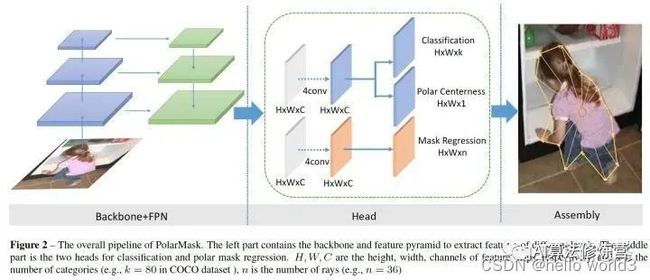
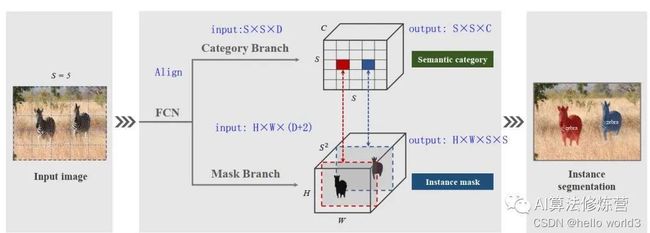
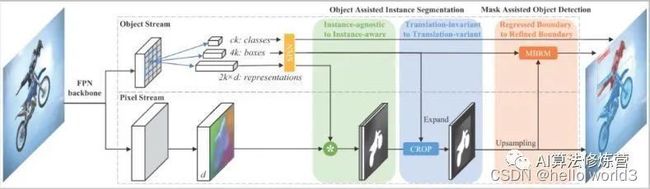
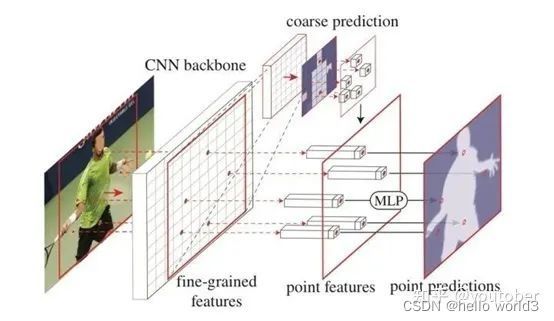
Mask RCNN综述以及建筑物实例分割
基于Mask RCNN建筑物轮廓识别
- 介绍
- 实例分割研究综述
-
- 问题与难点
- 实例分割的基本流程
-
- 实例分割主要技术路线
-
- 自上而下的实例分割方法
- 自下而上的实例分割方法
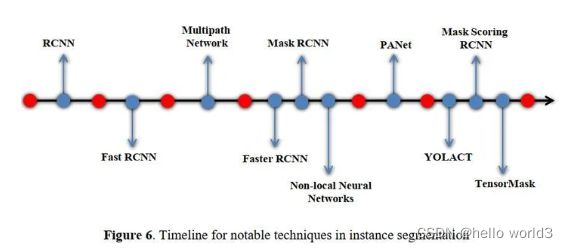
- 实例分割方法的发展历程
- 实例分割方法主要网络架构方法分类
-
- 掩膜建议分类法
- 先检测再分割法
- 标记像素后聚类法
- 密集滑动窗口法
- 实例分割经典方法
- Mask RCNN
-
- 网络结构
- Faster-RCNN
- ResNet-FPN
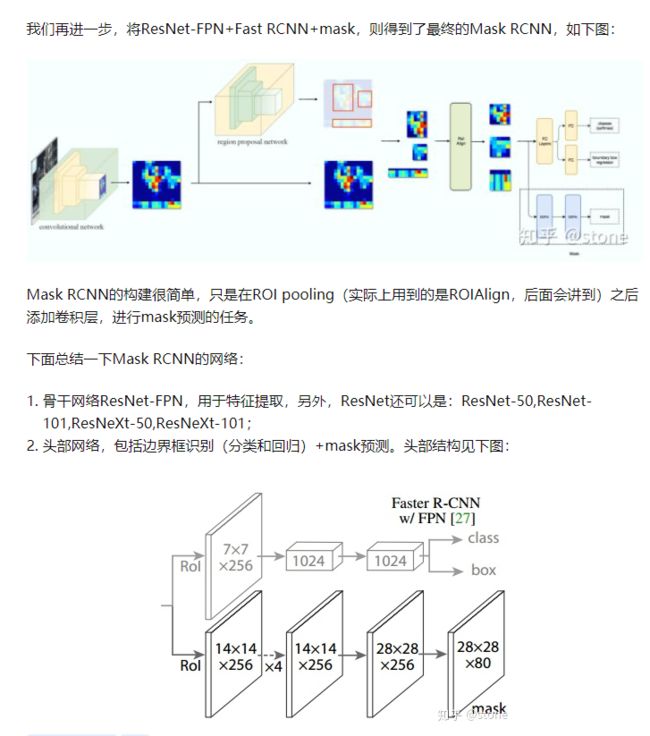
- ResNet-FPN+Fat RCNN+mask
- SpineNet
- ROI Align
- Loss
- Tensorflow实现
-
- 数据载入
-
- 文件结构
- 代码实现
- 模型实现
- 输入处理
- Loss函数实现
- Boundary Regularization
-
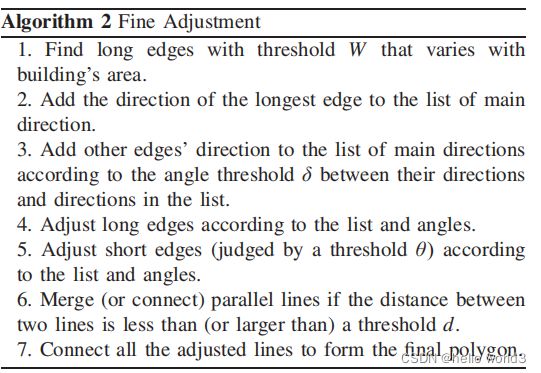
- Algorithm1:大致调整
- Algorithm2:细化算法
- 代码实现
介绍
之前有个任务是对建筑物轮廓识别,使用了U-Net算法,见地物分类:基于Unet的建筑物轮廓识别。选择这个算法原因是训练数据集较小少,而且建筑物轮廓比较稳定,因此选择参数量较少的U-Net算法。其实训练数据少有两个原因,一方面是只有我做数据集,包括数据采集、清洗以及标注一条龙服务,我一个人确实handle不了。数据标注是个苦差,比目标检测的数据集制作还要花一倍的工作量。另一方面训练集是在百度地图、腾讯地图或谷歌地图上截图,如果各位客官有相应可以爬取的数据集的网站或者API,希望大家不吝指导,在评论区上留言,在下定会不胜感激。
在该功能上线后,发现识别率并不怎么高,除了上面提及到的数据原因外,还有一个比较重要的原因是训练样本(建筑物)的风格比较单一,训练得出的模型并不能很好地cover所有数据。基于此,为了优化该功能,我主要从两个方面入手,一方面是提升数据集的数量以及质量;另一方面使用Mask RCNN算法,选择这个算法的原因是一些论文或者实际应用中使用Mask RCNN能够达到比较好的效果,如:让卫星读懂乡村:新老建筑足迹怎么识别?、【可计算乡村】一键解锁全国村庄形态肌理和matterport/Mask_RCNN。
本篇博客先介绍Mask RCNN的原理,然后基于Tensorflow2.X的实现Mask RCNN算法。
实例分割研究综述
在计算机视觉领域,实例分割是一个很重要的研究主题,在地理信息系统、医学影像、自动驾驶、机器人等领域有着很重要的应用技术支持作用,具有十分重要的研究意义。实例分割是目标检测和语义分割的结合,在图像中将目标检测出来(目标检测),然后对每个像素打上标签(语义分割)。实例分割目的是将输入图像中的目标检测出来,并且对目标的每个像素分配类别标签.实例分割能够对前景语义类别相同的不同实例进行区分,这是它与语义分割的最大区别.相比语义分割,实例分割发展较晚,因此实例分割模型主要基于深度学习技术, 但它也是图像分割一个重要的组成部分.随着深度学习的发展,实例分割相继出现了 SDS(Simultaneous detection and segmentation)、DeepMask、MultiPath network 等方法,分割精度和效率逐渐得到提升。
问题与难点
- 小物体分割问题:深层神经网络一般有更大的感受野,对姿态、形变、光照等具有鲁棒性,但是分辨率比较低,细节也丢失了;浅层神经网络的感受野比较窄,细节比较丰富,分辨率比较大,但缺少了语义上的信息。因此如果一个物体比较小时,它的细节在浅层的CNN层中会更少,同样的细节在深层网络中几乎会消失。解决这个问题的方法有空洞卷积核增大特征的分辨率。
- 处理几何变换的问题:对于几何变换,CNN本质上并不是空间不变的。
- 处理遮挡问题:遮挡会造成目标信息的丢失。目前提出了一些方法来解决这个问题。如deformable ROI pooling,deformable convolution和adversarial network。
- 处理图像退化的问题:造成图像退化的原因有光照,低质量的摄像机和图像压缩等。不过目前大多数数据集(如ImageNet,COCO和PASCAL VOC等)都不存在图像退化的问题
实例分割的基本流程
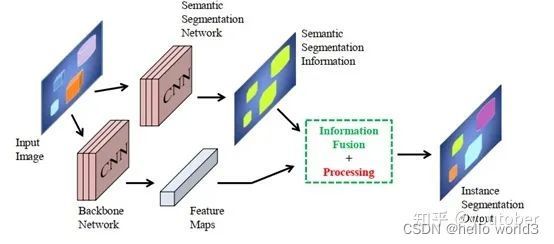
实例分割一般由三部分组成:图像输入、实例分割处理、分割结果输出。图像输入后,模型一般使用VGGNet、ResNet等骨干网络提取图像特征,然后通过实例分割模型进行处理。模型中可以先通过目标检测判定目标实例的位置和类别,然后在所选定区域位置进行分割,或者先执行语义分割任务,再区分不同的实例,最后输出实例分割的结果。
实例分割主要技术路线
实例分割长期以来都有着两条线,分别是自下而上的基于语义分割的方法和自上而下的基于检测的方法,这两种方法都属于两阶段的方法。
自上而下的实例分割方法
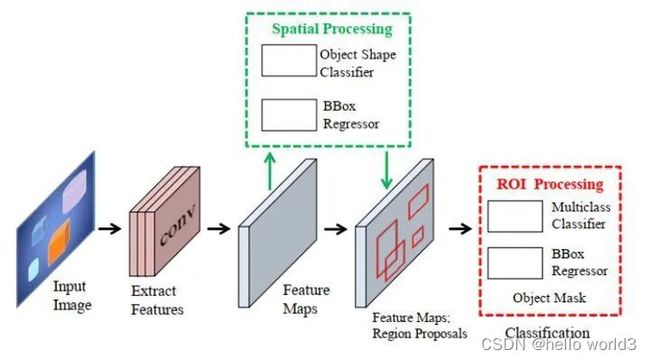
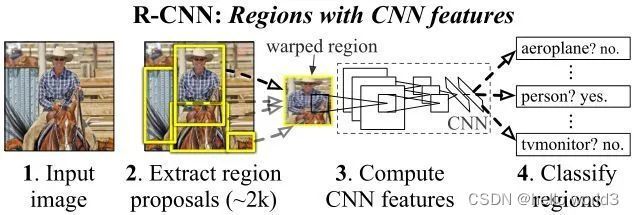
首先通过目标检测的方法找出实例所在的区域(bounding box),再在检测框内进行语义分割,每个分割结果都作为一个不同实例的输出。通常先检测后分割,如FCIS,Mask-RCNN,PANet,Mask Scoring R-CNN;自上而下的密集实例分割的开山鼻祖是DeepMask,它通过滑动窗口的方法,在每个空间区域上都预测一个mask proposal。这个方法有如下三个缺点:
- mask与特征的联系(局部一致性)丢失了,如DeepMask中使用全连接网络去提取mask
- 特征的提取表示是冗余的,如Deepmask对每个前景特征都回去提取一次mask
- 下采样(使用步长大于1的卷积)导致的位置信息丢失
自下而上的实例分割方法
将每个实例看成一个类别,然后按照聚类的思路,最大类间距,最小类间距,对每个像素做embedding,最后做grouping分出不同的instance。Grouping的方法:一般bottom-up效果差于top-down。思路是首先进行像素级别的语义分割,再通过聚类、度量学习等手段区分不同的实例。这种方法虽然保持了更好的底层特征(细节信息和位置信息),但是也存在以下缺点:
- 对密集分割的质量要求很高,会导致非最有的分割
- 泛化能力较差,无法应对类别多的复杂场景
- 后处理方法繁琐
实例分割方法的发展历程
实例分割方法主要网络架构方法分类
主要有四种:掩膜建议分类法、先检测再分割法、标记像素后聚类法和密集滑动窗口法
| Group | Technique |
|---|---|
| Classfification of mask proposals | RCNN, Fast RCNN, Faster RCNN |
| Detection followed by segmentation | HTC, PANet, Mask Scoring RCNN, MPN, YOLACT |
| Labelling pixels followed by clustering | Deep Watershed Transform, Instance Cut |
| Detection followed by segmentation | HTC, PANet, Mask Scoring RCNN, MPN, YOLACT |
| Dense sliding window methods | Deep Mask, Instance FCN, Tensor Mask |
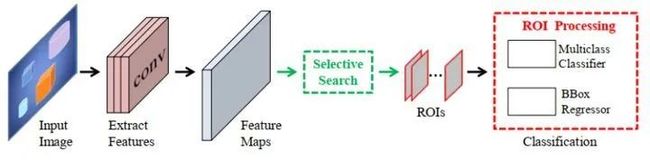
掩膜建议分类法
先检测再分割法
标记像素后聚类法
密集滑动窗口法
实例分割经典方法
-
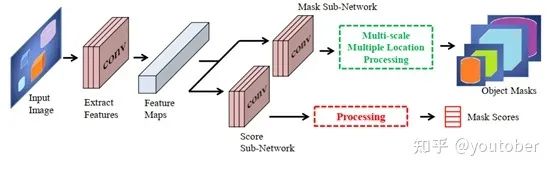
Deepmask
DeepMask 网络采用 VGGNet 对输入图像提 取特征, 生成分割提议, 提取的特征为两个分支所 共享, 第 1 个分支对选中的物体预测一个分割掩码, 第 2 个分支对输入的 Patch 预测一个目标得分. 该 网络在 PASCAL VOC 2007 和 MS COCO 数据集 上进行了验证, 分割精度良好。
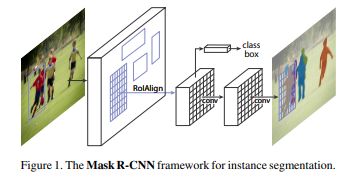
Mask RCNN
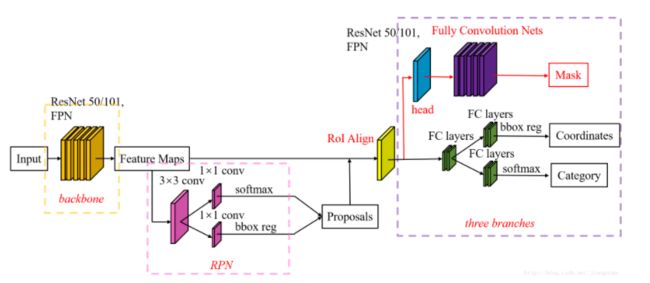
关于Mask RCNN在此只做简单的介绍,抄一下别人的博客内容搬过来。Mask-RCNN主要完成三件事情:1. 目标检测(直接在结果上绘制了目标框);2. 目标分类;3. 像素级目标分割。Mask-RCNN继承的是Faster-RCNN,在Faster-RCNN基础上添加了Mask Prediction Branch(MASK预测分支),并且改良了ROI Pooling,提出了ROI Align。
网络结构
Faster-RCNN
Faster-RCNN使用CNN提取图像特征,然后使用region proposal network(RPN)去提取出ROI,然后使用ROI pooling将这些ROI全部编程固定尺寸,再喂给全连接层进行Bounding box回归和分类预测。
- Conv layers:作为一种CNN网络目标检测方法,Faster RCNN首先使用一组基础的conv+relu+pooling层提取image的feature maps。该feature maps被共享用于后续RPN层和全连接层。
- Region Proposal Networks:RPN网络用于生成region proposals。该层通过softmax判断anchors属于positive或者negative,再利用bounding box regression修正anchors获得精确的proposals。
- Roi Pooling:该层收集输入的feature maps和proposals,综合这些信息后提取proposal feature maps,送入后续全连接层判定目标类别。
- Classification:利用proposal feature maps计算proposal的类别,同时再次bounding box regression获得检测框最终的精确位置。
Anchor:
一文读懂Faster RCNN
令人拍案称奇的Mask RCNN
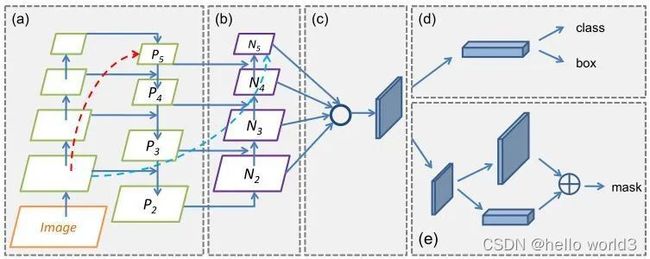
ResNet-FPN
ResNet-FPN+Fat RCNN+mask
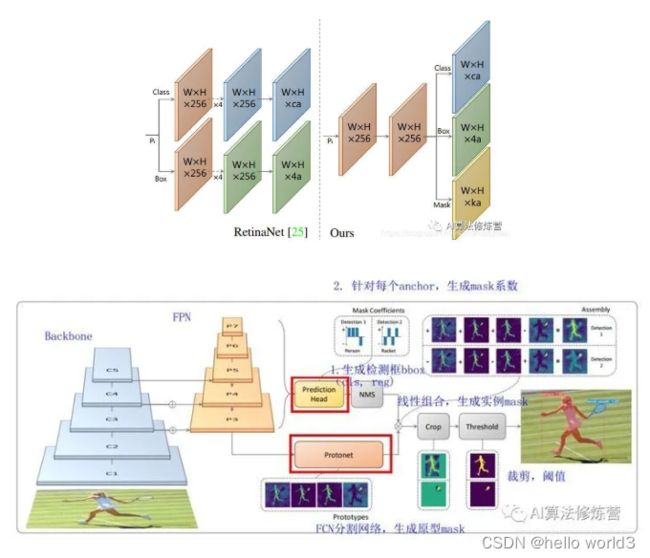
SpineNet

代码可以查看:https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/tree/master/models/official/detection
ROI Align
实际上,Mask RCNN中还有一个很重要的改进,就是ROIAlign。Faster R-CNN存在的问题是:特征图与原始图像是不对准的(mis-alignment),所以会影响检测精度。而Mask R-CNN提出了RoIAlign的方法来取代ROI pooling,RoIAlign可以保留大致的空间位置。RoIAlign层输入rpn网络的proposal以及卷积层输出的5个尺度特征。输出是不同proposal对应到不同尺度下的特征,利用proposal对该特征进行裁剪resize,池化提取特征。
详细可以参考详解 Mask-RCNN 中的 “RoIAlign” 作用 / 双线性插值的方法
Loss
Tensorflow实现
mask rcnn的实现在matterport/Mask_RCNN已经实现了。里面有balloon,shape的Demo,根据这些Demo只需要改造数据读入的方式即可训练自身的数据集。
数据载入
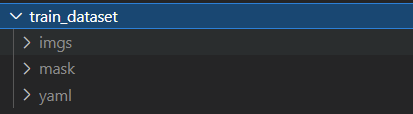
文件结构
- imgs:保存训练图像的原图
- mask:原图对应的掩膜图像
- yaml:保存yaml的文档
yaml:
label_names:
- _background_
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
- building
关于怎么制作数据集,可以参考:图像分割数据集制作。
代码实现
在制作完数据集之后,在看看如何实现读入数据。
定义一个dataset.py类:
class Dataset(object):
# 数据集训练的基本格式
def __init__(self, class_map=None):
self._image_ids = []
self.image_info = []
# 背景作为第一分类
self.class_info = [{"source": "", "id": 0, "name": "BG"}]
self.source_class_ids = {}
def add_class(self, source, class_id, class_name):
assert "." not in source, "Source name cannot contain a dot"
# 用于增加新的类
for info in self.class_info:
if info['source'] == source and info["id"] == class_id:
return
self.class_info.append({
"source": source,
"id": class_id,
"name": class_name,
})
def add_image(self, source, image_id, path, **kwargs):
# 用于增加用于训练的图片
image_info = {
"id": image_id,
"source": source,
"path": path,
}
image_info.update(kwargs)
self.image_info.append(image_info)
def image_reference(self, image_id):
return ""
def prepare(self, class_map=None):
# 准备数据
def clean_name(name):
"""Returns a shorter version of object names for cleaner display."""
return ",".join(name.split(",")[:1])
# 分多少类
self.num_classes = len(self.class_info)
# 种类的id
self.class_ids = np.arange(self.num_classes)
# 搞个简称出来,用于显示
self.class_names = [clean_name(c["name"]) for c in self.class_info]
# 计算一共有多少个图片
self.num_images = len(self.image_info)
# 图片的id
self._image_ids = np.arange(self.num_images)
# 从源类和图像id到内部id的映射
self.class_from_source_map = {"{}.{}".format(info['source'], info['id']): id
for info, id in zip(self.class_info, self.class_ids)}
self.image_from_source_map = {"{}.{}".format(info['source'], info['id']): id
for info, id in zip(self.image_info, self.image_ids)}
# 建立sources
self.sources = list(set([i['source'] for i in self.class_info]))
self.source_class_ids = {}
# Loop over datasets
for source in self.sources:
self.source_class_ids[source] = []
# Find classes that belong to this dataset
for i, info in enumerate(self.class_info):
# Include BG class in all datasets
if i == 0 or source == info['source']:
self.source_class_ids[source].append(i)
def map_source_class_id(self, source_class_id):
"""Takes a source class ID and returns the int class ID assigned to it.
For example:
dataset.map_source_class_id("coco.12") -> 23
"""
return self.class_from_source_map[source_class_id]
def get_source_class_id(self, class_id, source):
"""Map an internal class ID to the corresponding class ID in the source dataset."""
info = self.class_info[class_id]
assert info['source'] == source
return info['id']
@property
def image_ids(self):
return self._image_ids
def source_image_link(self, image_id):
return self.image_info[image_id]["path"]
def load_image(self, image_id):
"""
载入图片
"""
# Load image
image = skimage.io.imread(self.image_info[image_id]['path'])
if image.ndim != 3:
image = skimage.color.gray2rgb(image)
if image.shape[-1] == 4:
image = image[..., :3]
return image
def load_mask(self, image_id):
'''
载入语义分割内容
'''
logging.warning("You are using the default load_mask(), maybe you need to define your own one.")
mask = np.empty([0, 0, 0])
class_ids = np.empty([0], np.int32)
return mask, class_ids
定义一个customer.py类,继承dataset class:
class CustomerDataset(Dataset):
#得到该图中有多少个实例(物体)
def get_obj_index(self, image):
n = np.max(image)
return n
#解析labelme中得到的yaml文件,从而得到mask每一层对应的实例标签
def from_yaml_get_class(self,image_id):
info=self.image_info[image_id]
with open(info['yaml_path']) as f:
temp=yaml.load(f.read(), Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
labels=temp['label_names']
del labels[0]
return labels
#重新写draw_mask
def draw_mask(self, num_obj, mask, image, image_id):
info = self.image_info[image_id]
for index in range(num_obj):
for i in range(np.shape(mask)[1]):
for j in range(np.shape(mask)[0]):
at_pixel = image.getpixel((i, j))
if at_pixel == index + 1:
mask[j, i, index] =1
return mask
#并在self.image_info信息中添加了path、mask_path 、yaml_path
def load_shapes(self, shape_name, count, classes, img_floder, mask_floder, imglist, yaml_floder):
for index, item in enumerate(classes):
self.add_class(shape_name, index+1, item)
for i in range(count):
img = imglist[i]
if img.endswith(".jpg"):
img_name = img.split(".")[0]
img_path = os.path.join(img_floder, img)
mask_path = os.path.join(mask_floder, img_name + ".png")
yaml_path = os.path.join(yaml_floder, img_name + ".yaml")
self.add_image(shape_name, image_id=i, path=img_path, mask_path=mask_path,yaml_path=yaml_path)
#重写load_mask
def load_mask(self, image_id):
info = self.image_info[image_id]
img = Image.open(info['mask_path'])
num_obj = self.get_obj_index(img)
mask = np.zeros([np.shape(img)[0], np.shape(img)[1], num_obj], dtype=np.uint8)
mask = self.draw_mask(num_obj, mask, img, image_id)
labels=[]
labels=self.from_yaml_get_class(image_id)
# labels_form=[]
# for i in range(len(labels)):
# if labels[i].find("circle")!=-1:
# labels_form.append("circle")
# elif labels[i].find("square")!=-1:
# labels_form.append("square")
# elif labels[i].find("triangle")!=-1:
# labels_form.append("triangle")
class_ids = np.array([self.class_names.index(s) for s in labels])
return mask, class_ids.astype(np.int32)
模型数据定义在data_generator方法中,具体细节如下:
- input_image/mask是经过resize和padding,统一了尺寸
- input_rpn_match和input_rpn_bbox是为了计算rpn损失的目标数据,match数据是每个生成的anchor对应的0/1背景前景类别,bbox数据是match=1那些bbox的平移缩放量。
data_generator.py
def data_generator(dataset, config, shuffle=True, augment=False, augmentation=None,
batch_size=1, detection_targets=False,
no_augmentation_sources=None):
"""
网络输入清单
- images: [batch, H, W, C]
- image_meta: [batch, (meta data)] 图像详细信息。
- rpn_match: [batch, N] 代表建议框的匹配情况 (1=正样本, -1=负样本, 0=中性)
- rpn_bbox: [batch, N, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] 建议框网络应该有的预测结果.
- gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES] 种类ID
- gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
- gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES].
网络输出清单:
在常规训练中通常是空的。
"""
b = 0 # batch item index
image_index = -1
image_ids = np.copy(dataset.image_ids)
no_augmentation_sources = no_augmentation_sources or []
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# 计算获得先验框
backbone_shapes = compute_backbone_shapes(config, config.IMAGE_SHAPE)
anchors = generate_pyramid_anchors(config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS,
backbone_shapes,
config.BACKBONE_STRIDES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE)
while True:
image_index = (image_index + 1) % len(image_ids)
if shuffle and image_index == 0:
np.random.shuffle(image_ids)
# 获得id
image_id = image_ids[image_index]
# 获得图片,真实框,语义分割结果等
if dataset.image_info[image_id]['source'] in no_augmentation_sources:
image, image_meta, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks = \
load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=augment,
augmentation=None,
use_mini_mask=config.USE_MINI_MASK)
else:
image, image_meta, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks = \
load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=augment,
augmentation=augmentation,
use_mini_mask=config.USE_MINI_MASK)
if not np.any(gt_class_ids > 0):
continue
# RPN Targets
rpn_match, rpn_bbox = build_rpn_targets(image.shape, anchors,
gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, config)
# 如果某张图片里面物体的数量大于最大值的话,则进行筛选,防止过大
if gt_boxes.shape[0] > config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES:
ids = np.random.choice(
np.arange(gt_boxes.shape[0]), config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES, replace=False)
gt_class_ids = gt_class_ids[ids]
gt_boxes = gt_boxes[ids]
gt_masks = gt_masks[:, :, ids]
# 初始化用于训练的内容
if b == 0:
batch_image_meta = np.zeros(
(batch_size,) + image_meta.shape, dtype=image_meta.dtype)
batch_rpn_match = np.zeros(
[batch_size, anchors.shape[0], 1], dtype=rpn_match.dtype)
batch_rpn_bbox = np.zeros(
[batch_size, config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE, 4], dtype=rpn_bbox.dtype)
batch_images = np.zeros(
(batch_size,) + image.shape, dtype=np.float32)
batch_gt_class_ids = np.zeros(
(batch_size, config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES), dtype=np.int32)
batch_gt_boxes = np.zeros(
(batch_size, config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES, 4), dtype=np.int32)
batch_gt_masks = np.zeros(
(batch_size, gt_masks.shape[0], gt_masks.shape[1],
config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES), dtype=gt_masks.dtype)
# 将当前信息加载进batch
batch_image_meta[b] = image_meta
batch_rpn_match[b] = rpn_match[:, np.newaxis]
batch_rpn_bbox[b] = rpn_bbox
batch_images[b] = utils.mold_image(image.astype(np.float32), config)
batch_gt_class_ids[b, :gt_class_ids.shape[0]] = gt_class_ids
batch_gt_boxes[b, :gt_boxes.shape[0]] = gt_boxes
batch_gt_masks[b, :, :, :gt_masks.shape[-1]] = gt_masks
b += 1
# 判断是否已经将batch_size全部载入
if b >= batch_size:
inputs = [batch_images, batch_image_meta, batch_rpn_match, batch_rpn_bbox,
batch_gt_class_ids, batch_gt_boxes, batch_gt_masks]
outputs = []
yield inputs, outputs
# 开始一个新的batch_size
b = 0
模型实现
training部分的代码整体情况:
- inputs:input_image、input_image_meta、input_rpn_match、input_rpn_bbox、input_gt_class_ids、input_gt_boxes、input_gt_masks(normal mask, mini mask)
- model:
-
前卷积网络:
C2,C3, C4, C5 = resnet_graph(*) P2, P3, P4, P5, P6 = top_down_layer(*) -
rpn网络ROI筛选以及目标值计算
-
ROI,scores,mask预测
-
mrcnn_training.py
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import tensorflow.keras.layers as KL
import tensorflow.keras.utils as KU
from tensorflow.python.eager import context
import random
import numpy as np
import logging
from utils import utils
from utils.anchors import compute_backbone_shapes,generate_pyramid_anchors
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
def batch_pack_graph(x, counts, num_rows):
outputs = []
for i in range(num_rows):
outputs.append(x[i, :counts[i]])
return tf.concat(outputs, axis=0)
def smooth_l1_loss(y_true, y_pred):
"""
smmoth_l1 损失函数
"""
diff = K.abs(y_true - y_pred)
less_than_one = K.cast(K.less(diff, 1.0), "float32")
loss = (less_than_one * 0.5 * diff**2) + (1 - less_than_one) * (diff - 0.5)
return loss
def rpn_class_loss_graph(rpn_match, rpn_class_logits):
"""
建议框分类损失函数
"""
# 在最后一维度添加一维度
rpn_match = tf.squeeze(rpn_match, -1)
# 获得正样本
anchor_class = K.cast(K.equal(rpn_match, 1), tf.int32)
# 获得未被忽略的样本
indices = tf.where(K.not_equal(rpn_match, 0))
# 获得预测结果和实际结果
rpn_class_logits = tf.gather_nd(rpn_class_logits, indices)
anchor_class = tf.gather_nd(anchor_class, indices)
# 计算二者之间的交叉熵
loss = K.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(target=anchor_class,
output=rpn_class_logits,
from_logits=True)
loss = K.switch(tf.size(loss) > 0, K.mean(loss), tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.switch(tf.math.is_nan(loss), tf.constant([0.0]), loss)
return loss
def rpn_bbox_loss_graph(config, target_bbox, rpn_match, rpn_bbox):
"""
建议框回归损失
"""
# 在最后一维度添加一维度
rpn_match = K.squeeze(rpn_match, -1)
# 获得正样本
indices = tf.where(K.equal(rpn_match, 1))
# 获得预测结果与实际结果
rpn_bbox = tf.gather_nd(rpn_bbox, indices)
# 将目标边界框修剪为与rpn_bbox相同的长度。
batch_counts = K.sum(K.cast(K.equal(rpn_match, 1), tf.int32), axis=1)
target_bbox = batch_pack_graph(target_bbox, batch_counts,
config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
# 计算smooth_l1损失函数
loss = smooth_l1_loss(target_bbox, rpn_bbox)
loss = K.switch(tf.size(loss) > 0, K.mean(loss), tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.switch(tf.math.is_nan(loss), tf.constant([0.0]), loss)
return loss
def mrcnn_class_loss_graph(target_class_ids, pred_class_logits,
active_class_ids):
"""
classifier的分类损失函数
"""
# 目标信息
target_class_ids = tf.cast(target_class_ids, 'int64')
# 预测信息
pred_class_ids = tf.argmax(pred_class_logits, axis=2)
pred_active = tf.gather(active_class_ids[0], pred_class_ids)
# 求二者交叉熵损失
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=target_class_ids, logits=pred_class_logits)
# 去除无用的损失
loss = loss * pred_active
# 求平均
loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / tf.maximum(tf.reduce_sum(pred_active), 1)
return loss
def mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph(target_bbox, target_class_ids, pred_bbox):
"""
classifier的回归损失函数
"""
# Reshape
target_class_ids = K.reshape(target_class_ids, (-1,))
target_bbox = K.reshape(target_bbox, (-1, 4))
pred_bbox = K.reshape(pred_bbox, (-1, K.int_shape(pred_bbox)[2], 4))
# 只有属于正样本的建议框用于训练
positive_roi_ix = tf.where(target_class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
positive_roi_class_ids = tf.cast(tf.gather(target_class_ids, positive_roi_ix), tf.int64)
indices = tf.stack([positive_roi_ix, positive_roi_class_ids], axis=1)
# 获得对应预测结果与实际结果
target_bbox = tf.gather(target_bbox, positive_roi_ix)
pred_bbox = tf.gather_nd(pred_bbox, indices)
# Smooth-L1 Loss
loss = K.switch(tf.size(target_bbox) > 0,
smooth_l1_loss(y_true=target_bbox, y_pred=pred_bbox),
tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.mean(loss)
return loss
def mrcnn_mask_loss_graph(target_masks, target_class_ids, pred_masks):
"""
交叉熵损失
"""
target_class_ids = K.reshape(target_class_ids, (-1,))
# 实际结果
mask_shape = tf.shape(target_masks)
target_masks = K.reshape(target_masks, (-1, mask_shape[2], mask_shape[3]))
# 预测结果
pred_shape = tf.shape(pred_masks)
pred_masks = K.reshape(pred_masks, (-1, pred_shape[2], pred_shape[3], pred_shape[4]))
# 进行维度变换 [N, num_classes, height, width]
pred_masks = tf.transpose(pred_masks, [0, 3, 1, 2])
# 只有正样本有效
positive_ix = tf.where(target_class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
positive_class_ids = tf.cast(tf.gather(target_class_ids, positive_ix), tf.int64)
indices = tf.stack([positive_ix, positive_class_ids], axis=1)
# 获得实际结果与预测结果
y_true = tf.gather(target_masks, positive_ix)
y_pred = tf.gather_nd(pred_masks, indices)
# shape: [batch, roi, num_classes]
loss = K.switch(tf.size(y_true) > 0,
K.binary_crossentropy(target=y_true, output=y_pred),
tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.mean(loss)
return loss
def load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=False, augmentation=None,
use_mini_mask=False):
# 载入图片和语义分割效果
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
# print("\nbefore:",image_id,np.shape(mask),np.shape(class_ids))
# 原始shape
original_shape = image.shape
# 获得新图片,原图片在新图片中的位置,变化的尺度,填充的情况等
image, window, scale, padding, crop = utils.resize_image(
image,
min_dim=config.IMAGE_MIN_DIM,
min_scale=config.IMAGE_MIN_SCALE,
max_dim=config.IMAGE_MAX_DIM,
mode=config.IMAGE_RESIZE_MODE)
mask = utils.resize_mask(mask, scale, padding, crop)
# print("\nafter:",np.shape(mask),np.shape(class_ids))
# print(np.shape(image),np.shape(mask))
# 可以把图片进行翻转
if augment:
logging.warning("'augment' is deprecated. Use 'augmentation' instead.")
if random.randint(0, 1):
image = np.fliplr(image)
mask = np.fliplr(mask)
if augmentation:
import imgaug
# 可用于图像增强
MASK_AUGMENTERS = ["Sequential", "SomeOf", "OneOf", "Sometimes",
"Fliplr", "Flipud", "CropAndPad",
"Affine", "PiecewiseAffine"]
def hook(images, augmenter, parents, default):
"""Determines which augmenters to apply to masks."""
return augmenter.__class__.__name__ in MASK_AUGMENTERS
image_shape = image.shape
mask_shape = mask.shape
det = augmentation.to_deterministic()
image = det.augment_image(image)
mask = det.augment_image(mask.astype(np.uint8),
hooks=imgaug.HooksImages(activator=hook))
assert image.shape == image_shape, "Augmentation shouldn't change image size"
assert mask.shape == mask_shape, "Augmentation shouldn't change mask size"
mask = mask.astype(np.bool)
# 检漏,防止某些层内部实际上不存在语义分割情况
_idx = np.sum(mask, axis=(0, 1)) > 0
# print("\nafterer:",np.shape(mask),np.shape(_idx))
mask = mask[:, :, _idx]
class_ids = class_ids[_idx]
# 找到mask对应的box
bbox = utils.extract_bboxes(mask)
active_class_ids = np.zeros([dataset.num_classes], dtype=np.int32)
source_class_ids = dataset.source_class_ids[dataset.image_info[image_id]["source"]]
active_class_ids[source_class_ids] = 1
if use_mini_mask:
mask = utils.minimize_mask(bbox, mask, config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE)
# 生成Image_meta
image_meta = utils.compose_image_meta(image_id, original_shape, image.shape,
window, scale, active_class_ids)
return image, image_meta, class_ids, bbox, mask
def build_rpn_targets(image_shape, anchors, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, config):
# 1代表正样本
# -1代表负样本
# 0代表忽略
rpn_match = np.zeros([anchors.shape[0]], dtype=np.int32)
# 创建该部分内容利用先验框和真实框进行编码
rpn_bbox = np.zeros((config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE, 4))
'''
iscrowd=0的时候,表示这是一个单独的物体,轮廓用Polygon(多边形的点)表示,
iscrowd=1的时候表示两个没有分开的物体,轮廓用RLE编码表示,比如说一张图片里面有三个人,
一个人单独站一边,另外两个搂在一起(标注的时候距离太近分不开了),这个时候,
单独的那个人的注释里面的iscrowing=0,segmentation用Polygon表示,
而另外两个用放在同一个anatation的数组里面用一个segmention的RLE编码形式表示
'''
crowd_ix = np.where(gt_class_ids < 0)[0]
if crowd_ix.shape[0] > 0:
non_crowd_ix = np.where(gt_class_ids > 0)[0]
crowd_boxes = gt_boxes[crowd_ix]
gt_class_ids = gt_class_ids[non_crowd_ix]
gt_boxes = gt_boxes[non_crowd_ix]
crowd_overlaps = utils.compute_overlaps(anchors, crowd_boxes)
crowd_iou_max = np.amax(crowd_overlaps, axis=1)
no_crowd_bool = (crowd_iou_max < 0.001)
else:
no_crowd_bool = np.ones([anchors.shape[0]], dtype=bool)
# 计算先验框和真实框的重合程度 [num_anchors, num_gt_boxes]
overlaps = utils.compute_overlaps(anchors, gt_boxes)
# 1. 重合程度小于0.3则代表为负样本
anchor_iou_argmax = np.argmax(overlaps, axis=1)
anchor_iou_max = overlaps[np.arange(overlaps.shape[0]), anchor_iou_argmax]
rpn_match[(anchor_iou_max < 0.3) & (no_crowd_bool)] = -1
# 2. 每个真实框重合度最大的先验框是正样本
gt_iou_argmax = np.argwhere(overlaps == np.max(overlaps, axis=0))[:,0]
rpn_match[gt_iou_argmax] = 1
# 3. 重合度大于0.7则代表为正样本
rpn_match[anchor_iou_max >= 0.7] = 1
# 正负样本平衡
# 找到正样本的索引
ids = np.where(rpn_match == 1)[0]
# 如果大于(config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE // 2)则删掉一些
extra = len(ids) - (config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE // 2)
if extra > 0:
ids = np.random.choice(ids, extra, replace=False)
rpn_match[ids] = 0
# 找到负样本的索引
ids = np.where(rpn_match == -1)[0]
# 使得总数为config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE
extra = len(ids) - (config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE -
np.sum(rpn_match == 1))
if extra > 0:
# Rest the extra ones to neutral
ids = np.random.choice(ids, extra, replace=False)
rpn_match[ids] = 0
# 找到内部真实存在物体的先验框,进行编码
ids = np.where(rpn_match == 1)[0]
ix = 0
for i, a in zip(ids, anchors[ids]):
gt = gt_boxes[anchor_iou_argmax[i]]
# 计算真实框的中心,高宽
gt_h = gt[2] - gt[0]
gt_w = gt[3] - gt[1]
gt_center_y = gt[0] + 0.5 * gt_h
gt_center_x = gt[1] + 0.5 * gt_w
# 计算先验框中心,高宽
a_h = a[2] - a[0]
a_w = a[3] - a[1]
a_center_y = a[0] + 0.5 * a_h
a_center_x = a[1] + 0.5 * a_w
# 编码运算
rpn_bbox[ix] = [
(gt_center_y - a_center_y) / np.maximum(a_h, 1),
(gt_center_x - a_center_x) / np.maximum(a_w, 1),
np.log(np.maximum(gt_h / np.maximum(a_h, 1), 1e-5)),
np.log(np.maximum(gt_w / np.maximum(a_w, 1), 1e-5)),
]
# 改变数量级
rpn_bbox[ix] /= config.RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV
ix += 1
return rpn_match, rpn_bbox
def data_generator(dataset, config, shuffle=True, augment=False, augmentation=None,
batch_size=1, detection_targets=False,
no_augmentation_sources=None):
"""
网络输入清单
- images: [batch, H, W, C]
- image_meta: [batch, (meta data)] 图像详细信息。
- rpn_match: [batch, N] 代表建议框的匹配情况 (1=正样本, -1=负样本, 0=中性)
- rpn_bbox: [batch, N, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] 建议框网络应该有的预测结果.
- gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES] 种类ID
- gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
- gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES].
网络输出清单:
在常规训练中通常是空的。
"""
b = 0 # batch item index
image_index = -1
image_ids = np.copy(dataset.image_ids)
no_augmentation_sources = no_augmentation_sources or []
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# 计算获得先验框
backbone_shapes = compute_backbone_shapes(config, config.IMAGE_SHAPE)
anchors = generate_pyramid_anchors(config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS,
backbone_shapes,
config.BACKBONE_STRIDES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE)
while True:
image_index = (image_index + 1) % len(image_ids)
if shuffle and image_index == 0:
np.random.shuffle(image_ids)
# 获得id
image_id = image_ids[image_index]
# 获得图片,真实框,语义分割结果等
if dataset.image_info[image_id]['source'] in no_augmentation_sources:
image, image_meta, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks = \
load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=augment,
augmentation=None,
use_mini_mask=config.USE_MINI_MASK)
else:
image, image_meta, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks = \
load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=augment,
augmentation=augmentation,
use_mini_mask=config.USE_MINI_MASK)
if not np.any(gt_class_ids > 0):
continue
# RPN Targets
rpn_match, rpn_bbox = build_rpn_targets(image.shape, anchors,
gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, config)
# 如果某张图片里面物体的数量大于最大值的话,则进行筛选,防止过大
if gt_boxes.shape[0] > config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES:
ids = np.random.choice(
np.arange(gt_boxes.shape[0]), config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES, replace=False)
gt_class_ids = gt_class_ids[ids]
gt_boxes = gt_boxes[ids]
gt_masks = gt_masks[:, :, ids]
# 初始化用于训练的内容
if b == 0:
batch_image_meta = np.zeros(
(batch_size,) + image_meta.shape, dtype=image_meta.dtype)
batch_rpn_match = np.zeros(
[batch_size, anchors.shape[0], 1], dtype=rpn_match.dtype)
batch_rpn_bbox = np.zeros(
[batch_size, config.RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE, 4], dtype=rpn_bbox.dtype)
batch_images = np.zeros(
(batch_size,) + image.shape, dtype=np.float32)
batch_gt_class_ids = np.zeros(
(batch_size, config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES), dtype=np.int32)
batch_gt_boxes = np.zeros(
(batch_size, config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES, 4), dtype=np.int32)
batch_gt_masks = np.zeros(
(batch_size, gt_masks.shape[0], gt_masks.shape[1],
config.MAX_GT_INSTANCES), dtype=gt_masks.dtype)
# 将当前信息加载进batch
batch_image_meta[b] = image_meta
batch_rpn_match[b] = rpn_match[:, np.newaxis]
batch_rpn_bbox[b] = rpn_bbox
batch_images[b] = utils.mold_image(image.astype(np.float32), config)
batch_gt_class_ids[b, :gt_class_ids.shape[0]] = gt_class_ids
batch_gt_boxes[b, :gt_boxes.shape[0]] = gt_boxes
batch_gt_masks[b, :, :, :gt_masks.shape[-1]] = gt_masks
b += 1
# 判断是否已经将batch_size全部载入
if b >= batch_size:
inputs = [batch_images, batch_image_meta, batch_rpn_match, batch_rpn_bbox,
batch_gt_class_ids, batch_gt_boxes, batch_gt_masks]
outputs = []
yield inputs, outputs
# 开始一个新的batch_size
b = 0
mrcnn.py
from .layers import ProposalLayer,PyramidROIAlign,DetectionLayer,DetectionTargetLayer
from .mrcnn_training import *
from utils.anchors import get_anchors
from utils.utils import norm_boxes_graph,parse_image_meta_graph
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.keras as keras
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import tensorflow.keras.layers as KL
import tensorflow.keras.utils as KU
from tensorflow.python.eager import context
import tensorflow.keras.models as KM
from mrcnn.restnet import get_resnet
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
#------------------------------------#
# 五个不同大小的特征层会传入到
# RPN当中,获得建议框
#------------------------------------#
def rpn_graph(feature_map, anchors_per_location, anchor_stride):
shared = KL.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu',strides=anchor_stride,
name='rpn_conv_shared')(feature_map)
x = KL.Conv2D(2 * anchors_per_location, (1, 1), padding='valid',
activation='linear', name='rpn_class_raw')(shared)
# batch_size,num_anchors,2
# 代表这个先验框对应的类
rpn_class_logits = KL.Reshape([-1,2])(x)
rpn_probs = KL.Activation(
"softmax", name="rpn_class_xxx")(rpn_class_logits)
x = KL.Conv2D(anchors_per_location * 4, (1, 1), padding="valid",
activation='linear', name='rpn_bbox_pred')(shared)
# batch_size,num_anchors,4
# 这个先验框的调整参数
rpn_bbox = KL.Reshape([-1,4])(x)
return [rpn_class_logits, rpn_probs, rpn_bbox]
#------------------------------------#
# 建立建议框网络模型
# RPN模型
#------------------------------------#
def build_rpn_model(anchor_stride, anchors_per_location, depth):
"""Builds a Keras model of the Region Proposal Network.
It wraps the RPN graph so it can be used multiple times with shared
weights.
anchors_per_location: number of anchors per pixel in the feature map
anchor_stride: Controls the density of anchors. Typically 1 (anchors for
every pixel in the feature map), or 2 (every other pixel).
depth: Depth of the backbone feature map.
Returns a Keras Model object. The model outputs, when called, are:
rpn_class_logits: [batch, H * W * anchors_per_location, 2] Anchor classifier logits (before softmax)
rpn_probs: [batch, H * W * anchors_per_location, 2] Anchor classifier probabilities.
rpn_bbox: [batch, H * W * anchors_per_location, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] Deltas to be
applied to anchors.
"""
input_feature_map = KL.Input(shape=[None, None, depth],
name="input_rpn_feature_map")
outputs = rpn_graph(input_feature_map, anchors_per_location, anchor_stride)
return KM.Model([input_feature_map], outputs, name="rpn_model")
#------------------------------------#
# 建立classifier模型
# 这个模型的预测结果会调整建议框
# 获得最终的预测框
#------------------------------------#
def fpn_classifier_graph(rois, feature_maps, image_meta,
pool_size, num_classes, train_bn=True,
fc_layers_size=1024):
# ROI Pooling,利用建议框在特征层上进行截取
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, POOL_SIZE, POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = PyramidROIAlign([pool_size, pool_size],
name="roi_align_classifier")([rois, image_meta] + feature_maps)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, 1, 1, fc_layers_size],相当于两次全连接
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Conv2D(fc_layers_size, (pool_size, pool_size), padding="valid"),
name="mrcnn_class_conv1")(x)
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.BatchNormalization(), name='mrcnn_class_bn1')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, 1, 1, fc_layers_size]
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Conv2D(fc_layers_size, (1, 1)),
name="mrcnn_class_conv2")(x)
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.BatchNormalization(), name='mrcnn_class_bn2')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, fc_layers_size]
shared = KL.Lambda(lambda x: K.squeeze(K.squeeze(x, 3), 2),
name="pool_squeeze")(x)
# Classifier head
# 这个的预测结果代表这个先验框内部的物体的种类
mrcnn_class_logits = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Dense(num_classes),
name='mrcnn_class_logits')(shared)
mrcnn_probs = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Activation("softmax"),
name="mrcnn_class")(mrcnn_class_logits)
# BBox head
# 这个的预测结果会对先验框进行调整
# [batch, num_rois, NUM_CLASSES * (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Dense(num_classes * 4, activation='linear'),
name='mrcnn_bbox_fc')(shared)
# Reshape to [batch, num_rois, NUM_CLASSES, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]
s = K.int_shape(x)
if s[1] is None:
mrcnn_bbox = KL.Reshape((-1, num_classes, 4), name="mrcnn_bbox")(x)
else:
mrcnn_bbox = KL.Reshape((s[1], num_classes, 4), name="mrcnn_bbox")(x)
return mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_probs, mrcnn_bbox
def build_fpn_mask_graph(rois, feature_maps, image_meta,
pool_size, num_classes, train_bn=True):
# ROI Pooling,利用建议框在特征层上进行截取
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = PyramidROIAlign([pool_size, pool_size],
name="roi_align_mask")([rois, image_meta] + feature_maps)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"),
name="mrcnn_mask_conv1")(x)
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.BatchNormalization(),
name='mrcnn_mask_bn1')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"),
name="mrcnn_mask_conv2")(x)
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.BatchNormalization(),
name='mrcnn_mask_bn2')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"),
name="mrcnn_mask_conv3")(x)
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.BatchNormalization(),
name='mrcnn_mask_bn3')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, MASK_POOL_SIZE, MASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same"),
name="mrcnn_mask_conv4")(x)
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.BatchNormalization(),
name='mrcnn_mask_bn4')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, 2xMASK_POOL_SIZE, 2xMASK_POOL_SIZE, channels]
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Conv2DTranspose(256, (2, 2), strides=2, activation="relu"),
name="mrcnn_mask_deconv")(x)
# 反卷积后再次进行一个1x1卷积调整通道,使其最终数量为numclasses,代表分的类
x = KL.TimeDistributed(KL.Conv2D(num_classes, (1, 1), strides=1, activation="sigmoid"),
name="mrcnn_mask")(x)
return x
def get_predict_model(config):
h, w = config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2]
if h / 2**6 != int(h / 2**6) or w / 2**6 != int(w / 2**6):
raise Exception("Image size must be dividable by 2 at least 6 times "
"to avoid fractions when downscaling and upscaling."
"For example, use 256, 320, 384, 448, 512, ... etc. ")
# 输入进来的图片必须是2的6次方以上的倍数
input_image = KL.Input(shape=[None, None, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[2]], name="input_image")
# meta包含了一些必要信息
input_image_meta = KL.Input(shape=[config.IMAGE_META_SIZE],name="input_image_meta")
# 输入进来的先验框
input_anchors = KL.Input(shape=[None, 4], name="input_anchors")
# 获得Resnet里的压缩程度不同的一些层
_, C2, C3, C4, C5 = get_resnet(input_image, stage5=True, train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
# 组合成特征金字塔的结构
# P5长宽共压缩了5次
# Height/32,Width/32,256
P5 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c5p5')(C5)
# P4长宽共压缩了4次
# Height/16,Width/16,256
P4 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p4add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p5upsampled")(P5),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c4p4')(C4)])
# P4长宽共压缩了3次
# Height/8,Width/8,256
P3 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p3add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p4upsampled")(P4),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c3p3')(C3)])
# P4长宽共压缩了2次
# Height/4,Width/4,256
P2 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p2add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p3upsampled")(P3),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c2p2')(C2)])
# 各自进行一次256通道的卷积,此时P2、P3、P4、P5通道数相同
# Height/4,Width/4,256
P2 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p2")(P2)
# Height/8,Width/8,256
P3 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p3")(P3)
# Height/16,Width/16,256
P4 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p4")(P4)
# Height/32,Width/32,256
P5 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p5")(P5)
# 在建议框网络里面还有一个P6用于获取建议框
# Height/64,Width/64,256
P6 = KL.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(1, 1), strides=2, name="fpn_p6")(P5)
# P2, P3, P4, P5, P6可以用于获取建议框
rpn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5, P6]
# P2, P3, P4, P5用于获取mask信息
mrcnn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5]
anchors = input_anchors
# 建立RPN模型
rpn = build_rpn_model(config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE, len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS), config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE)
rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox = [],[],[]
# 获得RPN网络的预测结果,进行格式调整,把五个特征层的结果进行堆叠
for p in rpn_feature_maps:
logits,classes,bbox = rpn([p])
rpn_class_logits.append(logits)
rpn_class.append(classes)
rpn_bbox.append(bbox)
rpn_class_logits = KL.Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_class_logits")(rpn_class_logits)
rpn_class =KL.Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_class")(rpn_class)
rpn_bbox = KL.Concatenate(axis=1,name="rpn_bbox")(rpn_bbox)
# 此时获得的rpn_class_logits、rpn_class、rpn_bbox的维度是
# rpn_class_logits : Batch_size, num_anchors, 2
# rpn_class : Batch_size, num_anchors, 2
# rpn_bbox : Batch_size, num_anchors, 4
proposal_count = config.POST_NMS_ROIS_INFERENCE
# Batch_size, proposal_count, 4
# 对先验框进行解码
rpn_rois = ProposalLayer(
proposal_count=proposal_count,
nms_threshold=config.RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD,
name="ROI",
config=config)([rpn_class, rpn_bbox, anchors])
# 获得classifier的结果
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox =\
fpn_classifier_graph(rpn_rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, input_image_meta,
config.POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN,
fc_layers_size=config.FPN_CLASSIF_FC_LAYERS_SIZE)
detections = DetectionLayer(config, name="mrcnn_detection")(
[rpn_rois, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, input_image_meta])
detection_boxes = KL.Lambda(lambda x: x[..., :4])(detections)
# 获得mask的结果
mrcnn_mask = build_fpn_mask_graph(detection_boxes, mrcnn_feature_maps,
input_image_meta,
config.MASK_POOL_SIZE,
config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
# 作为输出
model = KM.Model([input_image, input_image_meta, input_anchors],
[detections, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox,
mrcnn_mask, rpn_rois, rpn_class, rpn_bbox],
name='mask_rcnn')
return model
def get_train_model(config):
# Image size must be dividable by 2 multiple times
h, w = config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2]
if h / 2**6 != int(h / 2**6) or w / 2**6 != int(w / 2**6):
raise Exception("Image size must be dividable by 2 at least 6 times "
"to avoid fractions when downscaling and upscaling."
"For example, use 256, 320, 384, 448, 512, ... etc. ")
# Inputs
input_image = KL.Input(
shape=[None, None, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[2]], name="input_image")
input_image_meta = KL.Input(shape=[config.IMAGE_META_SIZE],
name="input_image_meta")
# RPN建议框网络的真实框信息
input_rpn_match = KL.Input(
shape=[None, 1], name="input_rpn_match", dtype=tf.int32)
input_rpn_bbox = KL.Input(
shape=[None, 4], name="input_rpn_bbox", dtype=tf.float32)
# Detection GT (class IDs, bounding boxes, and masks)
# 1. GT Class IDs (zero padded)
input_gt_class_ids = KL.Input(
shape=[None], name="input_gt_class_ids", dtype=tf.int32)
# 2. GT Boxes in pixels (zero padded)
# [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in image coordinates
input_gt_boxes = KL.Input(
shape=[None, 4], name="input_gt_boxes", dtype=tf.float32)
# Normalize coordinates
gt_boxes = KL.Lambda(lambda x: norm_boxes_graph(
x, K.shape(input_image)[1:3]))(input_gt_boxes)
# mask语义分析信息
# [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]
if config.USE_MINI_MASK:
input_gt_masks = KL.Input(shape=[config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE[0],config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE[1], None],name="input_gt_masks", dtype=bool)
else:
input_gt_masks = KL.Input(shape=[config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1], None],name="input_gt_masks", dtype=bool)
# 获得Resnet里的压缩程度不同的一些层
_, C2, C3, C4, C5 = get_resnet(input_image, stage5=True, train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
# 组合成特征金字塔的结构
# P5长宽共压缩了5次
# Height/32,Width/32,256
P5 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c5p5')(C5)
# P4长宽共压缩了4次
# Height/16,Width/16,256
P4 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p4add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p5upsampled")(P5),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c4p4')(C4)])
# P4长宽共压缩了3次
# Height/8,Width/8,256
P3 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p3add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p4upsampled")(P4),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c3p3')(C3)])
# P4长宽共压缩了2次
# Height/4,Width/4,256
P2 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p2add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p3upsampled")(P3),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c2p2')(C2)])
# 各自进行一次256通道的卷积,此时P2、P3、P4、P5通道数相同
# Height/4,Width/4,256
P2 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p2")(P2)
# Height/8,Width/8,256
P3 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p3")(P3)
# Height/16,Width/16,256
P4 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p4")(P4)
# Height/32,Width/32,256
P5 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p5")(P5)
# 在建议框网络里面还有一个P6用于获取建议框
# Height/64,Width/64,256
P6 = KL.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(1, 1), strides=2, name="fpn_p6")(P5)
# P2, P3, P4, P5, P6可以用于获取建议框
rpn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5, P6]
# P2, P3, P4, P5用于获取mask信息
mrcnn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5]
anchors = get_anchors(config,config.IMAGE_SHAPE)
# 拓展anchors的shape,第一个维度拓展为batch_size
anchors = np.broadcast_to(anchors, (config.BATCH_SIZE,) + anchors.shape)
# 将anchors转化成tensor的形式
class ConstLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, x, name=None):
super(ConstLayer, self).__init__(name=name)
self.x = tf.Variable(x)
def call(self, input):
return self.x
anchors = ConstLayer(anchors, name="anchors")(input_image)
# anchors = KL.Lambda(lambda x: tf.Variable(anchors), name="anchors")(input_image)
# 建立RPN模型
rpn = build_rpn_model(config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE, len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS), config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE)
# Loop through pyramid layers
layer_outputs = [] # list of lists
for p in rpn_feature_maps:
layer_outputs.append(rpn([p]))
# 获得RPN网络的预测结果,进行格式调整,把五个特征层的结果进行堆叠
output_names = ["rpn_class_logits", "rpn_class", "rpn_bbox"]
outputs = list(zip(*layer_outputs))
outputs = [KL.Concatenate(axis=1, name=n)(list(o))
for o, n in zip(outputs, output_names)]
rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox = outputs
# 此时获得的rpn_class_logits、rpn_class、rpn_bbox的维度是
# rpn_class_logits : Batch_size, num_anchors, 2
# rpn_class : Batch_size, num_anchors, 2
# rpn_bbox : Batch_size, num_anchors, 4
proposal_count = config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING
# Batch_size, proposal_count, 4
rpn_rois = ProposalLayer(
proposal_count=proposal_count,
nms_threshold=config.RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD,
name="ROI",
config=config)([rpn_class, rpn_bbox, anchors])
active_class_ids = KL.Lambda(
lambda x: parse_image_meta_graph(x)["active_class_ids"]
)(input_image_meta)
if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS:
# 使用外部输入的建议框
input_rois = KL.Input(shape=[config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING, 4],
name="input_roi", dtype=np.int32)
# Normalize coordinates
target_rois = KL.Lambda(lambda x: norm_boxes_graph(
x, K.shape(input_image)[1:3]))(input_rois)
else:
# 利用预测到的建议框进行下一步的操作
target_rois = rpn_rois
"""找到建议框的ground_truth
Inputs:
proposals: [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]建议框
gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]每个真实框对应的类
gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]真实框的位置
gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]真实框的语义分割情况
Returns:
rois: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]内部真实存在目标的建议框
target_class_ids: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE]每个建议框对应的类
target_deltas: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw)]每个建议框应该有的调整参数
target_mask: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, height, width]每个建议框语义分割情况
"""
rois, target_class_ids, target_bbox, target_mask =\
DetectionTargetLayer(config, name="proposal_targets")([
target_rois, input_gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, input_gt_masks])
# 找到合适的建议框的classifier预测结果
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox =\
fpn_classifier_graph(rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, input_image_meta,
config.POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN,
fc_layers_size=config.FPN_CLASSIF_FC_LAYERS_SIZE)
# 找到合适的建议框的mask预测结果
mrcnn_mask = build_fpn_mask_graph(rois, mrcnn_feature_maps,
input_image_meta,
config.MASK_POOL_SIZE,
config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
output_rois = KL.Lambda(lambda x: x * 1, name="output_rois")(rois)
# Losses
rpn_class_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: rpn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="rpn_class_loss")(
[input_rpn_match, rpn_class_logits])
rpn_bbox_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: rpn_bbox_loss_graph(config, *x), name="rpn_bbox_loss")(
[input_rpn_bbox, input_rpn_match, rpn_bbox])
class_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_class_loss")(
[target_class_ids, mrcnn_class_logits, active_class_ids])
bbox_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_bbox_loss")(
[target_bbox, target_class_ids, mrcnn_bbox])
mask_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_mask_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_mask_loss")(
[target_mask, target_class_ids, mrcnn_mask])
# Model
inputs = [input_image, input_image_meta,
input_rpn_match, input_rpn_bbox, input_gt_class_ids, input_gt_boxes, input_gt_masks]
if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS:
inputs.append(input_rois)
outputs = [rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox,
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, mrcnn_mask,
rpn_rois, output_rois,
rpn_class_loss, rpn_bbox_loss, class_loss, bbox_loss, mask_loss]
model = KM.Model(inputs, outputs, name='mask_rcnn')
return model
layers.py
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.keras as keras
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import tensorflow.keras.layers as KL
import tensorflow.keras.utils as KU
from tensorflow.python.eager import context
import tensorflow.keras.models as KM
import numpy as np
from utils import utils
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
def apply_box_deltas_graph(boxes, deltas):
# 计算先验框的中心和宽高
height = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
width = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
center_y = boxes[:, 0] + 0.5 * height
center_x = boxes[:, 1] + 0.5 * width
# 计算出调整后的先验框的中心和宽高
center_y += deltas[:, 0] * height
center_x += deltas[:, 1] * width
height *= tf.exp(deltas[:, 2])
width *= tf.exp(deltas[:, 3])
# 计算左上角和右下角的点的坐标
y1 = center_y - 0.5 * height
x1 = center_x - 0.5 * width
y2 = y1 + height
x2 = x1 + width
result = tf.stack([y1, x1, y2, x2], axis=1, name="apply_box_deltas_out")
return result
def clip_boxes_graph(boxes, window):
"""
boxes: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
window: [4] in the form y1, x1, y2, x2
"""
# Split
wy1, wx1, wy2, wx2 = tf.split(window, 4)
y1, x1, y2, x2 = tf.split(boxes, 4, axis=1)
# Clip
y1 = tf.maximum(tf.minimum(y1, wy2), wy1)
x1 = tf.maximum(tf.minimum(x1, wx2), wx1)
y2 = tf.maximum(tf.minimum(y2, wy2), wy1)
x2 = tf.maximum(tf.minimum(x2, wx2), wx1)
clipped = tf.concat([y1, x1, y2, x2], axis=1, name="clipped_boxes")
clipped.set_shape((clipped.shape[0], 4))
return clipped
class ProposalLayer(KL.Layer):
def __init__(self, proposal_count, nms_threshold, config=None, **kwargs):
super(ProposalLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.config = config
self.proposal_count = proposal_count
self.nms_threshold = nms_threshold
# [rpn_class, rpn_bbox, anchors]
def call(self, inputs):
# 代表这个先验框内部是否有物体[batch, num_rois, 1]
scores = inputs[0][:, :, 1]
# 代表这个先验框的调整参数[batch, num_rois, 4]
deltas = inputs[1]
# [0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2],改变数量级
deltas = deltas * np.reshape(self.config.RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV, [1, 1, 4])
# Anchors
anchors = inputs[2]
# 筛选出得分前6000个的框
pre_nms_limit = tf.minimum(self.config.PRE_NMS_LIMIT, tf.shape(anchors)[1])
# 获得这些框的索引
ix = tf.nn.top_k(scores, pre_nms_limit, sorted=True,
name="top_anchors").indices
# 获得这些框的得分
scores = utils.batch_slice([scores, ix], lambda x, y: tf.gather(x, y),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
# 获得这些框的调整参数
deltas = utils.batch_slice([deltas, ix], lambda x, y: tf.gather(x, y),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
# 获得这些框对应的先验框
pre_nms_anchors = utils.batch_slice([anchors, ix], lambda a, x: tf.gather(a, x),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU,
names=["pre_nms_anchors"])
# [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# 对先验框进行解码
boxes = utils.batch_slice([pre_nms_anchors, deltas],
lambda x, y: apply_box_deltas_graph(x, y),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU,
names=["refined_anchors"])
# [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# 防止超出图片范围
window = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1], dtype=np.float32)
boxes = utils.batch_slice(boxes,
lambda x: clip_boxes_graph(x, window),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU,
names=["refined_anchors_clipped"])
# 非极大抑制
def nms(boxes, scores):
indices = tf.image.non_max_suppression(
boxes, scores, self.proposal_count,
self.nms_threshold, name="rpn_non_max_suppression")
proposals = tf.gather(boxes, indices)
# 如果数量达不到设置的建议框数量的话
# 就padding
padding = tf.maximum(self.proposal_count - tf.shape(proposals)[0], 0)
proposals = tf.pad(proposals, [(0, padding), (0, 0)])
return proposals
proposals = utils.batch_slice([boxes, scores], nms,
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
if not context.executing_eagerly():
# Infer the static output shape:
out_shape = self.compute_output_shape(None)
proposals.set_shape(out_shape)
return proposals
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return (None, self.proposal_count, 4)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# ROIAlign Layer
# 利用建议框在特征层上截取内容
#----------------------------------------------------------#
def log2_graph(x):
return tf.math.log(x) / tf.math.log(2.0)
def parse_image_meta_graph(meta):
"""
将meta里面的参数进行分割
"""
image_id = meta[:, 0]
original_image_shape = meta[:, 1:4]
image_shape = meta[:, 4:7]
window = meta[:, 7:11] # (y1, x1, y2, x2) window of image in in pixels
scale = meta[:, 11]
active_class_ids = meta[:, 12:]
return {
"image_id": image_id,
"original_image_shape": original_image_shape,
"image_shape": image_shape,
"window": window,
"scale": scale,
"active_class_ids": active_class_ids,
}
class PyramidROIAlign(KL.Layer):
def __init__(self, pool_shape, **kwargs):
super(PyramidROIAlign, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.pool_shape = tuple(pool_shape)
def call(self, inputs):
# 建议框的位置
boxes = inputs[0]
# image_meta包含了一些必要的图片信息
image_meta = inputs[1]
# 取出所有的特征层[batch, height, width, channels]
feature_maps = inputs[2:]
y1, x1, y2, x2 = tf.split(boxes, 4, axis=2)
h = y2 - y1
w = x2 - x1
# 获得输入进来的图像的大小
image_shape = parse_image_meta_graph(image_meta)['image_shape'][0]
# 通过建议框的大小找到这个建议框属于哪个特征层
image_area = tf.cast(image_shape[0] * image_shape[1], tf.float32)
roi_level = log2_graph(tf.sqrt(h * w) / (224.0 / tf.sqrt(image_area)))
roi_level = tf.minimum(5, tf.maximum(
2, 4 + tf.cast(tf.round(roi_level), tf.int32)))
# batch_size, box_num
roi_level = tf.squeeze(roi_level, 2)
# Loop through levels and apply ROI pooling to each. P2 to P5.
pooled = []
box_to_level = []
# 分别在P2-P5中进行截取
for i, level in enumerate(range(2, 6)):
# 找到每个特征层对应box
ix = tf.compat.v1.where(tf.equal(roi_level, level))
level_boxes = tf.gather_nd(boxes, ix)
box_to_level.append(ix)
# 获得这些box所属的图片
box_indices = tf.cast(ix[:, 0], tf.int32)
# 停止梯度下降
level_boxes = tf.stop_gradient(level_boxes)
box_indices = tf.stop_gradient(box_indices)
# Result: [batch * num_boxes, pool_height, pool_width, channels]
pooled.append(tf.image.crop_and_resize(
feature_maps[i], level_boxes, box_indices, self.pool_shape,
method="bilinear"))
pooled = tf.concat(pooled, axis=0)
# 将顺序和所属的图片进行堆叠
box_to_level = tf.concat(box_to_level, axis=0)
box_range = tf.expand_dims(tf.range(tf.shape(box_to_level)[0]), 1)
box_to_level = tf.concat([tf.cast(box_to_level, tf.int32), box_range],
axis=1)
# box_to_level[:, 0]表示第几张图
# box_to_level[:, 1]表示第几张图里的第几个框
sorting_tensor = box_to_level[:, 0] * 100000 + box_to_level[:, 1]
# 进行排序,将同一张图里的某一些聚集在一起
ix = tf.nn.top_k(sorting_tensor, k=tf.shape(
box_to_level)[0]).indices[::-1]
# 按顺序获得图片的索引
ix = tf.gather(box_to_level[:, 2], ix)
pooled = tf.gather(pooled, ix)
# 重新reshape为原来的格式
# 也就是
# Shape: [batch, num_rois, POOL_SIZE, POOL_SIZE, channels]
shape = tf.concat([tf.shape(boxes)[:2], tf.shape(pooled)[1:]], axis=0)
pooled = tf.reshape(pooled, shape)
return pooled
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return input_shape[0][:2] + self.pool_shape + (input_shape[2][-1], )
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# Detection Layer
#
#----------------------------------------------------------#
def refine_detections_graph(rois, probs, deltas, window, config):
"""细化分类建议并过滤重叠部分并返回最终结果探测。
Inputs:
rois: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates
probs: [N, num_classes]. Class probabilities.
deltas: [N, num_classes, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]. Class-specific
bounding box deltas.
window: (y1, x1, y2, x2) in normalized coordinates. The part of the image
that contains the image excluding the padding.
Returns detections shaped: [num_detections, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, score)] where
coordinates are normalized.
"""
# 找到得分最高的类
class_ids = tf.argmax(probs, axis=1, output_type=tf.int32)
# 序号+类
indices = tf.stack([tf.range(probs.shape[0]), class_ids], axis=1)
# 取出成绩
class_scores = tf.gather_nd(probs, indices)
# 还有框的调整参数
deltas_specific = tf.gather_nd(deltas, indices)
# 进行解码
# Shape: [boxes, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates
refined_rois = apply_box_deltas_graph(
rois, deltas_specific * config.BBOX_STD_DEV)
# 防止超出0-1
refined_rois = clip_boxes_graph(refined_rois, window)
# 去除背景
keep = tf.compat.v1.where(class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
# 去除背景和得分小的区域
if config.DETECTION_MIN_CONFIDENCE:
conf_keep = tf.compat.v1.where(class_scores >= config.DETECTION_MIN_CONFIDENCE)[:, 0]
keep = tf.sets.intersection(tf.expand_dims(keep, 0),
tf.expand_dims(conf_keep, 0))
keep = tf.sparse.to_dense(keep)[0]
# 获得除去背景并且得分较高的框还有种类与得分
# 1. Prepare variables
pre_nms_class_ids = tf.gather(class_ids, keep)
pre_nms_scores = tf.gather(class_scores, keep)
pre_nms_rois = tf.gather(refined_rois, keep)
unique_pre_nms_class_ids = tf.unique(pre_nms_class_ids)[0]
def nms_keep_map(class_id):
ixs = tf.where(tf.equal(pre_nms_class_ids, class_id))[:, 0]
class_keep = tf.image.non_max_suppression(
tf.gather(pre_nms_rois, ixs),
tf.gather(pre_nms_scores, ixs),
max_output_size=config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES,
iou_threshold=config.DETECTION_NMS_THRESHOLD)
class_keep = tf.gather(keep, tf.gather(ixs, class_keep))
gap = config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES - tf.shape(class_keep)[0]
class_keep = tf.pad(class_keep, [(0, gap)],
mode='CONSTANT', constant_values=-1)
class_keep.set_shape([config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES])
return class_keep
# 2. 进行非极大抑制
nms_keep = tf.map_fn(nms_keep_map, unique_pre_nms_class_ids,
dtype=tf.int64)
# 3. 找到符合要求的需要被保留的建议框
nms_keep = tf.reshape(nms_keep, [-1])
nms_keep = tf.gather(nms_keep, tf.where(nms_keep > -1)[:, 0])
# 4. Compute intersection between keep and nms_keep
keep = tf.sets.intersection(tf.expand_dims(keep, 0),
tf.expand_dims(nms_keep, 0))
keep = tf.sparse.to_dense(keep)[0]
# 寻找得分最高的num_keep个框
roi_count = config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES
class_scores_keep = tf.gather(class_scores, keep)
num_keep = tf.minimum(tf.shape(class_scores_keep)[0], roi_count)
top_ids = tf.nn.top_k(class_scores_keep, k=num_keep, sorted=True)[1]
keep = tf.gather(keep, top_ids)
# Arrange output as [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, score)]
detections = tf.concat([
tf.gather(refined_rois, keep),
tf.dtypes.cast(tf.gather(class_ids, keep), tf.float32)[..., tf.newaxis],
tf.gather(class_scores, keep)[..., tf.newaxis]
], axis=1)
# 如果达不到数量的话就padding
gap = config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES - tf.shape(detections)[0]
detections = tf.pad(tensor=detections, paddings=[(0, gap), (0, 0)], mode="CONSTANT")
return detections
def norm_boxes_graph(boxes, shape):
h, w = tf.split(tf.cast(shape, tf.float32), 2)
scale = tf.concat([h, w, h, w], axis=-1) - tf.constant(1.0)
shift = tf.constant([0., 0., 1., 1.])
return tf.divide(boxes - shift, scale)
class DetectionLayer(KL.Layer):
def __init__(self, config=None, **kwargs):
super(DetectionLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.config = config
def call(self, inputs):
rois = inputs[0]
mrcnn_class = inputs[1]
mrcnn_bbox = inputs[2]
image_meta = inputs[3]
# 找到window的小数形式
m = parse_image_meta_graph(image_meta)
image_shape = m['image_shape'][0]
window = norm_boxes_graph(m['window'], image_shape[:2])
# Run detection refinement graph on each item in the batch
detections_batch = utils.batch_slice(
[rois, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, window],
lambda x, y, w, z: refine_detections_graph(x, y, w, z, self.config),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
# Reshape output
# [batch, num_detections, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, class_score)] in
# normalized coordinates
return tf.reshape(
detections_batch,
[self.config.BATCH_SIZE, self.config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES, 6])
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return (None, self.config.DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES, 6)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# Detection Target Layer
# 该部分代码会输入建议框
# 判断建议框和真实框的重合情况
# 筛选出内部包含物体的建议框
# 利用建议框和真实框编码
# 调整mask的格式使得其和预测格式相同
#----------------------------------------------------------#
def overlaps_graph(boxes1, boxes2):
"""
用于计算boxes1和boxes2的重合程度
boxes1, boxes2: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)].
返回 [len(boxes1), len(boxes2)]
"""
b1 = tf.reshape(tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(boxes1, 1),
[1, 1, tf.shape(boxes2)[0]]), [-1, 4])
b2 = tf.tile(boxes2, [tf.shape(boxes1)[0], 1])
b1_y1, b1_x1, b1_y2, b1_x2 = tf.split(b1, 4, axis=1)
b2_y1, b2_x1, b2_y2, b2_x2 = tf.split(b2, 4, axis=1)
y1 = tf.maximum(b1_y1, b2_y1)
x1 = tf.maximum(b1_x1, b2_x1)
y2 = tf.minimum(b1_y2, b2_y2)
x2 = tf.minimum(b1_x2, b2_x2)
intersection = tf.maximum(x2 - x1, 0) * tf.maximum(y2 - y1, 0)
b1_area = (b1_y2 - b1_y1) * (b1_x2 - b1_x1)
b2_area = (b2_y2 - b2_y1) * (b2_x2 - b2_x1)
union = b1_area + b2_area - intersection
iou = intersection / union
overlaps = tf.reshape(iou, [tf.shape(boxes1)[0], tf.shape(boxes2)[0]])
return overlaps
def detection_targets_graph(proposals, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks, config):
asserts = [
tf.Assert(tf.greater(tf.shape(proposals)[0], 0), [proposals],
name="roi_assertion"),
]
with tf.control_dependencies(asserts):
proposals = tf.identity(proposals)
# 移除之前获得的padding的部分
proposals, _ = trim_zeros_graph(proposals, name="trim_proposals")
gt_boxes, non_zeros = trim_zeros_graph(gt_boxes, name="trim_gt_boxes")
gt_class_ids = tf.boolean_mask(gt_class_ids, non_zeros,
name="trim_gt_class_ids")
gt_masks = tf.gather(gt_masks, tf.compat.v1.where(non_zeros)[:, 0], axis=2,
name="trim_gt_masks")
# Handle COCO crowds
# A crowd box in COCO is a bounding box around several instances. Exclude
# them from training. A crowd box is given a negative class ID.
crowd_ix = tf.compat.v1.where(gt_class_ids < 0)[:, 0]
non_crowd_ix = tf.compat.v1.where(gt_class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
crowd_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, crowd_ix)
gt_class_ids = tf.gather(gt_class_ids, non_crowd_ix)
gt_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, non_crowd_ix)
gt_masks = tf.gather(gt_masks, non_crowd_ix, axis=2)
# 计算建议框和所有真实框的重合程度 [proposals, gt_boxes]
overlaps = overlaps_graph(proposals, gt_boxes)
# 计算和 crowd boxes 的重合程度 [proposals, crowd_boxes]
crowd_overlaps = overlaps_graph(proposals, crowd_boxes)
crowd_iou_max = tf.reduce_max(crowd_overlaps, axis=1)
no_crowd_bool = (crowd_iou_max < 0.001)
# Determine positive and negative ROIs
roi_iou_max = tf.reduce_max(overlaps, axis=1)
# 1. 正样本建议框和真实框的重合程度大于0.5
positive_roi_bool = (roi_iou_max >= 0.5)
positive_indices = tf.where(positive_roi_bool)[:, 0]
# 2. 负样本建议框和真实框的重合程度小于0.5,Skip crowds.
negative_indices = tf.where(tf.logical_and(roi_iou_max < 0.5, no_crowd_bool))[:, 0]
# Subsample ROIs. Aim for 33% positive
# 进行正负样本的平衡
# 取出最大33%的正样本
positive_count = int(config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE *
config.ROI_POSITIVE_RATIO)
positive_indices = tf.random.shuffle(positive_indices)[:positive_count]
positive_count = tf.shape(positive_indices)[0]
# 保持正负样本比例
r = 1.0 / config.ROI_POSITIVE_RATIO
negative_count = tf.cast(r * tf.cast(positive_count, tf.float32), tf.int32) - positive_count
negative_indices = tf.random.shuffle(negative_indices)[:negative_count]
# 获得正样本和负样本
positive_rois = tf.gather(proposals, positive_indices)
negative_rois = tf.gather(proposals, negative_indices)
# 获取建议框和真实框重合程度
positive_overlaps = tf.gather(overlaps, positive_indices)
# 判断是否有真实框
roi_gt_box_assignment = tf.cond(
tf.greater(tf.shape(positive_overlaps)[1], 0),
true_fn = lambda: tf.argmax(positive_overlaps, axis=1),
false_fn = lambda: tf.cast(tf.constant([]),tf.int64)
)
# 找到每一个建议框对应的真实框和种类
roi_gt_boxes = tf.gather(gt_boxes, roi_gt_box_assignment)
roi_gt_class_ids = tf.gather(gt_class_ids, roi_gt_box_assignment)
# 解码获得网络应该有得预测结果
deltas = utils.box_refinement_graph(positive_rois, roi_gt_boxes)
deltas /= config.BBOX_STD_DEV
# 切换mask的形式[N, height, width, 1]
transposed_masks = tf.expand_dims(tf.transpose(gt_masks, [2, 0, 1]), -1)
# 取出对应的层
roi_masks = tf.gather(transposed_masks, roi_gt_box_assignment)
# Compute mask targets
boxes = positive_rois
if config.USE_MINI_MASK:
# Transform ROI coordinates from normalized image space
# to normalized mini-mask space.
y1, x1, y2, x2 = tf.split(positive_rois, 4, axis=1)
gt_y1, gt_x1, gt_y2, gt_x2 = tf.split(roi_gt_boxes, 4, axis=1)
gt_h = gt_y2 - gt_y1
gt_w = gt_x2 - gt_x1
y1 = (y1 - gt_y1) / gt_h
x1 = (x1 - gt_x1) / gt_w
y2 = (y2 - gt_y1) / gt_h
x2 = (x2 - gt_x1) / gt_w
boxes = tf.concat([y1, x1, y2, x2], 1)
box_ids = tf.range(0, tf.shape(roi_masks)[0])
masks = tf.image.crop_and_resize(tf.cast(roi_masks, tf.float32), boxes,
box_ids,
config.MASK_SHAPE)
# Remove the extra dimension from masks.
masks = tf.squeeze(masks, axis=3)
# 防止resize后的结果不是1或者0
masks = tf.round(masks)
# 一般传入config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE个建议框进行训练,
# 如果数量不够则padding
rois = tf.concat([positive_rois, negative_rois], axis=0)
N = tf.shape(negative_rois)[0]
P = tf.maximum(config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE - tf.shape(rois)[0], 0)
rois = tf.pad(rois, [(0, P), (0, 0)])
roi_gt_boxes = tf.pad(roi_gt_boxes, [(0, N + P), (0, 0)])
roi_gt_class_ids = tf.pad(roi_gt_class_ids, [(0, N + P)])
deltas = tf.pad(deltas, [(0, N + P), (0, 0)])
masks = tf.pad(masks, [[0, N + P], (0, 0), (0, 0)])
return rois, roi_gt_class_ids, deltas, masks
def trim_zeros_graph(boxes, name='trim_zeros'):
"""
如果前一步没有满POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING个建议框,会有padding
要去掉padding
"""
non_zeros = tf.cast(tf.reduce_sum(tf.abs(boxes), axis=1), tf.bool)
boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, non_zeros, name=name)
return boxes, non_zeros
class DetectionTargetLayer(KL.Layer):
"""找到建议框的ground_truth
Inputs:
proposals: [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]建议框
gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]每个真实框对应的类
gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]真实框的位置
gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]真实框的语义分割情况
Returns:
rois: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]内部真实存在目标的建议框
target_class_ids: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE]每个建议框对应的类
target_deltas: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw)]每个建议框应该有的调整参数
target_mask: [batch, TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, height, width]每个建议框语义分割情况
"""
def __init__(self, config, **kwargs):
super(DetectionTargetLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.config = config
def call(self, inputs):
proposals = inputs[0]
gt_class_ids = inputs[1]
gt_boxes = inputs[2]
gt_masks = inputs[3]
# 对真实框进行编码
names = ["rois", "target_class_ids", "target_bbox", "target_mask"]
outputs = utils.batch_slice(
[proposals, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks],
lambda w, x, y, z: detection_targets_graph(
w, x, y, z, self.config),
self.config.IMAGES_PER_GPU, names=names)
return outputs
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return [
(None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, 4), # rois
(None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE), # class_ids
(None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, 4), # deltas
(None, self.config.TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE, self.config.MASK_SHAPE[0],
self.config.MASK_SHAPE[1]) # masks
]
def compute_mask(self, inputs, mask=None):
return [None, None, None, None]
输入处理
送入Mask RCNN的输入分为三个部分:molded_images、image_metas以及anchors。首先看下molded_images和image_metas怎么生成的。
def mold_inputs(config, images):
molded_images = []
image_metas = []
windows = []
for image in images:
# Resize image
# TODO: move resizing to mold_image()
# molded_image表示尺度归一化的图包括原图和padding部分;window只包括原图而不包括padding部分。
molded_image, window, scale, padding, crop = resize_image(
image,
min_dim=config.IMAGE_MIN_DIM,
min_scale=config.IMAGE_MIN_SCALE,
max_dim=config.IMAGE_MAX_DIM,
mode=config.IMAGE_RESIZE_MODE)
# print(np.shape(molded_image))
molded_image = mold_image(molded_image, config)
# Build image_meta
image_meta = compose_image_meta(
0, image.shape, molded_image.shape, window, scale,
np.zeros([config.NUM_CLASSES], dtype=np.int32))
# Append
molded_images.append(molded_image)
windows.append(window)
image_metas.append(image_meta)
# Pack into arrays
molded_images = np.stack(molded_images)
image_metas = np.stack(image_metas)
windows = np.stack(windows)
return molded_images, image_metas, windows
Build image_meta,compose_image_meta
def compose_image_meta(image_id, original_image_shape, image_shape,
window, scale, active_class_ids):
"""Takes attributes of an image and puts them in one 1D array.
image_id: An int ID of the image. Useful for debugging.
original_image_shape: [H, W, C] before resizing or padding.
image_shape: [H, W, C] after resizing and padding
window: (y1, x1, y2, x2) in pixels. The area of the image where the real
image is (excluding the padding)
scale: The scaling factor applied to the original image (float32)
active_class_ids: List of class_ids available in the dataset from which
the image came. Useful if training on images from multiple datasets
where not all classes are present in all datasets.
"""
meta = np.array(
[image_id] + # size=1
list(original_image_shape) + # size=3
list(image_shape) + # size=3
list(window) + # size=4 (y1, x1, y2, x2) in image cooredinates
[scale] + # size=1
list(active_class_ids) # size=num_classes
)
return meta
anchors的生成是由get_anchors
def get_anchors(config, image_shape):
backbone_shapes = compute_backbone_shapes(config, image_shape)
anchor_cache = {}
if not tuple(image_shape) in anchor_cache:
a = generate_pyramid_anchors(
config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS,
backbone_shapes,
config.BACKBONE_STRIDES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE)
anchor_cache[tuple(image_shape)] = norm_boxes(a, image_shape[:2])
return anchor_cache[tuple(image_shape)]
compute_backbone_shapes
def compute_backbone_shapes(config, image_shape):
# 用于计算主干特征提取网络的shape
if callable(config.BACKBONE):
return config.COMPUTE_BACKBONE_SHAPE(image_shape)
# 其实就是计算P2、P3、P4、P5、P6这些特征层的宽和高
assert config.BACKBONE in ["resnet50", "resnet101"]
return np.array(
[[int(math.ceil(image_shape[0] / stride)),
int(math.ceil(image_shape[1] / stride))]
for stride in config.BACKBONE_STRIDES])
generate_pyramid_anchors
def generate_pyramid_anchors(scales, ratios, feature_shapes, feature_strides,
anchor_stride):
"""
生成不同特征层的anchors,并利用concatenate进行堆叠
"""
# Anchors
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# P2对应的scale是32
# P3对应的scale是64
# P4对应的scale是128
# P5对应的scale是256
# P6对应的scale是512
anchors = []
for i in range(len(scales)):
anchors.append(generate_anchors(scales[i], ratios, feature_shapes[i],
feature_strides[i], anchor_stride))
return np.concatenate(anchors, axis=0)
Loss函数实现
L = L c l s + L b o x + L m a s k L = L_{cls}+L_{box}+L_{mask} L=Lcls+Lbox+Lmask
L c l s L_{cls} Lcls类别损失:rpn_class和mrcnn_class的类别损失都是交叉熵损失。
L b o x L_{box} Lbox边框损失:
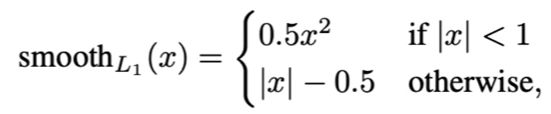
L m a s k L_{mask} Lmask遮罩掩码损失:只对mrcnn_target_class下的mrcnn_mask计算0/1交叉熵损失。
rpn_class_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: rpn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="rpn_class_loss")(
[input_rpn_match, rpn_class_logits])
rpn_bbox_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: rpn_bbox_loss_graph(config, *x), name="rpn_bbox_loss")(
[input_rpn_bbox, input_rpn_match, rpn_bbox])
class_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_class_loss")(
[target_class_ids, mrcnn_class_logits, active_class_ids])
bbox_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_bbox_loss")(
[target_bbox, target_class_ids, mrcnn_bbox])
mask_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_mask_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_mask_loss")(
[target_mask, target_class_ids, mrcnn_mask])
rpn_class_loss_graph
def rpn_class_loss_graph(rpn_match, rpn_class_logits):
"""
建议框分类损失函数
"""
# 在最后一维度添加一维度
rpn_match = tf.squeeze(rpn_match, -1)
# 获得正样本
anchor_class = K.cast(K.equal(rpn_match, 1), tf.int32)
# 获得未被忽略的样本
indices = tf.where(K.not_equal(rpn_match, 0))
# 获得预测结果和实际结果
rpn_class_logits = tf.gather_nd(rpn_class_logits, indices)
anchor_class = tf.gather_nd(anchor_class, indices)
# 计算二者之间的交叉熵
loss = K.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(target=anchor_class,
output=rpn_class_logits,
from_logits=True)
loss = K.switch(tf.size(loss) > 0, K.mean(loss), tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.switch(tf.math.is_nan(loss), tf.constant([0.0]), loss)
return loss
rpn_bbox_loss_graph
def rpn_bbox_loss_graph(config, target_bbox, rpn_match, rpn_bbox):
"""
建议框回归损失
"""
# 在最后一维度添加一维度
rpn_match = K.squeeze(rpn_match, -1)
# 获得正样本
indices = tf.where(K.equal(rpn_match, 1))
# 获得预测结果与实际结果
rpn_bbox = tf.gather_nd(rpn_bbox, indices)
# 将目标边界框修剪为与rpn_bbox相同的长度。
batch_counts = K.sum(K.cast(K.equal(rpn_match, 1), tf.int32), axis=1)
target_bbox = batch_pack_graph(target_bbox, batch_counts,
config.IMAGES_PER_GPU)
# 计算smooth_l1损失函数
loss = smooth_l1_loss(target_bbox, rpn_bbox)
loss = K.switch(tf.size(loss) > 0, K.mean(loss), tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.switch(tf.math.is_nan(loss), tf.constant([0.0]), loss)
return loss
mrcnn_class_loss_graph
def mrcnn_class_loss_graph(target_class_ids, pred_class_logits,
active_class_ids):
"""
classifier的分类损失函数
"""
# 目标信息
target_class_ids = tf.cast(target_class_ids, 'int64')
# 预测信息
pred_class_ids = tf.argmax(pred_class_logits, axis=2)
pred_active = tf.gather(active_class_ids[0], pred_class_ids)
# 求二者交叉熵损失
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=target_class_ids, logits=pred_class_logits)
# 去除无用的损失
loss = loss * pred_active
# 求平均
loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / tf.maximum(tf.reduce_sum(pred_active), 1)
return loss
mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph
def mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph(target_bbox, target_class_ids, pred_bbox):
"""
classifier的回归损失函数
"""
# Reshape
target_class_ids = K.reshape(target_class_ids, (-1,))
target_bbox = K.reshape(target_bbox, (-1, 4))
pred_bbox = K.reshape(pred_bbox, (-1, K.int_shape(pred_bbox)[2], 4))
# 只有属于正样本的建议框用于训练
positive_roi_ix = tf.where(target_class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
positive_roi_class_ids = tf.cast(tf.gather(target_class_ids, positive_roi_ix), tf.int64)
indices = tf.stack([positive_roi_ix, positive_roi_class_ids], axis=1)
# 获得对应预测结果与实际结果
target_bbox = tf.gather(target_bbox, positive_roi_ix)
pred_bbox = tf.gather_nd(pred_bbox, indices)
# Smooth-L1 Loss
loss = K.switch(tf.size(target_bbox) > 0,
smooth_l1_loss(y_true=target_bbox, y_pred=pred_bbox),
tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.mean(loss)
return loss
mrcnn_mask_loss_graph
def mrcnn_mask_loss_graph(target_masks, target_class_ids, pred_masks):
"""
交叉熵损失
"""
target_class_ids = K.reshape(target_class_ids, (-1,))
# 实际结果
mask_shape = tf.shape(target_masks)
target_masks = K.reshape(target_masks, (-1, mask_shape[2], mask_shape[3]))
# 预测结果
pred_shape = tf.shape(pred_masks)
pred_masks = K.reshape(pred_masks, (-1, pred_shape[2], pred_shape[3], pred_shape[4]))
# 进行维度变换 [N, num_classes, height, width]
pred_masks = tf.transpose(pred_masks, [0, 3, 1, 2])
# 只有正样本有效
positive_ix = tf.where(target_class_ids > 0)[:, 0]
positive_class_ids = tf.cast(tf.gather(target_class_ids, positive_ix), tf.int64)
indices = tf.stack([positive_ix, positive_class_ids], axis=1)
# 获得实际结果与预测结果
y_true = tf.gather(target_masks, positive_ix)
y_pred = tf.gather_nd(pred_masks, indices)
# shape: [batch, roi, num_classes]
loss = K.switch(tf.size(y_true) > 0,
K.binary_crossentropy(target=y_true, output=y_pred),
tf.constant(0.0))
loss = K.mean(loss)
return loss
Boundary Regularization
边界的规则化主要参考一下文章:《Toward Automatic Building Footprint Delineation From Aerial Images Using CNN and Regularization》。Mask RCNN提取出来了建筑物轮廓的掩膜,提取出来的掩膜轮廓需要进行正则化,正则化的方法如下:1. 大致调整:消除分割与多边形造成的明显错误;2. 调整线的方向和节点位置的细化。这里面包含了算法1(Algorithm1)以及算法2(Algorithm2)。
Algorithm1:大致调整
使用简单有效的规则,排除了那些最不可能出现的点、行和多边形。

具体的解释:


Algorithm2:细化算法
代码实现
实现部分具体参考我的git仓库:mask_RCNN里面的tensorflow2 分支,函数代码都放在contourprocess文件夹下,可以通过调用regularization.py文件调试运行代码。