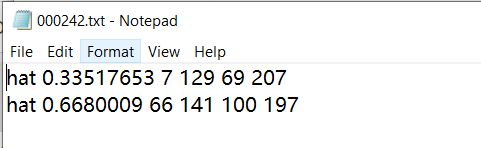
每一个txt文本内容如下图样式,以图片00242为例:
3.2 生成ground-truth
在上一篇博客中我们生成了test.txt文件,我们则要将它转化为符合ground-truth格式要求的txt文本。

此文件中,没有score,其中“1”代表“hat”,“2”代表“person”。
我们通过如下代码进行转换:
import re
import os
dir_project = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../..")) # 获取上上级目录
dir_ground_truth = '/mAP/input/ground-truth' # detection-results目录
surplus = 'A05_helmet/JPEGImages/' # result.txt文件中图片名称多余的部分
if __name__ == '__main__':
with open(dir_project + '/test.txt', 'r') as f: # 打开文件
filename = f.readlines() # 读取文件
# print(filename)
for i in range(len(filename)):
filename[i] = re.sub(surplus, '', filename[i]) # 去除文件名多余的部分
for i in range(len(filename)): # 中按行存放的检测内容,为列表的形式
r = filename[i].split('.jpg ')
print(r[0])
file = open(dir_project + dir_ground_truth + '/' + r[0] + '.txt', 'w')
t = r[1].split(' ')
for j in range(len(t)):
class_t = t[j].split(',')[-1]
pos_t = t[j].split(',')
if class_t == '0' or class_t == '0\n':
file.write('person ' + pos_t[0] + ' ' + pos_t[1] + ' '+ pos_t[2] + ' '+ pos_t[3] + '\n')
elif class_t == '1' or class_t == '1\n':
file.write('hat ' + pos_t[0] + ' ' + pos_t[1] + ' '+ pos_t[2] + ' '+ pos_t[3] + '\n')
3.3 计算mAP
如果你的类中包含空格(如cargo ship、ore carrier),则需要进行小小的修改,参考本篇博客:计算mAP去除类之间空格(remove_space)。
之后可直接运行mAP项目中的main.py,可生成result文件夹,在该文件夹内保存各类结果。
如果你的类中不包含空格(如person、hat),可直接运行mAP项目中的main.py,可生成result文件夹,在该文件夹内保存各类结果。
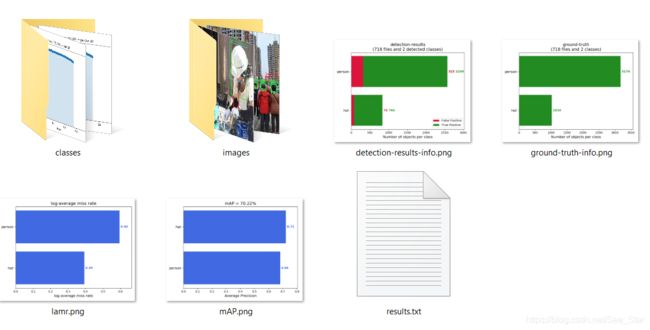
单一图像,预测和实际的对比:
各类结果都比较齐全,可慢慢分析。
参考:【YOLOV3-keras-MAP】YOLOV3-keras版本的mAP计算