【STL】刷题
果然还得多做题……
unique
P1138 第 k 小整数 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
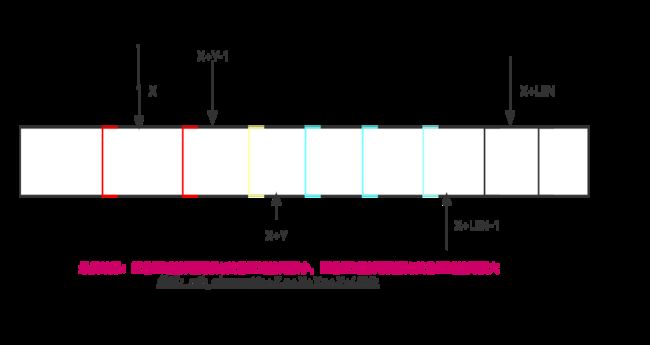
unique()是C++标准库函数里面的函数,其功能是去除相邻的重复元素(只保留一个),所以使用前需要对数组进行排序。
那它是怎么实现去重的呢?删除?
不是,它并没有将重复的元素删除,而是把重复的元素放到数组的最后面藏起来了
#include
using namespace std;
int n,k,a[10000];//定义变量和数组
int main()
{
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=0;i>a[i];
sort(a,a+n);//快排数组a
int ans=unique(a,a+n)-a;
//给数组a去重,并保留ans=去重后非伪的长度
if(k stable_sort
P5143 攀爬者 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=5e4+10;
int n;//点的个数
struct point{
int x,y,z;
}a[N];
double ans;
bool cmp(point X,point Y)
{
return X.z P5740 【深基7.例9】最厉害的学生 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
这题跟上面基本一样,但看漏了一个条件,导致有一个点一直WA
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e3+10;
int n;//n名同学
struct student{
string name;
int ch,ma,en;
int score,id; /*注意这里除了要存总分还要再存一个ID
题面上说如果有多个总分相同的学生,输出靠前的那位*/
}stu[N];
bool cmp(student a,student b)
{
if(a.score==b.score) return a.idb.score;//分数从大到小
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i>stu[i].name;
scanf("%d %d %d",&stu[i].ch,&stu[i].ma,&stu[i].en);
stu[i].score=stu[i].ch+stu[i].ma+stu[i].en;
stu[i].id=i;
}
sort(stu,stu+n,cmp);
cout< 如果最初用stable_sort就能直接AC
C++ stable_sort()用法详解 (biancheng.net)
当指定范围内包含多个相等的元素时,sort() 排序函数无法保证不改变它们的相对位置。那么,如果既要完成排序又要保证相等元素的相对位置,该怎么办呢?可以使用 stable_sort() 函数。
值得一提的是,stable_sort() 函数完全可以看作是 sort() 函数在功能方面的升级版。换句话说,stable_sort() 和 sort() 具有相同的使用场景,就连语法格式也是相同的(后续会讲),只不过前者在功能上除了可以实现排序,还可以保证不改变相等元素的相对位置。
哦吼也就是说stable_sort是sort的加强版咯
以后就用stable_sort,用它就不需要存id了
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e3+10;
int n;//n名同学
struct student{
string name;
int ch,ma,en;
int score;
}stu[N];
bool cmp(student a,student b)
{
return a.score>b.score;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i>stu[i].name;
scanf("%d %d %d",&stu[i].ch,&stu[i].ma,&stu[i].en);
stu[i].score=stu[i].ch+stu[i].ma+stu[i].en;
}
stable_sort(stu,stu+n,cmp);
cout< nth_element
C++ nth_element()用法详解 (biancheng.net)
P1923 【深基9.例4】求第 k 小的数 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
用sort直接写只有60分
C++ 的宝库:STL
#include
using namespace std;
int x[5000005],k;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=0;i 二分查找
P2249 【深基13.例1】查找 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
就是一个二分,练习一下。不多说看看stl提供的函数。
手写二分
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
const int M=1e5+10;
int n,m;//单调递增
int a[N];
int b[M];
int flag;
bool check(int mid,int y)
{
if(a[mid]>=b[y])
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
//二分查找
int l=1,r=n,res=-1;
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(check(mid,i))
{
res=mid;
r=mid-1;
if(a[mid]!=b[i]) res=-1;
}else{
l=mid+1;
}
}
printf("%d ",res);
}
return 0;
} lower_bound
STL中的二分查找 (bbsmax.com)
lower_bound(start, end, target):从在start到end区间内查找target,如果找到了,返回一个指针,如果没找到,返回第一个比它大的值的指针。
binary_search:查找某个元素 是否出现。
lower_bound:查找第一个大于或等于某个元素的 位置。 返回第一个>=的元素位置
upper_bound:查找第一个大于某个元素的 位置。 返回第一个 > 的元素位置
equal_range:查找某个元素出现的 起止位置。注意,终止位置为最后一次出现的位置加一。
返回两个元素的位置
equal_range的返回值本质上结合了lower_bound和upper_bound两者的返回值。其返回值是一对iterator i 和 j , 其中i是value可安插的第一个位置,j则是value可安插的最后一个位置。可以推演出:[i,j)中的每个元素都等价于value,而且[i, j)是[first, last)之中符合上述性质的一个最大子区间。 算法lower_bound返回该range的第一个iterator, 算法upper_bound返回该range的past-the-end iterator,算法equal_range则是 以pair的形式将两者都返回。
大佬的代码注释很详细,我就直接copy了
#include
// 边长数组,这样我们就不用担心数据装不下了
#include
using namespace std;
vector vec;
int main() {
int n, m;
int t;
cin >> n >> m;
int index;
// 向数组尾部放入数据,因为这个特性,vector也可以当成stack用
while(n--) cin >> t, vec.push_back(t);
while(m--) {
cin >> t;
// 在序列里查找目标数据
index = lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), t) - vec.begin();
// 如果目标数据找到了,输出答案,注意我们的数组下标是从0开始的
if (t == vec[index]) cout << index + 1 << ' ';
// 没找到记得输出-1哦
else cout << -1 << ' ';
}
return 0;
} 注意使用lower_bound或upper_bound时,用int类型的变量去接受位置时,lower_bound或upper_bound要减去一个v.begin();(因为函数的返回值是指针
P5745 【深基附B例】区间最大和 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
双重循环,后面三个样例直接tle了。
#include
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
const int N=4e6+10;
int a[N];
typedef pair PII;
PII p;
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
int pos1=lower_bound(a+1,a+n+1,m)-a;//查找第一个大于等于m的位置
int thissum,maxsum;
thissum=maxsum=0;
p.first=p.second=1;
for(int i=1;i<=pos1;i++)
{
thissum=0;
for(int j=i;j<=pos1;j++)
{
thissum+=a[j];
if(thissum>m)
{
continue;
}
if(thissum>maxsum)
{
p.first=i;
p.second=j;
maxsum=thissum;
}
}
}
printf("%d %d %d",p.first,p.second,maxsum);
return 0;
} 在线处理法,不能AC,所有点全WA,但我照着标答敲的几个样例答案都跟这个码答案是一样的,疯了要。。。。。。好多大佬在题解区说要用前缀和+二分,我还是跳过吧。。。。
#include
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
const int N=4e6+10;
int a[N];
typedef pair PII;
PII p;
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
int pos1=lower_bound(a+1,a+n+1,m)-a;//查找第一个大于等于m的位置
int thissum,maxsum;
thissum=maxsum=0;
p.first=p.second=1;
int temp=1;
for(int j=1;j<=pos1;j++)
{
thissum+=a[j];
if(thissum>m)//这种情况肯定是比maxsum还要大了,first直接更新到下一个开头
{
thissum=0;//开始遍历下一个子列
temp=j+1;
continue;
}
if(thissum>maxsum)
{
p.second=j;//只要大了当前这个位置就可以是最后一位
p.first=temp;
maxsum=thissum;
}
}
printf("%d %d %d",p.first,p.second,maxsum);
return 0;
} 挖个坑,以后再更。
全排列
(1条消息) C++中全排列函数next_permutation 用法_Marcus-Bao的博客-CSDN博客
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num[3]={1,2,3};
do
{
cout<