spring boot入门与理解MVC三层架构
一、SpringMVC分层框架
分层是为了实现“高内聚,低耦合”,把问题划分开来,各个解决,易于控制,延展和分配资源,最重要有利于后期维护项目;
MVC指的是model,view,controller;
在SpringMVC编程中一般分为四层:
1.表示层:(jsp、html 主要就是界面的展示),负责前后端交互,接收前端发送的请求,然后调用service层,service层再返回数据给它,它再返回给前端。
2.控制层:(Contoller、Action)控制界面跳转,负责前后端交互,接收前端发送的请求,然后调用service层,service层再返回数据给它,它再返回给前端。
3.业务层:(Service)写主要的业务逻辑,调用DAO层,操作数据库,再对返回的数据进行各种业务上的处理,再返回给控制层。实现解耦合目的,虽然不要它也可以运行项目,但是会使项目后期的延展和维护变得困难
4.持久层:(DAO)也叫数据访问层,实现对数据库的访问。完成增删改查功能,把数据返回给service层。
5.实体层:(Model)数据库实体层,存放实体类,实现get、set方法。属性要和数据库的一样。
二、注解的使用
在SpringMVC中经常用到注解,使用注解可以极大的节省开发者的时间,下面是几个最重要的注解介绍:
@Repository:标注数据访问层,可以告诉SpringMVC这是一个数据访问层,并将其申明为一个bean,例如UserDao接口的实现类UserDaoImpl,在类上加注解@Repository("userDao"),bean的名称为userDao
@Service:标注业务层,例如UserService接口的实现类,在类上加@Service("userService"),bean的名称为userService
@Controller:控制层,在控制层类上加@Controller即可,确认其是一个控制层类
@Component:当不确定是属于哪层是用这个注解
三、实践代码演示
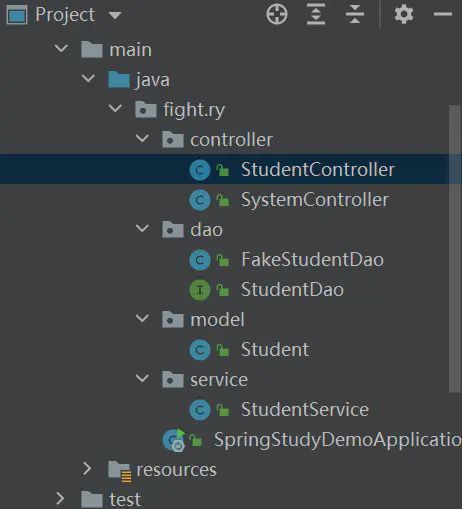
项目结构:
(1) Model 层
存放实体类,实现get、set方法,属性要和数据库的一样。
//一个model对应一张表中的字段
public class Student {
private UUID id;
private String name;
public UUID getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(UUID id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Student(UUID id, String name){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Student(){}
}(2)Dao层
数据访问层,和Model层交互。实现接口,对数据库的访问。完成增删改查功能
//定义操作数据库的方法
public interface StudentDao {
Optional selectStudentById(UUID id);
List selectAllStudents();
int insertStudent(Student student);
int upgradeStudent(Student student);
int deleteStudent(UUID id);
} 定义接口的实现,因为没有实现和数据库直接相连,就使用假数据。
@Repository
@Resource
public class FakeStudentDao implements StudentDao {
private static List database = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public Optional selectStudentById(UUID id) {
for(Student s : database){
if(s.getId().equals(id)){
return Optional.of(s);
}
}
return Optional.empty();
}
@Override
public List selectAllStudents() {
return database;
}
@Override
public int insertStudent(Student student) {
UUID id = UUID.randomUUID();
database.add(new Student(id,student.getName()));
return 1;
}
@Override
public int upgradeStudent(Student student) {
// 先找到这个要更新的student的信息
int indexToUpdate = -1;
for(int i = 0;i optionalStudent = selectStudentById(id);
if(!optionalStudent.isPresent()){
return -1;
}
database.remove(optionalStudent.get());
return 1;
}
} (3)Service层
主要的业务逻辑,调用DAO层,操作数据库,再对返回的数据进行各种业务上的处理,再返回给控制层。实现解耦合目的.
@Service
public class StudentService {
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Autowired
public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao) {
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
public List getAllStudents(){
return studentDao.selectAllStudents();
}
public int addStudent(Student student ){
return studentDao.insertStudent(student);
}
public int upgradeStudent(Student student ){
return studentDao.upgradeStudent(student);
}
public int deleteStudent(UUID id){
return studentDao.deleteStudent(id);
}
} (4) Controller层
控制界面跳转,负责前后端交互,接收前端发送的请求,然后调用service层,service层再返回数据给它,它再返回给前端。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/springboot")
public class StudentController {
private StudentService studentService;
@Autowired
public StudentController(StudentService studentService) {
this.studentService = studentService;
}
@GetMapping
public List getAllStudents() {
return studentService.getAllStudents();
}
@PostMapping
public String addStudent(@RequestBody Student student){
studentService.addStudent(student);
return "Added student";
}
@PutMapping
public String upgradeStudent(@RequestBody Student student){
studentService.upgradeStudent(student);
return "Upgrade student";
}
@DeleteMapping(path = "{id}")
// localhost:8080/springboot/123
public String deleteStudent(@PathVariable("id") UUID id){
studentService.deleteStudent(id);
return "Deleted student";
}
}