数据挖掘(作业1)
实验开始前先配置环境
以实验室2023安装的版本为例:
1、安装anaconda:(anaconda自带Python,安装了anaconda就不用再安装Python了)
下载并安装 Anaconda3-2022.10-Windows-x86_64.exe
镜像站下载地址(点击即可)
自己选择安装路径,其他使用默认选项。
(1)在“Advanced Installation Options”中,
勾选“Add Anaconda3 to my PATH environment variable.”(“添加Anaconda至我的环境变量。”)。
(2)勾选“Register Anaconda3 as my default Python 3.9”。
2、安装pycharm(在官网安装社区版就够用了)
pycharm官网
下载并安装 pycharm-community-2022.2.4.exe
3、打开cmd窗口,输入以下命令
conda create -n DMEv pip python=3.8记住DMEV所在的磁盘路径C:\Users\dell\.conda\envs\DMEV
# 如需删除环境,使用命令
conda remove -n DMEv --all安装要用到的Python库:
activate DMEv pip install numpy==1.20.0 --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/pip install matplotlib==3.3.4 --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/pip install opencv_python==4.4.0.40 --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/pip install scipy==1.6.0 --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/pip install scikit-learn==0.24.1 --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ pip install h5py==2.10.0 --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ pip install mnist==0.2.2 --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
4、测试
在Pycharm中创建项目时,DMEV所在的路径下选择python.exe(和上面配置的对应)
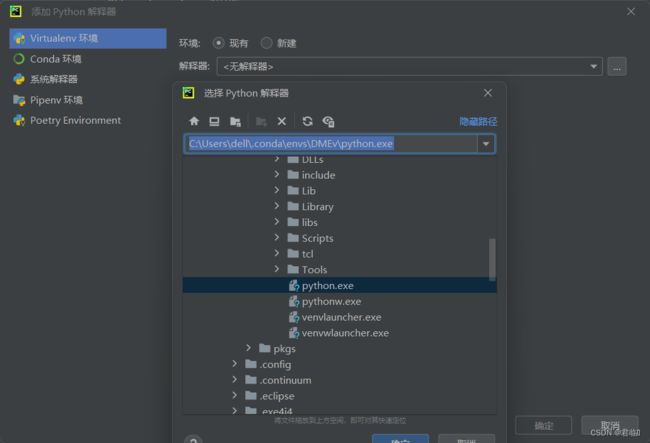
在Pycharm中新建项目,配置 interpreter,运行以下代码:(没有报错,则导入成功)
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
import mnist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 实验1 数据
一、实验目的
(1)练习和掌握python的基本使用。
(2)理解数据类型、数据质量、数据预处理、相似性和相异性度量的概念
(3)理解各种相似性和相异性度量(测度)及其含义,并且能编程计算。
二、实验内容
1编程实现任意给定两个相同维度的向量之间的欧氏距离计算函数dist_E(x,y)。
输入:两个任意k维向量x和y,其中k的值随由数据决定。如x=[3,20,3.5], y=[-3,34,7]。
import numpy as np
def dist_E(vect1, vect2):
return np.sqrt(sum(np.power((vect1-vect2),2)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
x=np.array([3,20,3.5])
y=np.array([-3,34,7])
dist=dist_E(x,y)
print(dist)
2编程实现任意给定两个相同维度的向量之间的夹角余弦相似度计算函数sim=sim_COS(x,y)。输入:两个任意k维向量x和y,其中k的值由数据决定。
import numpy as np
def sim_COS(x, y):
num = x.dot(y.T)
denom = np.linalg.norm(x) * np.linalg.norm(y)
return num / denom
if __name__ == "__main__":
x=np.array([3, 2, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0])
y=np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2])
sim=sim_COS(x,y)
print(sim)
3编程实现任意给定两个相同维度的布尔向量之间的Jaccard系数计算函数dist1=dist_Jaccard(x,y)。
import numpy as np
def sim_Jaccard(vect1, vect2):
sim=-1
if(vect1.size!=vect2.size):
print("length of input vectors must agree")
else:
ind1=np.logical_and(vect1==1,vect2==1)
ind2=np.logical_or(vect1==1,vect2==1)
x=vect1[ind1]
y=vect2[ind2]
n1=np.size(x)
n2=np.size(y)
sim=n1/n2
return sim
if __name__ == "__main__":
x=np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0])
y=np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1])
dist=sim_Jaccard(x,y)
print(dist)
4编程实现任意给定两个相同维度的布尔向量之间的简单匹配系数计算函数dist1=dist_SMC(x,y)。
import numpy as np
def sim_SMC(vect1, vect2):
sim = -1
if (vect1.size != vect2.size):
print("length of input vectors must agree")
else:
ind0 = np.logical_and(vect1 == 0, vect2 == 0)
ind1 = np.logical_and(vect1 == 1, vect2 == 1)
ind2 = np.logical_or(vect1 == 1, vect2 == 1)
x = vect1[ind1]
y = vect1[ind2]
z=vect1[ind0]
n1 = np.size(x)
n2 = np.size(y)
n3 = np.size(z)
sim = (n1+n3) / (n2+n3)
return sim
if __name__ == "__main__":
x=np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0])
y=np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1])
dist=sim_SMC(x,y)
print(dist)