Codeforces Round #799 (Div. 4) 赛后总结
文章目录
-
-
- A. Marathon
- B. All Distinct
- C.Where's the Bishop?
- D. The Clock
- E.Binary Deque
- F.3SUM
- G.2^Sort
- H.Gambling
-
A. Marathon
思路:将 a n s ans ans 初始化为 3 3 3,剩下三个数跟第一个数比,若第一个数比剩下的数大则 ans -- ,最终剩下的数即为答案!
Code:
#include B. All Distinct
思路:我们可以用 s e t set set 将数组内的元素去重,故设数组的大小为 n n n,所有出现过元素所构成的集合的大小是 s e t . s i z e ( ) set.size() set.size(),那么所有重复元素所构成集合的大小为 n − s e t . s i z e ( ) n-set.size() n−set.size(),我们可以不断的在所有重复元素所构成集合中一直消去两个元素,直到该集合内的元素为 0 0 0。此时我们开始分类讨论:
- 当 n − s e t . s i z e ( ) n-set.size() % 2 = 0 n−set.size() 时,此时可以说明所有重复元素所构成集合中的元素刚好可以被消耗殆尽,此时答案就是 s e t . s i z e ( ) set.size() set.size()。
- 当 n − s e t . s i z e ( ) n-set.size() % 2 = 1 n−set.size() 时,此时可以说明所有重复元素所构成集合中的元素被消耗殆尽时,还要添上1个才能使得被变化的集合中无重复元素,所以答案就是 s e t . s i z e ( ) − 1 set.size()-1 set.size()−1。
Code:
#include C.Where’s the Bishop?
思路:反正图也不大,直接遍历一下全图,找一下该点的四个方位是否都是#,若是则该位置就是答案,返回这个位置的下表即可!
Code:
#include D. The Clock
思路:把所有数全部化成分钟,然后预处理一下从0~1439中所有的回文时间,最后以 x x x 为偏移量,以所给的开始时间为初始时间,直到第二次循环到开始时间的时候停止,统计一下这段时间内的回文时间!
Code:
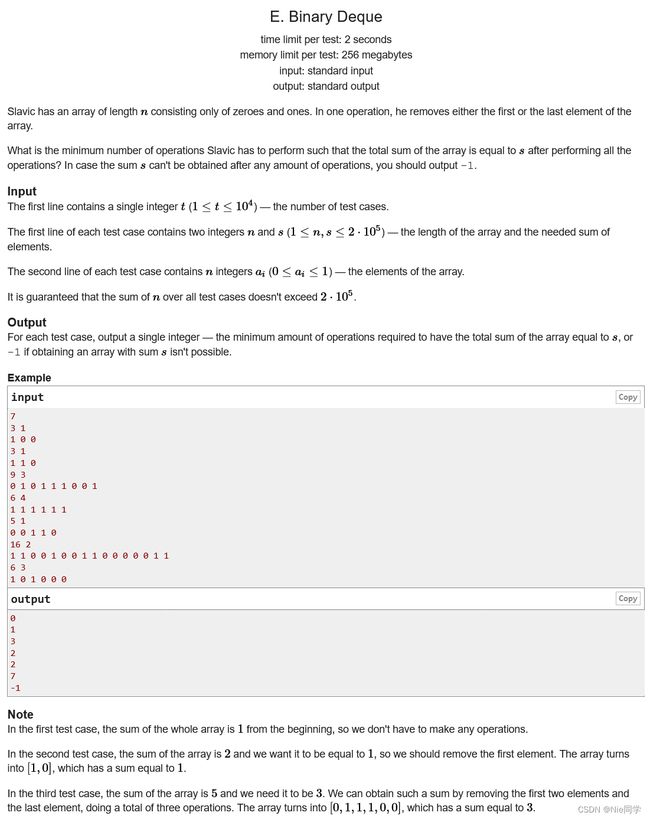
#include E.Binary Deque
思路:对于该题目来说我们只需要采用双指针,找出最长包含 s s s 个1的子序列,最终答案就是总长度-最长包含 s s s 个1的子序列的长度。
Code:
#include F.3SUM
思路:
-
先进行初始化操作,将所有可能构成尾数为 3 3 3 的3个数变为字符串送入set中。
-
然后将所有数的最后一位截取出来送入 a a a 数组里面(这样可保证所有数字都在0~9这个区间上),且保证 a a a 数组里面相同的数字不超过 3 3 3 个(因为在0~9这个区间内,最多可以凑出3,13,23这三个数字,凑出3只需要最多3个1,凑出13也最多只需要2个相同的数,凑出23也最多只需要2个相同的数,至此我们就把整个数组的范围压缩到27以内!)
-
最后三层遍历看一下这三组所构成的字符串在不在set中,如果在则直接输出
YES,若遍历完整个数组都没有的话,则输出NO。
Code:
#include G.2^Sort
思路:
- 我们只需要额外开辟一个 b b b 数组,来记录是否
a[i] < a[i + 1] * 2。 - 然后从0到 k k k 将所有的 b b b 数组元素加起来,记做 s u m sum sum。
- 若
sum == k,则答案ans ++。 - 然后再次从 k k k 开始到 n − 1 n - 1 n−1,每一次 s u m sum sum 加上当前的 b b b,然后再减去 k k k 之前的 b b b ,若
sum == k的话,则答案ans ++。
Code:
#include H.Gambling
思路:即找出一个区间使得众数的个数要比非众数的个数要大
- 先将所有相同的数字的下标存入一个数组中去。
- 然后遍历一下每个元素所存入的数组 a a a,算出在数组 a a a 中,值为 x x x 的元素减去值不为 x x x 元素的差,即 i − j + 1 − ( a i − a j − ( i − j + 1 ) ) i-j+1-(a_i-a_j-(i - j + 1)) i−j+1−(ai−aj−(i−j+1)),我们整理一下 2 i − a i − 1 + a j − 2 j 2i-a_i-1+a_j-2j 2i−ai−1+aj−2j,不变的是 2 i − a i − 1 2i-a_i-1 2i−ai−1,变化的是 a j − 2 j a_j-2j aj−2j我们记为 t t t 最后使得 t t t 最大,顺便记录一下左端点 a i a_i ai。
Code:
#include