String类——Java中常见的类(模拟登录案例练习)
目录
String类的概述及构造方法(String类是Java中最常见的类)
String的特点
String类的判断功能
模拟登录案例
String类的获取功能
两个小练习
String类的转换功能和String类的其他功能
string类练习
String类的概述及构造方法(String类是Java中最常见的类)
- String类概述
–字符串是由多个字符组成的一串数据
–字符串可以看成是字符数组
- 构造方法
–public String(String original)
–public String(char[] value)
–public String(char[] value,int offset,int count)
–直接赋值也可以是一个对象
4种字符方式赋值如下:
package com.demo02;
/*
* String:字符串类
* 由多个字符组成的一串数据
* 字符串本身就是一个字符数组
*
*构造方法:
* String(String original):把字符串数据封装成字符串对象
* String(char[] value):把字符数组的数据封装成字符串对象
* String(char[] value, int index, int count):把字符数组中的一部分数据封装成字符串对象
*
* 注意:字符串是一种比较特殊的引用数据类型,直接输出字符串对象输出的是该对象中的数据
*/
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方式1
//String(String original):把字符串数据封装成字符串对象
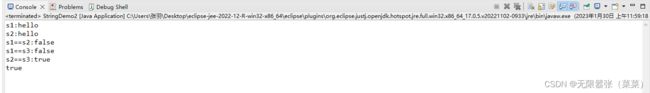
String s1 = new String("hello");
System.out.println("s1:"+s1);
System.out.println("---------");
//方式2
//String(char[] value):把字符数组的数据封装成字符串对象
char[] chs = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
String s2 = new String(chs);
System.out.println("s2:"+s2);
System.out.println("---------");
//方式3
//String(char[] value, int index, int count):把字符数组中的一部分数据封装成字符串对象
//String s3 = new String(chs,0,chs.length);
//char[] chs = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
String s3 = new String(chs,0,5);//从哪个位置开始,多长
System.out.println("s3:"+s3);
System.out.println("---------");
//方式4,比较常用的
String s4 = "hello";
System.out.println("s4:"+s4);
}
}String的特点
- 通过构造方法创建字符串对象
–String s = new String(“hello”);
- 直接赋值创建字符串对象
–String s = “hello”;区别是什么?
通过构造方法创建的字符串是在堆内存,直接复制方式创建对象的方法是在常量池。
基本数据类型:比较的是基本数据类型的值是否相同。
引用数据类型:比较的是引用数据类型的地址是否相同。
package com.demo02;
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = "hello";
System.out.println("s1:"+s1);
System.out.println("s2:"+s2);
System.out.println("s1==s2:"+(s1==s2)); //false
String s3 = "hello";
System.out.println("s1==s3:"+(s1==s3)); //false 放回的地址是不是相等
System.out.println("s2==s3:"+(s2==s3)); //true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));// 返回的值是不是相等
}
}
String类的判断功能
- boolean equals(Object obj)——比较两个字符串的值是否相等
- boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str)——不管大小写,都会转化成一样的去做比较
- boolean startsWith(String str)——从哪个字符串开始
- boolean endsWith(String str)——从哪个字符串结束
其中API有关equals
package com.demo03;
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串对象
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "Hello";
//boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println("-----------");
//boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));
System.out.println("-----------");
//boolean startsWith(String str):判断字符串对象是否以指定的str开头
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("he"));
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("ll"));
System.out.println("-----------");
//boolean endsWith(String str):判断字符串对象是否以指定的str结尾
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("ll"));
}
}模拟登录案例
package com.demo03;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* 给三次机会,并提示还有几次
*
* 分析:
* A:定义两个字符串对象,用于存储已经存在的用户名和密码
* B:键盘录入用户名和密码
* C:键盘录入用户名和密码和已经存在的用户名和密码做比较
* 如果内容相同,表示登录成功
* 如果内容不同,登录失败,并提示还有几次机会
*/
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义两个字符串对象,用于存储已经存在的用户名和密码
String username = "admin";
String password = "admin";
//给三次机会,用for循环
for(int x=0; x<3; x++) {
//键盘录入用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
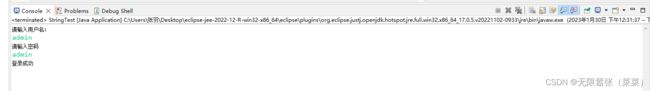
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String pwd = sc.nextLine();
if(username.equals(name) && password.equals(pwd)) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
}else {
if((2-x) ==0) {
System.out.println("用户名和密码被锁定,请与管理员联系");
}else {
System.out.println("登录失败,你还有"+(2-x)+"次机会"); //2,1,0
}
}
}
}
} String类的获取功能
String类的获取功能
- int length() —— 字符串长度,其实也就是字符个数
- char charAt(int index) —— 获取指定索引处的字符
- int indexOf(String str) —— 获取str的字符串对象中第一次出现的索引
- String substring(int start)——从start开始截取字符串
- String substring(int start,int end)——从start开始,到end结束截取字符串,包括start,不包括end
package com.demo04;
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串对象
String s = "helloworld";
//int length():获取字符串的长度,也就是字符个数
System.out.println(s.length());
System.out.println("--------");
//char charAt(int index):获取指定索引的字符
System.out.println(s.charAt(0));
System.out.println(s.charAt(1));
System.out.println("--------");
//int indexOf(String str):获取str的字符串对象中第一次出现的索引
System.out.println(s.indexOf("l"));
System.out.println(s.indexOf("owo"));
System.out.println(s.indexOf("ak"));
System.out.println("--------");
//String substring(int start):从start开始截取字符串
System.out.println(s.substring(0));
System.out.println(s.substring(5));
System.out.println("--------");
//String substring(int start,int end):从start开始,到end结束截取字符串,包括start,不包括end
System.out.println(s.substring(0, s.length()));
System.out.println(s.substring(3,8));
}
}
两个小练习:
练习1:遍历字符串
练习2:统计一个字符中大写字符。小写字符,数字字符出现的次数,不考虑其他字符
练习1:遍历字符串
package com.demo04;
/*
* 遍历字符串(获取字符串中的每一个字符串)
*/
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个字符串对象
String s = "abcde";
//原始做法
System.out.println(s.charAt(0));
System.out.println(s.charAt(1));
System.out.println(s.charAt(2));
System.out.println(s.charAt(3));
System.out.println(s.charAt(4));
System.out.println("---------");
//for循环好近
for(int x=0; x<5; x++) {
System.out.println(s.charAt(x));
}
System.out.println("---------");
//利用s.length()获取字符串长度
for(int x=0; x练习2:统计一个字符中大写字符。小写字符,数字字符出现的次数,不考虑其他字符
package com.demo04;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
* 练习2:统计一个字符中大写字符。小写字符,数字字符出现的次数,不考虑其他字符
*
* 分析
* A:键盘录入一个字符串数据
* B:定义三个统计变量,初始值都是0
* C:遍历每一个字符串,得到每一个字符
* D:拿字符进行判断
* 加入ch是一个字符
* 大写:ch>='A' && ch<='Z'
* 小写:ch>='a' && ch<='z'
* 数字ch>='0' && ch<='9'
* E:输出结果
*/
public class StringTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个对象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
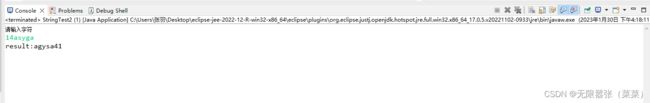
System.out.println("请输入字符");
// 接收数据
String s = sc.nextLine();
//定义统计字符
int bigCount = 0;
int smallCount = 0;
int numberCount = 0;
//遍历字符,得到每一个字符
for(int x=0; x='A' && ch<='Z') {
bigCount++;
}else if(ch>='a' && ch<='z') {
smallCount++;
}else if(ch>='0' && ch<='9') {
numberCount++;
}else {
System.out.println("该字符"+ch+"非法");
}
}
//输出结果
System.out.println("大写字符"+bigCount+"个");
System.out.println("小写字符"+smallCount+"个");
System.out.println("数字字符"+numberCount+"个");
}
}
String类的转换功能和String类的其他功能
- char[] toCharArray()——把字符串转换为字符数组
- String toLowerCase()——把字符串转换为小写字符串
- String toUpperCase()——把字符串转换为大写字符串
package com.demo05;
/*
*
* 字符串遍历
*/
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串
String s = "abcde";
//char[] toCharArray():把字符串转化成字符数组
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
for(int x=0; x去除字符串两端空格
–String trim()
按照指定符号分割字符串
–String[] split(String str)
package com.demo06;
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串对象
String s1 = "helloworld";
String s2 = " helloworld ";
String s3 = " hello world ";
System.out.println("---"+s1+"---");
System.out.println("---"+s1.trim()+"---");
System.out.println("---"+s2+"---");
System.out.println("---"+s2.trim()+"---");
System.out.println("---"+s3+"---");
System.out.println("---"+s3.trim()+"---");
System.out.println("-------------------");
//String[] split(String str)
//创建字符创对象
String s4 = "aa,bb,cc";
String[] strArray = s4.split(",");
for(int x=0; xstring类练习
练习1:把数组中的数据按照指定格式拼接成一个字符串–举例:int[] arr = {1,2,3};
输出结果:[1, 2, 3]
package com.demo07;
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
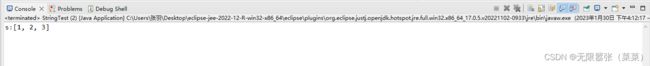
//定义一个int类型的数组
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
//定义方法
String s = arrayToString(arr);
//输出结果
System.out.println("s:"+s);
}
/*
* 两个明确
* 返回值类型:String
* 参数列表:int[] arr
*/
public static String arrayToString(int[] arr) {
String s = "";
//[1, 2, 3]
s += "[";
for(int x=0; x练习2:字符串反转–举例:键盘录入”abc” 输出结果:”cba”
package com.demo07;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StringTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个对象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入字符");
String s = sc.nextLine();
//创建方法
String result = reverse(s);
//输出结果
System.out.println("result:"+result);
}
public static String reverse(String s) {
// 将字符串转换成字符数组
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
for(int start=0,end=chs.length-1; start<=end; start++,end--) {
char temp = chs[start];
chs[start] = chs[end];
chs[end] = temp;
}
//把字符串数组封装成字符串对象
String ss = new String(chs);
return ss;
}
}