Acwing 第二讲 数据结构 STL
文章目录
- 1.单链表
-
- AcWing 826. 单链表
- 2. 双链表
-
- AcWing 827. 双链表
- 3. 栈
-
- AcWing 828. 模拟栈
- AcWing 3302. 表达式求值
- 4. 队列
-
- AcWing 829. 模拟队列
- 5. 单调栈
-
- AcWing 830. 单调栈
- 6.单调队列
-
- AcWing 154. 滑动窗口
- 7.KMP
-
- AcWing 831. KMP字符串
- 8. Trie
-
- AcWing 835. Trie字符串统计
- AcWing 142. 前缀统计
- AcWing 143. 最大异或对
- 9. 并查集
-
- AcWing 836. 合并集合
- AcWing 837. 连通块中点的数量
- AcWing 240. 食物链[diff]
- 10. 堆
-
- AcWing 838. 堆排序
- AcWing 839. 模拟堆
- 11 . 哈希表
-
- AcWing 840. 模拟散列表
- AcWing 841. 字符串哈希
- 12. STL
1.单链表
AcWing 826. 单链表
AcWing 826. 单链表
idx万岁
#include ne[0] = -1 存放头结点
#include 2. 双链表
AcWing 827. 双链表
AcWing 827. 双链表
#include 简化版
#include 3. 栈
AcWing 828. 模拟栈
AcWing 828. 模拟栈
#include #include AcWing 3302. 表达式求值
AcWing 3302. 表达式求值
- 核心思想就是建立表达式二叉树
- 父节点的运算符优先级低于子节点的运算符优先级
- 下面算完往上面运算代表该子树已经算完
- 遍历表达式,if当前运算符优先级 >= 父节点的运算符优先级,那么就先算栈内的eval(),直到栈内的运算符优先级 < 当前运算符优先级
- 同级运算从左向右计算[重要],先算乘除后算加减
#include 4. 队列
AcWing 829. 模拟队列
AcWing 829. 模拟队列
#include 5. 单调栈
AcWing 830. 单调栈
AcWing 830. 单调栈
单调栈:找一个距离该数离他最近且比他大或者小的数
栈可以保持最近
如果栈顶元素比 当前元素小,那么当前元素是距离右边最近的且最小的元素,当前元素入栈
如果栈顶元素比 当前元素大,那么栈里面的元素比当前元素大的元素都要删除
#include #include 6.单调队列
AcWing 154. 滑动窗口
AcWing 154. 滑动窗口
if(a[i] >= a[j] && i < j) delete a[i];
队列里面存放下标,可以判断队首元素是否出队列
#include 7.KMP
AcWing 831. KMP字符串
AcWing 831. KMP字符串
----------题解----------

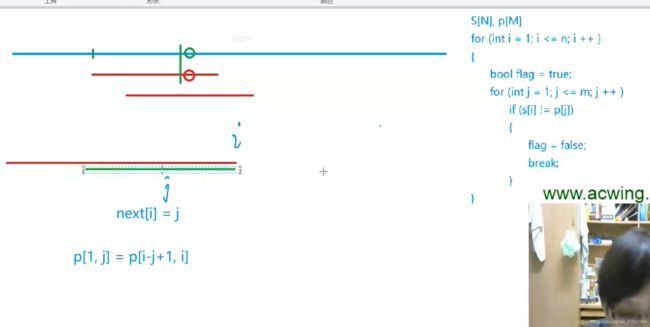
最长公共前后缀
next[1] = 0 肯定
so i = 2开始比较

#include 8. Trie
AcWing 835. Trie字符串统计
AcWing 835. Trie字符串统计
#include AcWing 142. 前缀统计
AcWing 142. 前缀统计
#include AcWing 143. 最大异或对
AcWing 143. 最大异或对
#include 9. 并查集

在找根节点的过程中,只要找到根节点,那么在寻找根节点的路径中节点的所有值都 = 父节点下标路径压缩
那么查找时间复杂度 ~= O(1)
AcWing 836. 合并集合
AcWing 836. 合并集合
没有路径压缩超时
#include 压缩一下
// int get(int x){ // 找 fa[x] == x 的下标 x
// while(fa[x] != x) x = fa[x];
// return x;
// }
int get(int x){ //找父节点的下标 fa[x] 存放的是父节点的下标, x 只是下标,x都不一样
if(fa[x] != x) fa[x] = get(fa[x]);
return fa[x];
}
AcWing 837. 连通块中点的数量
AcWing 837. 连通块中点的数量
#include AcWing 240. 食物链[diff]
AcWing 240. 食物链
#include 10. 堆
AcWing 838. 堆排序
AcWing 838. 堆排序
#include AcWing 839. 模拟堆
AcWing 839. 模拟堆
堆的下表要从1开始 hp[++si] = val
方便 down() 和 up() 操作
#include 11 . 哈希表
AcWing 840. 模拟散列表
AcWing 840. 模拟散列表
mod 取 质数
for(int i = 100000; ; i++){
bool flag = true;
for(int j = 2; j*j <= i; j++){
if(i % j == 0){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
cout << i <<endl;
break;
}
}
拉链法,邻接表
#include #include AcWing 841. 字符串哈希
AcWing 841. 字符串哈希
#include 








