数据结构与算法—排序算法
排序算法实验
1、实现选择排序、冒泡排序、合并排序、快速排序、插入排序算法;
2、以待排序数组的大小n为输入规模,固定n,随机产生20组测试样本,统计不同排序算法在20个样本上的平均运行时间;
3、分别以n=1000, n=10000, n=100,000,n=1,000,000, n=10,000,000(千万规模选做)重复2的实验
1、插入排序
基本思想:插入排序的思想时将待排序的序列分为已排序序列和未排序序列两部分,然后每次从未排序部分中取出一个元素,在已排序部分找到合适的位置插入。直到所有元素都被插入为止。
// 1、插入排序
template<class T>
void InsertSort(T R[],int nSize)
{
int i,j;
for(i = 0;i<nSize;i++)
{
int e = R[i]; //设置'哨兵'
for(j=i;j>0&&R[j-1]>e;j--){ //将大于待排序的元素往后移动
R[j] = R[j-1];
}
R[j] = e;
}
}
2、选择排序
基本思想:选择排序的主要思想是每次从待排序数组中选择一个最小的元素,方法已排序数组的末尾,以此类推,直到整个数组排序完成。
// 2、选择排序
template<class T>
void SelectSort(T R[],int nSize){
int i,j,nMin;
int pTemp; //临时中间变量
for(i=0;i<nSize-1;i++){
nMin = i; //先假设待排序区中下标为i的元素最小
//通过循环找出待排序中具有最小值的元素位置
for(j=i+1;j<=nSize-1;j++){
if(R[j]<R[nMin]){
nMin = j;
}
}
// 若待排序区中第一个元素具有最小值,则不需要进行交换
if(nMin==i){
continue;
}
//将待排序区中具有最小值的元素与第一个元素交换位置
pTemp = R[i];
R[i] = R[nMin];
R[nMin] = pTemp;
}
}
3、冒泡排序
基本思想:冒泡排序的的基本思想是通过比较相邻元素的大小,将较大的元素向数组的末端交换。首先从数组的第一个元素开始,比较相邻的两个元素,若第一个元素比第二个元素大,则交换这两个元素的位置。继续比较相邻的元素,重复上述步骤,直到将整个数组排好序。
// 3、冒泡排序
template<class T>
void BubbleSort(T R[],int nSize) {
int i,j;
int pTemp;
bool bSwap;
for(i=nSize-1;i>=0;i--){ //待排序区的终止位置
bSwap = false;
for(j=0;j<i;j++){
//若相邻两个元素次序相反,则交换他们的位置
if(R[j]>R[j+1]){
pTemp = R[j];
R[j] = R[j+1];
R[j+1] = pTemp;
bSwap = true;
}
}
//若没有出现相邻元素交换的情况,则冒泡排序结束
if(!bSwap){
break;
}
}
}
4、归并排序
基本思想:归并排序采用分治的思想,将带排序序列不断划分为子序列,直到子序列的长度为1,然后再将相邻的子序列合并,直到最终整个序列有序。
//4、归并排序
//将pSrc所指向的数组中的下标为[low,mid]的子序列与下标为[mid+1,high]的子序列归并,归并结果保存在pDst所指向数组中的相应的位置
template<class T>
void Merge(T* pSrc, T* pDst, int low, int mid, int high)
{
int i = low, j = mid + 1, k = low;
while (i <= mid && j <= high){
//比较下标为i和j的两个元素,将具有较小值的元素先取出添加到pDst所指向的数组中
if (pSrc[i] <= pSrc[j]){
pDst[k] = pSrc[i];
i++;
}
else{
pDst[k] = pSrc[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
while (i <= mid){ //当不满足j<=high条件退出循环时
pDst[k] = pSrc[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while (j <= high){ //当不满足j<=high条件退出循环时
pDst[k] = pSrc[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
//将pSRC所指向的数组中相邻的两个长度的子序列归并,归并结果保存至pDst所指的数组中
template<class T>
void MergePass(T* pSrc, T* pDst, int nsize, int nLength)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; (i + 2) * nLength < nsize; i+=2)
Merge(pSrc, pDst, i * nLength , (i + 1) * nLength-1, (i + 2) * nLength-1); //合并大小为s的相邻2段数组
if ((i + 1) * nLength < nsize) //最后一组情况为一个nLength长度的数组和一个长度的小于nLength的数组
Merge(pSrc, pDst, i * nLength , (i + 1) * nLength-1, nsize-1);
else //最后一组情况为只有一个nLength长度的数组或一个长度的小于nLength的数组
{
for (j = i * nLength ; j <=nsize; j++)
pDst[j] = pSrc[j];
}
}
//对数组R进行归并排序
template<class T>
void MergeSort(T R[], int nSize) {
int nLength;
T *MR = new T[nSize + 1]; // 动态盛情数组
T *pSrc = R, *pDst = MR, *p; //使用非递归的方式,可以避免递归栈溢出的问题(当排序输入规模超过1000000时,会发生栈溢出问题)
int i;
if (MR == NULL)
exit(1);
for (nLength = 1; nLength < nSize; nLength *= 2) {
MergePass(pSrc, pDst, nSize, nLength);
p = pSrc; // 交换指针指向
pSrc = pDst;
pDst = p;
}
if (pSrc != R) {
for (i = 0; i < nSize; i++)
R[i] = MR[i];
}
delete[]MR; // 手动删除数组,避免内存泄漏
}
5、快速排序
基本思想:快速排序是一种基于比较的排序算法。它的基本思想是选择一个枢轴,将待排序序列划分为两个子序列,其中一个子序列的元素比枢轴小,另一个序列的元素比枢轴大,然后对两个子序列递归地进行快速排序,最终得到一个有序序列。
// 5、快速排序
template<class T>
int Partition(T R[],int low,int high){
int temp;
int i=low,j=high;
temp=R[low];
while(i<j){
//冲后向前扫描
while(i<j&&R[j]>temp)
--j;
if(i<j){
R[i]=R[j];
i++;
}
//冲后向后扫描
while(i<j&&R[i]<temp)
i++;
if(i<j){
R[j]=R[i];
j--;
}
}
R[i]=temp;
return i;
}
template<class T>
void QuickSort(T R[],int low,int high){
int nBase; // 每次划分后基准元素所在的位置
if(low<high){
//以R[low]为基准对集合R[low] R[low+1] ...... R[high]进行划分
nBase = Partition(R,low,high);
//对划分后的两个子集合分别进行快速排序
QuickSort(R,low,nBase-1);
QuickSort(R,nBase+1,high);
}
}
全部代码
utils.h:
GenerateData():随机生成数据存储到文件中
Loader():读取文件中的数据
#include #include 将最终5种算法的20轮运行时间和平均运行时间保存到result.txt文件中。
用python的matplotlib包中画出对应的时间效率图。
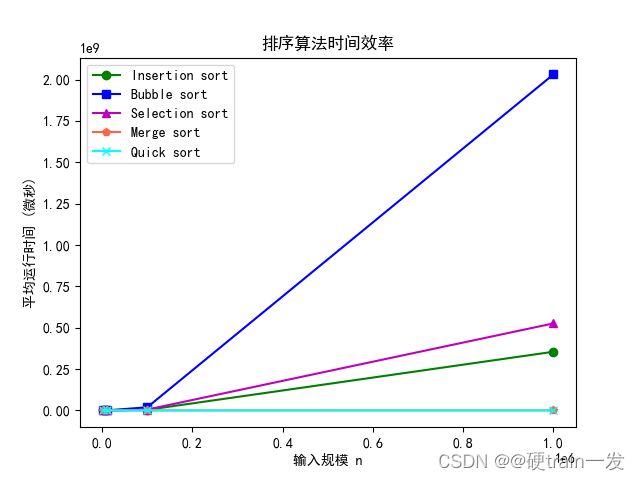
Time:2023.3.8
(好久没写博客了,这次复习了大学学过的基本算法和C++基本语法)
如果上面代码对您有帮助,欢迎点个赞!!!