matplotlib 到底该如何控制legend的位置?
matplotlib版本号:3.1.0
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
print(matplotlib.version) # 3.1.0
在使用matplotlib做图时,总免不了和图例(legend)打交道,那图例到底该放在哪?如何放到指定的位置?(本文只讨论legend的坐标系为axes的情况)
关于如何控制legend的位置,官网介绍了2个参数:loc 与 bbox_to_anchor 。
本篇文章看看loc如何控制legend的位置的,通过官网文档可以很容易得知loc参数有2种类型:
1.str类型,为我们准备了9种位置(可参考图1),示例:loc = 'upper left’
首先legend是一个bbox类型,是一个由4条边框围成的区域,轴域(axes)也是由4条边框围成的区域(x, y 轴,上边缘线,右边缘线),当loc为str类型时,表示 legend中str所代表的位置与轴域(axes)中str所代表的位置重合。
[‘upper left’ , ‘upper center’, ‘upper right’,
‘center left’, ‘center’, ‘center right’,
‘lower left’, ‘lower center’, ‘lower right’]
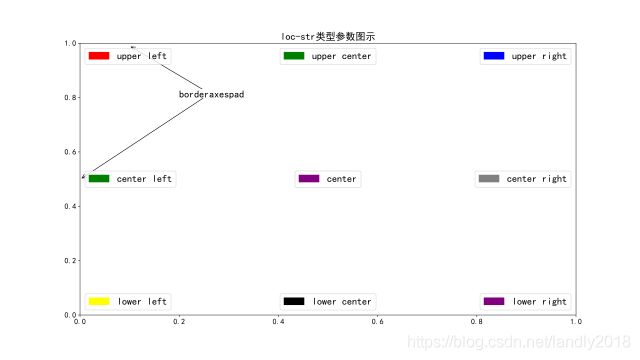
语法如下:
.legend(loc='center') # 通过设置loc = 'one of nine locations'即可
上图完整代码如下:
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
upper_left = mpatches.Patch(color='red', label='upper left')
upper_right = mpatches.Patch(color='blue', label='upper right')
lower_right = mpatches.Patch(color='purple', label='lower right')
lower_left = mpatches.Patch(color='yellow', label='lower left')
center_left = mpatches.Patch(color='green', label='center left')
center_right = mpatches.Patch(color='gray', label='center right')
lower_center = mpatches.Patch(color='black', label='lower center')
upper_center = mpatches.Patch(color='green', label='upper center')
center = mpatches.Patch(color='purple', label='center')
patches = [upper_left, upper_right, lower_left, lower_right, center_left, center_right, lower_center,
upper_center,center]
location = ['upper left', 'upper right', 'lower left', 'lower right', 'center left', 'center right',
'lower center', 'upper center', 'center']
lst = []
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16, 9))
for patch, loc in zip(patches, location):
lst.append(ax.legend(handles=[patch], loc=loc, fontsize=18))
for i in range(len(patches)):
plt.gca().add_artist(lst[i])
ax.annotate('borderaxespad', xy=(0.1, 0.99), xytext=(0.2, 0.8), fontsize=18,
arrowprops={'arrowstyle':'->'})
ax.annotate('', xy=(0.001, 0.5), xytext=(0.25, 0.8), fontsize=18,arrowprops={'arrowstyle':'->'})
ax.set_title('loc-str类型参数图示', fontsize=18, fontweight='bold')
ax.tick_params(labelsize=14)
# 至于那些缝隙,可以通过设置borderaxespad=0消除
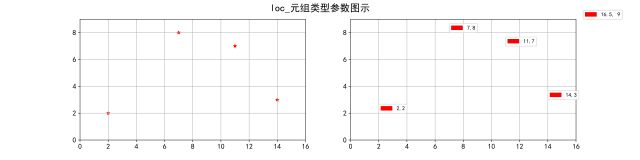
2. 一对浮点数(x,y),保存在元组中. 示例:loc = (0, 0)
(x, y):此种形式是将legend的左下角放置在点(x, y)上,可参考下图:
左图中红点坐标分别为(2,2), (7,8) , (11,7) , (14,5)
通过左右两张图比较,很容易看出,右图中legend的左下角与点(x, y)重合。
注意:当使用loc=(x,y)时,x, y并不是轴域中实际的x, y的值,而是将x轴, y轴分别看成1, 即:(m/(x_max-x_min), n/(y_max-y_min))(归1处理);
在绘制上图时,其中xlim=(0, 16), ylim=(0, 9),所以如果将legend放置到点(2, 2)上,那loc实际要写成:
.legend(loc=(2/16, 2/9))
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
fig, axes= plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(16, 4))
axes[0].set_xlim(0, 16)
axes[0].set_ylim(0, 9)
axes[1].set_xlim(0, 16)
axes[1].set_ylim(0, 9)
axes[0].grid()
axes[1].grid()
# 接下来利用(x, y)将legend分别放在图中(2,2) , (7,8), (11, 7), (14, 3)
axes[0].scatter(x=[2, 7, 11, 14, 16.5], y=[2, 8, 7, 3, 9], color='red', marker='*')
#
patch1 = mpatches.Patch(color='red', label='2,2')
patch2 = mpatches.Patch(color='red', label='7,8')
patch3 = mpatches.Patch(color='red', label='11,7')
patch4 = mpatches.Patch(color='red', label='14,3')
patch5 = mpatches.Patch(color='red', label='16.5, 9')
patches = [patch1, patch2, patch3, patch4, patch5]
# 可以看到设置x,y值时,分别进行了归1的处理
location = [(2/16,2/9), (7/16,8/9), (11/16,7/9), (14/16,3/9), (16.5/16, 9/9)]
#
lst = []
for pathc, loc in zip(patches, location):
lst.append(axes[1].legend(handles=[pathc], loc=loc))
#
for i in range(len(patches)):
axes[1].add_artist(lst[i])
#
fig.suptitle('loc_元组类型参数图示', fontweight='bold', fontsize=18)
axes[1].tick_params(labelsize=13)
axes[0].tick_params(labelsize=13)
3.总结,loc参数比较简单,提供了2种控制legend位置的格式
1)9个固定的位置(图1),loc=str,是设置legend的’str’位置与轴域(axes)的’str’位置重合
2)通过给定legend左下角的坐标,设置legend的位置(图2),无论是图内还是图外,只要小心设置,终将会把legend放到你想放的位置。
下篇文章将会介绍bbox_to_anchor,比较有意思的是bbox_to_anchor,其中weight,height又代表什么意思?和loc又会擦出怎样的火花?
水平有限,若有错误,欢迎指正,欢迎交流
参考:
https://matplotlib.org/api/legend_api.html?highlight=legend#module-matplotlib.legend