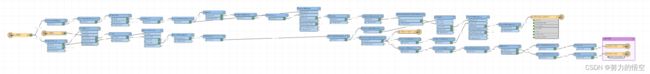
利用FME实现三调图斑地类自动提取与遥感影像自动分析监测
前言
我是一名giser也是一名开发者,刚入行时,第一件事情就是做三调图斑的矢量化,当时费劲心思一天也才只能画2平方公里左右的矢量数据,随着不断的学习和接触了各种各样的新技术,如果能把这些过程实现自动化,哪怕不能完美,都不知道能节约多少人力物力。带着这个想法,我一路研究,最终是通过fme结合深度学习模块,将整套完整流程集成到了模板内部。在介绍这套方案之前,我首先得感谢我的和尚哥,他作为FME资深大佬,在整套流程的搭建中,指导我攻破了许多难题。
一、环境搭建
1、FME
FME作为主角,在整套流程中扮演这至关重要的角色,我使用的是2021版本,搭载了较新的python3.8编译器,这点至关重要,因为深度学习的环境搭建对各种库,python版本,驱动版本和cuda版本都有限制。版本不对应,就会出现各种报错。
2、tensorflow 2.7
tensorflow是python的一个深度学习框架,我这里使用的版本是gpu-2.7版。
3、cuda11.4和对应的cudnn
这是深度学习的核心所在,也是数据能在gpu上计算的重要组件。
4、语义分割模型deeplapv3+
这是目前深度学习语义分割部分效果最好的模型之一,采用了空间卷积来提高了感受野的能力,能使提取的特征细节化,fcn等模型不具备的功能。
二、实现步骤
所有的深度学习项目都离不开5个步骤,训练数据制作,模型搭建,数据训练,模型保存,调用模型预测。
1.训练数据制作
这也是整个方案最厉害的部分,通过一个三调的基础影像,和一个三调的shp地类图斑数据,通过fme就能实现数据集的自动制作。如果没有fme,完成这一步则需要使用labelme工具一张图片一张图片一张图片的标注,这样非常的耗费人力。是我们开发者嗤之以鼻的。
首先我们得知道语义分割的训练集需要什么,我们需要准备需要训练的图片,以及对应的标注好的灰度图。然后将数据分为训练集和测试集。难点就是灰度图的制作,传统方式我们需要用labelme工具一张图片一张图片的标注,然后转换成灰度图。但是我们现在有和影像对应的shp数据,fme便能够将shp数据直接转换成栅格并和影像自动关联。
这是生成训练集的模板,只需要导入影像数据(img、tif等格式)和对应的shp数据就会直接生成训练集,其中的难点就是怎么更具三调地类生成对应的灰度图,这里我先将三调地类进行编码,用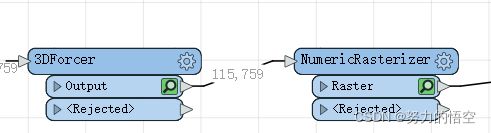
3Dforcer和NumericRasterizer两个转换器,完成灰度值的转换,需要注意的是灰度图必须是从1开始编号,再通过RasterExpressionEvaluator转换器将int8格式转换为gay8,然后通过cliiper转换器,完成裁剪和属性挂接。
生成成果如下:
用于拆分数据集的txt,上面是训练集,下面是测试集
切好片并做好编号的遥感影像数据
对应的灰度图
2.模型搭建
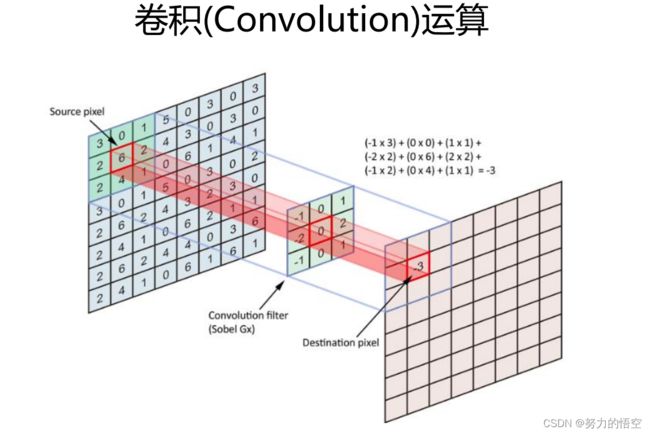
我们使用的是deeplapv3+模型,什么是deeplapv3+,传统的深度学习卷积网络,就是单纯的搭建神经网络模型,通过卷积核来对图像进行卷积运算。
并通过池化,让特征逐渐突出。这一部分也叫做下采样,encoder过程。语义分割的原理就是在完成特征提取后,通过上采样,一层一层的将特征值还原,这叫做上采样,也叫做decoder。deeplapv3+最为厉害的部分,则是在下采样的过程中使用了空洞卷积,就是卷积核中间带0的部分,这种卷积核,膨胀卷积在卷积核中插入零元素,对卷积核上采样,可避免池化层引起的信息损失,增大网络的感受野,减少特征图像尺寸的损失。如何在代码中搭建好这个模型,我们则需要对模型的全部有所认知。如下图所示
我们需要将以上模型,复刻到代码中
# 分支0
b0 = Conv2D(256, (1, 1), padding='same', use_bias=False, name='aspp0')(x)
b0 = BatchNormalization(name='aspp0_BN', epsilon=1e-5)(b0)
b0 = Activation('relu', name='aspp0_activation')(b0)
# 分支1 rate = 6 (12)
b1 = SepConv_BN(x, 256, 'aspp1',
rate=atrous_rates[0], depth_activation=True, epsilon=1e-5)
# 分支2 rate = 12 (24)
b2 = SepConv_BN(x, 256, 'aspp2',
rate=atrous_rates[1], depth_activation=True, epsilon=1e-5)
# 分支3 rate = 18 (36)
b3 = SepConv_BN(x, 256, 'aspp3',
rate=atrous_rates[2], depth_activation=True, epsilon=1e-5)
# 分支4 全部求平均后,再利用expand_dims扩充维度,之后利用1x1卷积调整通道
b4 = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
b4 = Lambda(lambda x: K.expand_dims(x, 1))(b4)
b4 = Lambda(lambda x: K.expand_dims(x, 1))(b4)
b4 = Conv2D(256, (1, 1), padding='same', use_bias=False, name='image_pooling')(b4)
b4 = BatchNormalization(name='image_pooling_BN', epsilon=1e-5)(b4)
b4 = Activation('relu')(b4)
# 直接利用resize_images扩充hw
b4 = Lambda(lambda x: tf.compat.v1.image.resize_images(x, size_before[1:3], align_corners=True))(b4)
#-----------------------------------------#
# 将五个分支的内容堆叠起来
# 然后1x1卷积整合特征。
#-----------------------------------------#
x = Concatenate()([b4, b0, b1, b2, b3])
# 利用conv2d压缩 32,32,256
x = Conv2D(256, (1, 1), padding='same', use_bias=False, name='concat_projection')(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name='concat_projection_BN', epsilon=1e-5)(x)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
x = Dropout(0.1)(x)
skip_size = tf.keras.backend.int_shape(skip1)
#-----------------------------------------#
# 将加强特征边上采样
#-----------------------------------------#
x = Lambda(lambda xx: tf.compat.v1.image.resize_images(xx, skip_size[1:3], align_corners=True))(x)
#----------------------------------#
# 浅层特征边
#----------------------------------#
dec_skip1 = Conv2D(48, (1, 1), padding='same',use_bias=False, name='feature_projection0')(skip1)
dec_skip1 = BatchNormalization(name='feature_projection0_BN', epsilon=1e-5)(dec_skip1)
dec_skip1 = Activation(tf.nn.relu)(dec_skip1)
#-----------------------------------------#
# 与浅层特征堆叠后利用卷积进行特征提取
#-----------------------------------------#
x = Concatenate()([x, dec_skip1])
x = SepConv_BN(x, 256, 'decoder_conv0',
depth_activation=True, epsilon=1e-5)
x = SepConv_BN(x, 256, 'decoder_conv1',
depth_activation=True, epsilon=1e-5)
#-----------------------------------------#
# 获得每个像素点的分类
#-----------------------------------------#
# 512,512
size_before3 = tf.keras.backend.int_shape(img_input)
# 512,512,21
x = Conv2D(num_classes, (1, 1), padding='same')(x)
x = Lambda(lambda xx:tf.compat.v1.image.resize_images(xx,size_before3[1:3], align_corners=True))(x)
x = Softmax()(x)
model = Model(img_input, x, name='deeplabv3plus')
成功搭建好模型后,我们就需要做一些基础数据处理的模块,这里是直接抄了deeplapv3+,github的源码
import math
import os
from random import shuffle
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from tensorflow import keras
from utils.utils import cvtColor, preprocess_input
class DeeplabDataset(keras.utils.Sequence):
def __init__(self, annotation_lines, input_shape, batch_size, num_classes, train, dataset_path):
self.annotation_lines = annotation_lines
self.length = len(self.annotation_lines)
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.train = train
self.dataset_path = dataset_path
def __len__(self):
return math.ceil(len(self.annotation_lines) / float(self.batch_size))
def __getitem__(self, index):
images = []
targets = []
for i in range(index * self.batch_size, (index + 1) * self.batch_size):
i = i % self.length
name = self.annotation_lines[i].split()[0]
#-------------------------------#
# 从文件中读取图像
#-------------------------------#
jpg = Image.open(os.path.join(os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "VOC2007/JPEGImages"), name + ".jpg"))
png = Image.open(os.path.join(os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "VOC2007/SegmentationClass"), name + ".png"))
#-------------------------------#
# 数据增强
#-------------------------------#
jpg, png = self.get_random_data(jpg, png, self.input_shape, random = self.train)
jpg = preprocess_input(np.array(jpg, np.float32))
png = np.array(png)
png[png >= self.num_classes] = self.num_classes
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 转化成one_hot的形式
# 在这里需要+1是因为voc数据集有些标签具有白边部分
# 我们需要将白边部分进行忽略,+1的目的是方便忽略。
#-------------------------------------------------------#
seg_labels = np.eye(self.num_classes+1 )[png.reshape([-1])]
seg_labels = seg_labels.reshape((int(self.input_shape[0]), int(self.input_shape[1]), self.num_classes+1 ))
images.append(jpg)
targets.append(seg_labels)
images = np.array(images)
targets = np.array(targets)
return images, targets
def generate(self):
i = 0
while True:
images = []
targets = []
for b in range(self.batch_size):
if i==0:
np.random.shuffle(self.annotation_lines)
name = self.annotation_lines[i].split()[0]
#-------------------------------#
# 从文件中读取图像
#-------------------------------#
jpg = Image.open(os.path.join(os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "VOC2007/JPEGImages"), name + ".jpg"))
png = Image.open(os.path.join(os.path.join(self.dataset_path, "VOC2007/SegmentationClass"), name + ".png"))
#-------------------------------#
# 数据增强
#-------------------------------#
jpg, png = self.get_random_data(jpg, png, self.input_shape, random = self.train)
jpg = preprocess_input(np.array(jpg, np.float32))
png = np.array(png)
png[png >= self.num_classes] = self.num_classes
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 转化成one_hot的形式
# 在这里需要+1是因为voc数据集有些标签具有白边部分
# 我们需要将白边部分进行忽略,+1的目的是方便忽略。
#-------------------------------------------------------#
seg_labels = np.eye(self.num_classes+1 )[png.reshape([-1])]
seg_labels = seg_labels.reshape((int(self.input_shape[0]), int(self.input_shape[1]), self.num_classes+1 ))
images.append(jpg)
targets.append(seg_labels)
i = (i + 1) % self.length
images = np.array(images)
targets = np.array(targets)
yield images, targets
def on_epoch_end(self):
shuffle(self.annotation_lines)
def rand(self, a=0, b=1):
return np.random.rand() * (b - a) + a
def get_random_data(self, image, label, input_shape, jitter=.3, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5, random=True):
image = cvtColor(image)
label = Image.fromarray(np.array(label))
h, w = input_shape
if not random:
iw, ih = image.size
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', [w, h], (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2))
label = label.resize((nw,nh), Image.NEAREST)
new_label = Image.new('L', [w, h], (0))
new_label.paste(label, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2))
return new_image, new_label
# resize image
rand_jit1 = self.rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
rand_jit2 = self.rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
new_ar = w/h * rand_jit1/rand_jit2
scale = self.rand(0.25, 2)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale*h)
nw = int(nh*new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale*w)
nh = int(nw/new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
label = label.resize((nw,nh), Image.NEAREST)
flip = self.rand()<.5
if flip:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
label = label.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
# place image
dx = int(self.rand(0, w-nw))
dy = int(self.rand(0, h-nh))
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_label = Image.new('L', (w,h), (0))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
new_label.paste(label, (dx, dy))
image = new_image
label = new_label
image_data = np.array(image, np.uint8)
#---------------------------------#
# 对图像进行色域变换
# 计算色域变换的参数
#---------------------------------#
r = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [hue, sat, val] + 1
#---------------------------------#
# 将图像转到HSV上
#---------------------------------#
hue, sat, val = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(image_data, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV))
dtype = image_data.dtype
#---------------------------------#
# 应用变换
#---------------------------------#
x = np.arange(0, 256, dtype=r.dtype)
lut_hue = ((x * r[0]) % 180).astype(dtype)
lut_sat = np.clip(x * r[1], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
lut_val = np.clip(x * r[2], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
image_data = cv2.merge((cv2.LUT(hue, lut_hue), cv2.LUT(sat, lut_sat), cv2.LUT(val, lut_val)))
image_data = cv2.cvtColor(image_data, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)
return image_data, label
3、模型训练
设置好参数,训练代码如下:这段代码是git上的源码,我将该代码封装到了fme中,在fme中就能直接进行训练。
import datetime
import os
from functools import partial
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import (EarlyStopping, LearningRateScheduler,
TensorBoard)
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD, Adam
from nets.deeplab import Deeplabv3
from nets.deeplab_training import (CE, Focal_Loss, dice_loss_with_CE,
dice_loss_with_Focal_Loss, get_lr_scheduler)
from utils.callbacks import (ExponentDecayScheduler, LossHistory,
ModelCheckpoint)
from utils.dataloader import DeeplabDataset
from utils.utils_fit import fit_one_epoch
from utils.utils_metrics import Iou_score, f_score
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices(device_type='GPU')
for gpu in gpus:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu, True)
'''
训练自己的语义分割模型一定需要注意以下几点:
1、训练前仔细检查自己的格式是否满足要求,该库要求数据集格式为VOC格式,需要准备好的内容有输入图片和标签
输入图片为.jpg图片,无需固定大小,传入训练前会自动进行resize。
灰度图会自动转成RGB图片进行训练,无需自己修改。
输入图片如果后缀非jpg,需要自己批量转成jpg后再开始训练。
标签为png图片,无需固定大小,传入训练前会自动进行resize。
由于许多同学的数据集是网络上下载的,标签格式并不符合,需要再度处理。一定要注意!标签的每个像素点的值就是这个像素点所属的种类。
网上常见的数据集总共对输入图片分两类,背景的像素点值为0,目标的像素点值为255。这样的数据集可以正常运行但是预测是没有效果的!
需要改成,背景的像素点值为0,目标的像素点值为1。
2、训练好的权值文件保存在logs文件夹中,每个epoch都会保存一次,如果只是训练了几个step是不会保存的,epoch和step的概念要捋清楚一下。
在训练过程中,该代码并没有设定只保存最低损失的,因此按默认参数训练完会有100个权值,如果空间不够可以自行删除。
这个并不是保存越少越好也不是保存越多越好,有人想要都保存、有人想只保存一点,为了满足大多数的需求,还是都保存可选择性高。
3、损失值的大小用于判断是否收敛,比较重要的是有收敛的趋势,即验证集损失不断下降,如果验证集损失基本上不改变的话,模型基本上就收敛了。
损失值的具体大小并没有什么意义,大和小只在于损失的计算方式,并不是接近于0才好。如果想要让损失好看点,可以直接到对应的损失函数里面除上10000。
训练过程中的损失值会保存在logs文件夹下的loss_%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S文件夹中
4、调参是一门蛮重要的学问,没有什么参数是一定好的,现有的参数是我测试过可以正常训练的参数,因此我会建议用现有的参数。
但是参数本身并不是绝对的,比如随着batch的增大学习率也可以增大,效果也会好一些;过深的网络不要用太大的学习率等等。
这些都是经验上,只能靠各位同学多查询资料和自己试试了。
'''
if __name__ == "__main__":
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 是否使用eager模式训练
#----------------------------------------------------#
eager = False
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# num_classes 训练自己的数据集必须要修改的
# 自己需要的分类个数+1,如2+1
#-----------------------------------------------------#
num_classes = 12
#---------------------------------#
# 所使用的的主干网络:
# mobilenet
# xception
#---------------------------------#
backbone = "mobilenet"
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 权值文件的下载请看README,可以通过网盘下载。模型的 预训练权重 对不同数据集是通用的,因为特征是通用的。
# 模型的 预训练权重 比较重要的部分是 主干特征提取网络的权值部分,用于进行特征提取。
# 预训练权重对于99%的情况都必须要用,不用的话主干部分的权值太过随机,特征提取效果不明显,网络训练的结果也不会好
# 训练自己的数据集时提示维度不匹配正常,预测的东西都不一样了自然维度不匹配
#
# 如果训练过程中存在中断训练的操作,可以将model_path设置成logs文件夹下的权值文件,将已经训练了一部分的权值再次载入。
# 同时修改下方的 冻结阶段 或者 解冻阶段 的参数,来保证模型epoch的连续性。
#
# 当model_path = ''的时候不加载整个模型的权值。
#
# 此处使用的是整个模型的权重,因此是在train.py进行加载的。
# 如果想要让模型从主干的预训练权值开始训练,则设置model_path为主干网络的权值,此时仅加载主干。
# 如果想要让模型从0开始训练,则设置model_path = '',下面的Freeze_Train = Fasle,此时从0开始训练,且没有冻结主干的过程。
# 一般来讲,从0开始训练效果会很差,因为权值太过随机,特征提取效果不明显。
#
# 网络一般不从0开始训练,至少会使用主干部分的权值,有些论文提到可以不用预训练,主要原因是他们 数据集较大 且 调参能力优秀。
# 如果一定要训练网络的主干部分,可以了解imagenet数据集,首先训练分类模型,分类模型的 主干部分 和该模型通用,基于此进行训练。
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
model_path = "model_data/deeplabv3_mobilenetv2.h5"
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# downsample_factor 下采样的倍数8、16
# 8下采样的倍数较小、理论上效果更好。
# 但也要求更大的显存
#---------------------------------------------------------#
downsample_factor = 8
#------------------------------#
# 输入图片的大小
#------------------------------#
input_shape = [512, 512]
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 训练分为两个阶段,分别是冻结阶段和解冻阶段。设置冻结阶段是为了满足机器性能不足的同学的训练需求。
# 冻结训练需要的显存较小,显卡非常差的情况下,可设置Freeze_Epoch等于UnFreeze_Epoch,此时仅仅进行冻结训练。
#
# 在此提供若干参数设置建议,各位训练者根据自己的需求进行灵活调整:
# (一)从整个模型的预训练权重开始训练:
# Init_Epoch = 0,Freeze_Epoch = 50,UnFreeze_Epoch = 100,Freeze_Train = True(默认参数)
# Init_Epoch = 0,UnFreeze_Epoch = 100,Freeze_Train = False(不冻结训练)
# 其中:UnFreeze_Epoch可以在100-300之间调整。optimizer_type = 'sgd',Init_lr = 1e-2。
# (二)从主干网络的预训练权重开始训练:
# Init_Epoch = 0,Freeze_Epoch = 50,UnFreeze_Epoch = 120,Freeze_Train = True(冻结训练)
# Init_Epoch = 0,UnFreeze_Epoch = 120,Freeze_Train = False(不冻结训练)
# 其中:由于从主干网络的预训练权重开始训练,主干的权值不一定适合语义分割,需要更多的训练跳出局部最优解。
# UnFreeze_Epoch可以在120-300之间调整。optimizer_type = 'sgd',Init_lr = 1e-2。
# (三)batch_size的设置:
# 在显卡能够接受的范围内,以大为好。显存不足与数据集大小无关,提示显存不足(OOM或者CUDA out of memory)请调小batch_size。
# 受到BatchNorm层影响,batch_size最小为2,不能为1。
# 正常情况下Freeze_batch_size建议为Unfreeze_batch_size的1-2倍。不建议设置的差距过大,因为关系到学习率的自动调整。
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 冻结阶段训练参数
# 此时模型的主干被冻结了,特征提取网络不发生改变
# 占用的显存较小,仅对网络进行微调
# Init_Epoch 模型当前开始的训练世代,其值可以大于Freeze_Epoch,如设置:
# Init_Epoch = 60、Freeze_Epoch = 50、UnFreeze_Epoch = 100
# 会跳过冻结阶段,直接从60代开始,并调整对应的学习率。
# (断点续练时使用)
# Freeze_Epoch 模型冻结训练的Freeze_Epoch
# (当Freeze_Train=False时失效)
# Freeze_batch_size 模型冻结训练的batch_size
# (当Freeze_Train=False时失效)
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
Init_Epoch = 0
Freeze_Epoch = 50
Freeze_batch_size = 6
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 解冻阶段训练参数
# 此时模型的主干不被冻结了,特征提取网络会发生改变
# 占用的显存较大,网络所有的参数都会发生改变
# UnFreeze_Epoch 模型总共训练的epoch
# Unfreeze_batch_size 模型在解冻后的batch_size
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
UnFreeze_Epoch = 50
Unfreeze_batch_size = 3
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Freeze_Train 是否进行冻结训练
# 默认先冻结主干训练后解冻训练。
# 如果设置Freeze_Train=False,建议使用优化器为sgd
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
Freeze_Train = False
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 其它训练参数:学习率、优化器、学习率下降有关
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Init_lr 模型的最大学习率
# 当使用Adam优化器时建议设置 Init_lr=1e-3
# 当使用SGD优化器时建议设置 Init_lr=1e-2
# Min_lr 模型的最小学习率,默认为最大学习率的0.01
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
Init_lr = 1e-2
Min_lr = Init_lr * 0.01
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# optimizer_type 使用到的优化器种类,可选的有adam、sgd
# 当使用Adam优化器时建议设置 Init_lr=1e-3
# 当使用SGD优化器时建议设置 Init_lr=1e-2
# momentum 优化器内部使用到的momentum参数
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
optimizer_type = "sgd"
momentum = 0.937
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# lr_decay_type 使用到的学习率下降方式,可选的有'step'、'cos'
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
lr_decay_type = 'cos'
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# save_period 多少个epoch保存一次权值,默认每个世代都保存
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
save_period = 1
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# save_dir 权值与日志文件保存的文件夹
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
save_dir = 'logs'
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# VOCdevkit_path 数据集路径
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
VOCdevkit_path = 'VOCdevkit'
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 建议选项:
# 种类少(几类)时,设置为True
# 种类多(十几类)时,如果batch_size比较大(10以上),那么设置为True
# 种类多(十几类)时,如果batch_size比较小(10以下),那么设置为False
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
dice_loss = True
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 是否使用focal loss来防止正负样本不平衡
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
focal_loss = False
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 是否给不同种类赋予不同的损失权值,默认是平衡的。
# 设置的话,注意设置成numpy形式的,长度和num_classes一样。
# 如:
# num_classes = 3
# cls_weights = np.array([1, 2, 3], np.float32)
#------------------------------------------------------------------#
cls_weights = np.ones([num_classes], np.float32)
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 用于设置是否使用多线程读取数据,1代表关闭多线程
# 开启后会加快数据读取速度,但是会占用更多内存
# 在IO为瓶颈的时候再开启多线程,即GPU运算速度远大于读取图片的速度。
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
num_workers = 3
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 获取model
#------------------------------------------------------#
model = Deeplabv3([input_shape[0], input_shape[1], 3], num_classes, backbone = backbone, downsample_factor = downsample_factor)
if model_path != '':
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 载入预训练权重
#------------------------------------------------------#
print('Load weights {}.'.format(model_path))
model.load_weights(model_path, by_name=True, skip_mismatch=True)
if focal_loss:
if dice_loss:
loss = dice_loss_with_Focal_Loss(cls_weights)
else:
loss = Focal_Loss(cls_weights)
else:
if dice_loss:
loss = dice_loss_with_CE(cls_weights)
else:
loss = CE(cls_weights)
#---------------------------#
# 读取数据集对应的txt
#---------------------------#
with open(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/ImageSets/Segmentation/train.txt"),"r",encoding='utf-8-sig') as f:
train_lines = f.readlines()
with open(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/ImageSets/Segmentation/val.txt"),"r",encoding='utf-8-sig') as f:
val_lines = f.readlines()
num_train = len(train_lines)
num_val = len(val_lines)
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 主干特征提取网络特征通用,冻结训练可以加快训练速度
# 也可以在训练初期防止权值被破坏。
# Init_Epoch为起始世代
# Freeze_Epoch为冻结训练的世代
# Epoch总训练世代
# 提示OOM或者显存不足请调小Batch_size
#------------------------------------------------------#
if True:
if Freeze_Train:
if backbone=="mobilenet":
freeze_layers = 146
else:
freeze_layers = 358
for i in range(freeze_layers): model.layers[i].trainable = False
print('Freeze the first {} layers of total {} layers.'.format(freeze_layers, len(model.layers)))
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 如果不冻结训练的话,直接设置batch_size为Unfreeze_batch_size
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
batch_size = Freeze_batch_size if Freeze_Train else Unfreeze_batch_size
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 判断当前batch_size与64的差别,自适应调整学习率
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
nbs = 64
Init_lr_fit = max(batch_size / nbs * Init_lr, 1e-4 if backbone == 'xception' else 3e-4)
Min_lr_fit = max(batch_size / nbs * Min_lr, 1e-6 if backbone == 'xception' else 3e-4)
#---------------------------------------#
# 获得学习率下降的公式
#---------------------------------------#
lr_scheduler_func = get_lr_scheduler(lr_decay_type, Init_lr_fit, Min_lr_fit, UnFreeze_Epoch)
epoch_step = num_train // batch_size
epoch_step_val = num_val // batch_size
if epoch_step == 0 or epoch_step_val == 0:
raise ValueError('数据集过小,无法进行训练,请扩充数据集。')
train_dataloader = DeeplabDataset(train_lines, input_shape, batch_size, num_classes, True, VOCdevkit_path)
val_dataloader = DeeplabDataset(val_lines, input_shape, batch_size, num_classes, False, VOCdevkit_path)
optimizer = {
'adam' : Adam(lr = Init_lr, beta_1 = momentum),
'sgd' : SGD(lr = Init_lr, momentum = momentum, nesterov=True)
}[optimizer_type]
if eager:
start_epoch = Init_Epoch
end_epoch = UnFreeze_Epoch
UnFreeze_flag = False
gen = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(partial(train_dataloader.generate), (tf.float32, tf.float32))
gen_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(partial(val_dataloader.generate), (tf.float32, tf.float32))
gen = gen.shuffle(buffer_size = batch_size).prefetch(buffer_size = batch_size)
gen_val = gen_val.shuffle(buffer_size = batch_size).prefetch(buffer_size = batch_size)
time_str = datetime.datetime.strftime(datetime.datetime.now(),'%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S')
log_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, "loss_" + str(time_str))
loss_history = LossHistory(log_dir)
#---------------------------------------#
# 开始模型训练
#---------------------------------------#
for epoch in range(start_epoch, end_epoch):
#---------------------------------------#
# 如果模型有冻结学习部分
# 则解冻,并设置参数
#---------------------------------------#
if epoch >= Freeze_Epoch and not UnFreeze_flag and Freeze_Train:
batch_size = Unfreeze_batch_size
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 判断当前batch_size与64的差别,自适应调整学习率
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
nbs = 64
Init_lr_fit = max(batch_size / nbs * Init_lr, 1e-4 if backbone == 'xception' else 3e-4)
Min_lr_fit = max(batch_size / nbs * Min_lr, 1e-6 if backbone == 'xception' else 3e-4)
#---------------------------------------#
# 获得学习率下降的公式
#---------------------------------------#
lr_scheduler_func = get_lr_scheduler(lr_decay_type, Init_lr_fit, Min_lr_fit, UnFreeze_Epoch)
for i in range(len(model.layers)):
model.layers[i].trainable = True
epoch_step = num_train // batch_size
epoch_step_val = num_val // batch_size
if epoch_step == 0 or epoch_step_val == 0:
raise ValueError("数据集过小,无法继续进行训练,请扩充数据集。")
train_dataloader.batch_size = batch_size
val_dataloader.batch_size = batch_size
gen = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(partial(train_dataloader.generate), (tf.float32, tf.float32))
gen_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(partial(val_dataloader.generate), (tf.float32, tf.float32))
gen = gen.shuffle(buffer_size = batch_size).prefetch(buffer_size = batch_size)
gen_val = gen_val.shuffle(buffer_size = batch_size).prefetch(buffer_size = batch_size)
UnFreeze_flag = True
lr = lr_scheduler_func(epoch)
K.set_value(optimizer.lr, lr)
fit_one_epoch(model, loss, loss_history, optimizer, epoch, epoch_step, epoch_step_val, gen, gen_val,
end_epoch, f_score(), save_period, save_dir)
train_dataloader.on_epoch_end()
val_dataloader.on_epoch_end()
else:
start_epoch = Init_Epoch
end_epoch = Freeze_Epoch if Freeze_Train else UnFreeze_Epoch
model.compile(loss = loss,
optimizer = optimizer,
metrics = [f_score()])
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 训练参数的设置
# logging 用于设置tensorboard的保存地址
# checkpoint 用于设置权值保存的细节,period用于修改多少epoch保存一次
# lr_scheduler 用于设置学习率下降的方式
# early_stopping 用于设定早停,val_loss多次不下降自动结束训练,表示模型基本收敛
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
time_str = datetime.datetime.strftime(datetime.datetime.now(),'%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S')
log_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, "loss_" + str(time_str))
logging = TensorBoard(log_dir)
loss_history = LossHistory(log_dir)
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(os.path.join(save_dir, "ep{epoch:03d}-loss{loss:.3f}-val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5"),
monitor = 'val_loss', save_weights_only = True, save_best_only = False, period = save_period)
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta = 0, patience = 10, verbose = 1)
lr_scheduler = LearningRateScheduler(lr_scheduler_func, verbose = 1)
callbacks = [logging, loss_history, checkpoint, lr_scheduler]
if start_epoch < end_epoch:
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
model.fit_generator(
generator = train_dataloader,
steps_per_epoch = epoch_step,
validation_data = val_dataloader,
validation_steps = epoch_step_val,
epochs = end_epoch,
initial_epoch = start_epoch,
use_multiprocessing = True if num_workers > 1 else False,
workers = num_workers,
callbacks = callbacks
)
#---------------------------------------#
# 如果模型有冻结学习部分
# 则解冻,并设置参数
#---------------------------------------#
if Freeze_Train:
batch_size = Unfreeze_batch_size
start_epoch = Freeze_Epoch if start_epoch < Freeze_Epoch else start_epoch
end_epoch = UnFreeze_Epoch
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 判断当前batch_size与64的差别,自适应调整学习率
#-------------------------------------------------------------------#
nbs = 64
Init_lr_fit = max(batch_size / nbs * Init_lr, 1e-4 if backbone == 'xception' else 3e-4)
Min_lr_fit = max(batch_size / nbs * Min_lr, 1e-6 if backbone == 'xception' else 3e-4)
#---------------------------------------#
# 获得学习率下降的公式
#---------------------------------------#
lr_scheduler_func = get_lr_scheduler(lr_decay_type, Init_lr_fit, Min_lr_fit, UnFreeze_Epoch)
lr_scheduler = LearningRateScheduler(lr_scheduler_func, verbose = 1)
callbacks = [logging, loss_history, checkpoint, lr_scheduler]
for i in range(len(model.layers)):
model.layers[i].trainable = True
model.compile(loss = loss,
optimizer = optimizer,
metrics = [f_score()])
epoch_step = num_train // batch_size
epoch_step_val = num_val // batch_size
if epoch_step == 0 or epoch_step_val == 0:
raise ValueError("数据集过小,无法继续进行训练,请扩充数据集。")
train_dataloader.batch_size = Unfreeze_batch_size
val_dataloader.batch_size = Unfreeze_batch_size
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
model.fit(
generator = train_dataloader,
steps_per_epoch = epoch_step,
validation_data = val_dataloader,
validation_steps = epoch_step_val,
epochs = end_epoch,
initial_epoch = start_epoch,
use_multiprocessing = True if num_workers > 1 else False,
workers = num_workers,
callbacks = callbacks
)
4、模型使用
fme在模型预测中还扮演了一个非常重要的角色,第一个就是将预测后的灰度图进行地理坐标配准,第二个是将配准后的灰度图转换为对应的矢量,并将地类属性附加到矢量内部。
这里运用了RasterToPolygonCoercer这个转换器,可以根据灰度值,自动生成面,并将灰度值属性保存到label字段内部,这个转换器直接让整套流程赋予了灵魂。
接下来是效果展示,可以看到图斑被精确的矢量化了出来。
由于训练集太少和设备限制(我的笔记本显卡3070ti),分类效果和精度没能达到最佳。但是能够证明整套方案是没得任何问题,并且在三调图斑地类自动提取与遥感影像自动分析监测的方向能够发挥非常强大的作用,比arcgispro和envi内置的影像分类更加强大。
总结
几个月没更新了,一致在学习、调试、完善这个研究,感谢和尚哥的支援。