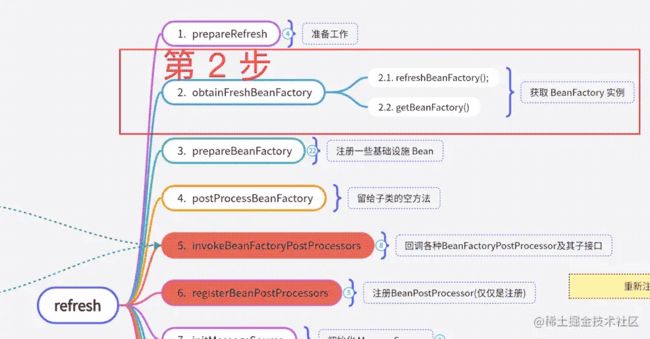
Spring容器刷新—02—obtainFreshBeanFactory
先声明一下,这篇文章是原创,不过首发在今日头条。
这次的内容是上图中的第2步,大概内容就是创建一个 BeanFactory 的实例。
BeanFactory和ApplicationContext
你要是看 spring 源码会发现 BeanFactory 的实现类相当多,而且还有各种子接口以及子接口的实现类。
ApplicationContext 是 BeanFactory,但是你不能说 BeanFactory 是 ApplicationContext。
ApplicationContext 实现了 BeanFactory 的同时增强了 BeanFactory,所谓的增强大体上指的是上图中 ApplicationContext 实现的除了 BeanFactory 接口之外的其他接口的功能。
本文仅仅列出常用的两类实现。如下图所示:
那么这么多的实现类,实际应用中到底实例化的是哪个?
这个问题嘛…… 看情况……
上图列出来两大类实现:
xml版的实现: 大体上指的是(不是绝对)AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的子类- 也就是当年我们哼哧哼哧集成
spring和servlet那个年代的事情 - 大多数不就是
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext吗?(略过)
- 也就是当年我们哼哧哼哧集成
- 注解版 的实现: 大体上指的是(不是绝对)
GenericApplicationContext的子类- Webflux 环境下一般是
AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext - Servlet 环境下一般是
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
- Webflux 环境下一般是
这里提到的实现类,无论是哪个,都是派生自 AbstractApplicationContext 的。他们都是 BeanFactory。
既然有 N 个 BeanFactory 的实现类,那么我们应用程序中到底使用的是哪一个呢? 文章末尾再说,先把我们本期的重点 obtainFreshBeanFactory() 的逻辑介绍完。
obtainFreshBeanFactory
obtainFreshBeanFactory() 的工作就是在刷新之前搞到一个 热乎的 BeanFactory 实例,涉及到的两个方法都是由子类实现的。
refreshBeanFactory(): 刷新BeanFactory,由不同的子类提供各自的实现。getBeanFactory(): 返回当前ApplicationContext中创建好的BeanFactory,简单的实现往往就是一个getter方法。
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
/**
* Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
* @return the fresh BeanFactory instance
* @see #refreshBeanFactory()
* @see #getBeanFactory()
*/
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
/**
* Subclasses must implement this method to perform the actual configuration load.
* The method is invoked by {@link #refresh()} before any other initialization work.
* <p>A subclass will either create a new bean factory and hold a reference to it,
* or return a single BeanFactory instance that it holds. In the latter case, it will
* usually throw an IllegalStateException if refreshing the context more than once.
* @throws BeansException if initialization of the bean factory failed
* @throws IllegalStateException if already initialized and multiple refresh
* attempts are not supported
*/
protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
/**
* Subclasses must return their internal bean factory here. They should implement the
* lookup efficiently, so that it can be called repeatedly without a performance penalty.
* <p>Note: Subclasses should check whether the context is still active before
* returning the internal bean factory. The internal factory should generally be
* considered unavailable once the context has been closed.
* @return this application context's internal bean factory (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalStateException if the context does not hold an internal bean factory yet
* (usually if {@link #refresh()} has never been called) or if the context has been
* closed already
* @see #refreshBeanFactory()
* @see #closeBeanFactory()
*/
@Override
public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
下面看看 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 和 GenericApplicationContext 这两种经典的实现类中 refreshBeanFactory() 和 getBeanFactory() 方法的的逻辑。
1.GenericApplicationContext系列的实现
GenericApplicationContext 对 obtainFreshBeanFactory() 的实现几乎什么也没做:
- 所有对 Bean的注册 相关的方法都委托给了内部维护的
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory。 - 该系列的实现是不支持多次刷新操作的
refreshBeanFactory()也仅仅是给内部的beanFactory初始化了一个ID。getBeanFactory()的实现更干脆: 直接将内部维护的beanFactory返回接结束了
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
// 和 BeanDefinitionRegistry 相关的方法都委托给了 `beanFactory` 这个成员变量
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
// 状态位: 当前容器是不是已经 `刷新`过了, 也就是说 GenericApplicationContext 是不支持多次刷新操作的
private final AtomicBoolean refreshed = new AtomicBoolean();
/**
* Do nothing: We hold a single internal BeanFactory and rely on callers
* to register beans through our public methods (or the BeanFactory's).
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}
@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
}
}
2.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext系列的实现
看 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 的名字就能知道,这个系列的实现是支持多次刷新操作的(不像上面说的 GenericApplicationContext 这种只支持刷新一次)。
内部也维护着一个 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory, 值得注意的是这个 beanFactory 是被 volatile 修饰的(涉及到多次刷新,频繁修改 beanFactory 的引用指向)。
对 refreshBeanFactory() 的实现分为两大步骤:
- 销毁之前可能存在的旧的
beanFactorydestroyBeans: 销毁beanFactory中所有单例(毕竟此时beanFactory都要销毁了,beanFactory中的单例肯定要顺带给销毁掉)closeBeanFactory: 实际上就是this.beanFactory = null; - 新建一个
beanFactory并做一些必要的初始化DefaultListableBeanFactory temp = createBeanFactory();: 重新创建一个BeanFactory实例temp.setSerializationId(getId());: 设置idcustomizeBeanFactory(temp);实际上就是给allowCircularReferences和allowBeanDefinitionOverriding赋值loadBeanDefinitions(temp);给新创建的BeanFactory中加载BeanDefinition- 这一步是抽象方法,不同子类的实现不同
- 但基本上都是委托各种各样的
BeanDefinitionReader给新创建的BeanFactory中添加BeanDefinition。
this.beanFactory = temp;新创建的temp上位
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
// 是否允许覆盖重复的 Bean 定义信息
@Nullable
private Boolean allowBeanDefinitionOverriding;
// 当前容器是不是要支持循环依赖(spring-boot-2.6中默认禁用)
@Nullable
private Boolean allowCircularReferences;
// 刷新之前可能已经存在的一个 beanFactory
// 每次刷新都会将当前 beanFactory 销毁重建
@Nullable
private volatile DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
/**
* This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying
* bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and
* initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle.
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) { // this.beanFactory != null: 刷新之前已经有一个 beanFactory
// 销毁旧的 beanFactory
// 1. 调用的实际是: getBeanFactory().destroySingletons();
destroyBeans();
// 2. this.beanFactory = null;
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 1. 重新创建一个 beanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
// 2.
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 3. 实际上是给 allowBeanDefinitionOverriding 和 allowCircularReferences 赋值
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 4. 这是一个抽象方法: 就是给新创建的 beanFactory 中加载 `BeanDefinition`
// BeanDefinition 的加载一般都是在子类中委托给了各种 `BeanDefinitionReader`
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
@Override
protected final void closeBeanFactory() {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.beanFactory;
if (beanFactory != null) {
beanFactory.setSerializationId(null);
this.beanFactory = null;
}
}
protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.allowCircularReferences != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
}
}
protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException, IOException;
@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.beanFactory;
if (beanFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("BeanFactory not initialized or already closed - " +
"call 'refresh' before accessing beans via the ApplicationContext");
}
return beanFactory;
}
}
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 对 getBeanFactory() 的实现也仅仅是返回了 this.beanFactory。
该使用哪个BeanFactory?
ApplicationContext 的实现类有一大堆,在应用程序中到底怎么确定使用哪个实现类的呢?下面就以传统的 Servlet 环境和 spring-boot 环境为例大概看一下流程。
Servlet环境
在传统的 Servlet 环境下,都会配置一个 ContextLoaderListener 来加载上下文。
- 获取名为
contextClass的Servlet初始化参数 - 如果能获取到
contextClass配置, 就直接反射创建一个contextClass指定的类作为ApplicationContext - 如果获取不到
contextClass配置,就走默认策略- 所谓默认策略就是从 spring-web.jar 的
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.ContextLoader.properties文件中读取默认的WebApplicationContext实现类型 - 默认的
WebApplicationContext的实现类是XmlWebApplicationContext
- 所谓默认策略就是从 spring-web.jar 的
下面是和这个过程相关的几个源码文件:
web.xml
contextClass org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderListener.java
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
// 就是在这里初始化 ApplicationContext 的
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
// 父类 ContextLoader 中的方法
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
}
ContextLoader.java
public class ContextLoader {
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
// 去 classpath 下加载 `ContextLoader.properties`
// 这个文件在 spring-web.jar 的 `org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.ContextLoader.properties`
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
// 这里就是创建具体的 ApplicationContext 实例
// 因为是 web 环境,所以创建的是 `WebApplicationContext` 的实现类的实例
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
// 这里才是确定到底创建什么类型的 `WebApplicationContext`
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
// CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM常量值就是: contextClass(在 web.xml 中配置的那个)
// 1. 如果你指定了 `contextClass` 就使用你指定的 `WebApplicationContext` 实现类
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
// 2. 如果没有指定 `contextClass` 配置就使用 `defaultStrategies` 来
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
}
ContextLoader.properties
# Default WebApplicationContext implementation class for ContextLoader. # Used as fallback when no explicit context implementation has been specified as context-param. # Not meant to be customized by application developers. # 指定默认的 `WebApplicationContext` 的实现类是: `XmlWebApplicationContext` org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
下面再简单提一下 spring-boot 环境中 ApplicationContext 的创建。
SpringBoot环境
这里特指基于 spring-boot 的 web 项目。他是通过 ApplicationContextFactory 来创建 ApplicationContext。
ApplicationContextFactory 就是一个专门用来生产 ApplicationContext 的工厂类。源码如下,具体细节会在 spring-boot 相关系列文章中提到,此处先略过。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationContextFactory {
// 省略几个 default 方法
/**
* Creates the {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext application context} for a
* {@link SpringApplication}, respecting the given {@code webApplicationType}.
* @param webApplicationType the web application type
* @return the newly created application context
*/
ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType);
}
以上就是Spring容器刷新obtainFreshBeanFactory示例详解的详细内容,更多关于Spring obtainFreshBeanFactory的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!