Mybatis源码分析(四)Mapper文件的解析
目录
- 一 Mapper的使用
- 二 MapperElement的解析
- 三 解析cache-ref节点
- 四 解析Cache节点
- 五 解析ParameterMap节点
- 六 解析ResultMap节点
- 七 解析Sql节点
- 八 处理各个数据库操作语句
系列文章:
| 文章 | 状态 | 时间 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (一)Mybatis 基本使用 | 已复习 | 2022-12-14 | 对Mybtais的基本使用,能够开发 |
| (二)Mybatis-config.xml的初始化 | 已复习 | 2023-02-10 | 对我们编写的mybatis配置文件的解析 |
| (三)SqlSessionFactory的初始化 | 已复习 | 2023-02-11 | SqlSession会话工厂的初始化 |
| (四)Mapper文件的解析 | 已复习 | 2023-02-12 | 主要对我们编写的Mapper.xml进行解析 |
| (五)SqlSession的创建 | 已复习 | 2023-02-13 | 主要介绍构建DefaultSqlSessionFactory |
| (六)Mapper的接口代理 | 已复习 | 2023-02-14 | 如何通过动态代理来执行我们编写的方法 |
| (七)MapperMethod的INSERT分析 | 已复习 | 2023-02-15 | 通过代理对象来执行Insert语句,返回结果 |
| (八)MapperMethod的Select分析 | 已复习 | 2023-02-16 | 通过代理对象来执行Select语句,返回结果 |
| (九)Mybatis的PreparedStatement | 已复习 | 2023-02-17 | 预处理语句的常见,以及与数据库打交道 |
| (十)Mybatis的结果隐射 | 已复习 | 2023-02-18 | 数据库结果与实体类对象的转换 |
| (十一)Mybatis中的缓存 | 计划中 | – | Mybatis中一级缓存与二级缓存 |
| (十二)Mybatis中的插件开发 | 计划中 | – | Mybatis中的插件运行机制与开发 |
| (十三)Mybatis中的四大组件梳理 | 计划中 | – | Mybatis中的四大组件的梳理 |
| (十四)Mybatis中的设计模式梳理 | 计划中 | – | Mybatis中设计模式的整理 |
| (十五)Spring-Mybatis整理 | 计划中 | – | Spring与Mybatis整合 |
| (十六)Mybatis疑惑总结 | 计划中 | – | 我遇到的疑惑与问题 |
官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 简介
在上篇文章末尾,我们解析Mapper 文件,这篇文件我们来看看Mapper的详细解析过程,相对于其他文件的解析Mapper文件的解析过程比较复杂,所以单独用一篇文件来解析。废话不多说我们来看看。
学习的知识?
Mybatis的SQL映射语句的配置方式- 接口的动态代理
XMLMapperBuilder类来解析Mapper.xml文件
过程梳理
- 首先判断我们的配置方式,
package, resource、url、class - 如果是包扫描,通过配置的
name属性获取包路径,通过configuration中的映射注册表注册接口方法,生成代理接口对象,配置到configuration中的MapperRegistry中 - 如果是其他三种方式,只能选择其中一种方式进行配置,通过
XMLMapperBuilder来解析配置文件 - 首先通过
Resources类来加载配置文件,创建XMLMapperBuilder对接进行对XML文件的处理 - 接着调用
configurationElement方法,注意必须以/mapper开头的XML文件,开始解析文件 - 第一步解析我们命名的表空间,
namespace,并设置当前命名空间 - 第二步解析
cache-ref元素,主要为了共享缓存,具体参考官网 - 第三步解析
- 第四步解析
/mapper/parameterMap元素,未来版本会移除 - 第五步解析
/mapper/resultMap元素,主要完成数据库对象与JAVA对象的类型转换 - 第六步解析
/mapper/sql元素,主要是我们定义的一些可以复用的Sql片段 - 第七步解析
select|insert|update|delete元素,主要解析我们编写的DDL语句,通过XMLStatementBuilder类的帮助下解析各种语句,生成MappedStatement隐式语句 - 最后完成了
Configuration类的全部初始化,方便后面参数配置的调用
一 Mapper的使用
参考官方网站:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html#mapper
既然 MyBatis 的行为已经由上述元素配置完了,我们现在就要来定义 SQL 映射语句了。 但首先,我们需要告诉 MyBatis 到哪里去找到这些语句。 在自动查找资源方面,Java 并没有提供一个很好的解决方案,所以最好的办法是直接告诉 MyBatis 到哪里去找映射文件。 你可以使用相对于类路径的资源引用,或完全限定资源定位符(包括 file:/// 形式的 URL),或类名和包名等。
mappers 标签下有许多 mapper 标签,每一个 mapper 标签中配置的都是一个独立的映射配置文件的路径,配置方式有以下几种。
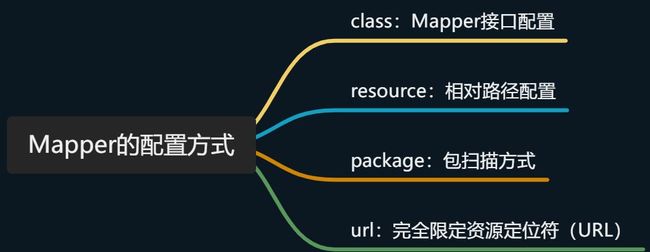
Mapper的接口配置
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.shu.mappers.UserMapper"/>
......
</mappers>
**注意:**这种方式必须保证接口名(例如UserMapper)和xml名(UserMapper.xml)相同,还必须在同一个包中。因为是通过获取mapper中的class属性,拼接上.xml来读取UserMapper.xml,如果xml文件名不同或者不在同一个包中是无法读取到xml的。
相对路径进行配置
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/shu/mappers/UserMapper.xml"/>
......
</mappers>
**注意:**这种方式不用保证同接口同包同名。但是要保证xml中的namespase和对应的接口名相同。
接口所在配置(包扫描方式)
<mappers>
<package name="com.shu.mappers"/>
</mappers>
这种方式和第一种方式要求一致,保证接口名(例如UserMapper)和xml名(UserMapper.xml)相同,还必须在同一个包中。
**注意:**以上所有的配置都要保证xml中的namespase和对应的接口名相同。
使用完全限定资源定位符(URL)
<mappers>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
二 MapperElement的解析
XMLConfigBuilder
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
- 我们可以看到mapperElement方法来解析Mappers节点信息,其中就有上门的四种方法,package,url,class,resource来解析我们的Mappers节点信息。
/**
* 解析mappers节点,例如:
*
*
* @param parent mappers节点
* @throws Exception
*/
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 处理mappers的子节点,即mapper节点或者package节点
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { // package节点
// 取出包的路径,其实就是包路径com.shu.mapper
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
// 全部加入Mappers中
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
// resource、url、class这三个属性只有一个生效
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// resource的解析方式
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
// 获取文件的输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 使用XMLMapperBuilder解析Mapper文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
}
// url 解析方式
else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
// 从网络获得输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
// 使用XMLMapperBuilder解析Mapper文件
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
}
// class 解析方式
else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
// 配置的不是Mapper文件,而是Mapper接口
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
}
// 都没有的话,扔出异常
else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
在 MyBatis 中,共有四种加载映射文件或信息的方式。第一种是从文件系统中加载映射文件;第二种是通过 URL 的方式加载和解析映射文件;第三种是通过 mapper 接口加载映射信息,映射信息可以配置在注解中,也可以配置在映射文件中。最后一种是通过包扫描的方式获取到某个包下的所有类,并使用第三种方式为每个类解析映射信息。
- 首先我们来看看包扫描的方式?交给映射器注册进行注册?,我们的目的通过我们的配置文件比如:com.shu.mapper获取到该包下面的接口信息?
Configuration
// 全部加入Mappers中
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
mapperRegistry.addMappers(packageName);
}
- 我们可以看到调用了mapperRegistry#addMappers()方法,我们来看看mapperRegistry这个类
MapperRegistry
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
// 知道的Mapper 接口信息存储在knownMappers中
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
// 添加方法,主要是通过ResolverUtil扫描报下的所有mapper接口信息
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
// `ResolverUtil`是一个能够筛选出某个路径下满足指定条件的所有类的工具类
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
// 筛选出某个包下Object的子类,其实就是包下所有类
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
// 拿到符合条件的类集合
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
// 获取方法 主要动态代理的时候使用
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
- 调用ResolverUtil#find方法找到Mapper接口对象
ResolverUtil
/** The set of matches being accumulated. */
private Set<Class<? extends T>> matches = new HashSet<>();
/**
* 筛选出指定路径下符合一定条件的类
* @param test 测试条件
* @param packageName 路径
* @return ResolverUtil本身
*/
public ResolverUtil<T> find(Test test, String packageName) {
// 获取起始包路径
String path = getPackagePath(packageName);
try {
// 找出包中的各个文件,其实就是通过 VFS(虚拟文件系统)获取指定包下的所有文件的Class,也就是所有的Mapper接口,
List<String> children = VFS.getInstance().list(path);
for (String child : children) {
// 对类文件进行测试
if (child.endsWith(".class")) { // 必须是类文件
// 测试是否满足测试条件。如果满足,则将该类文件记录下来
addIfMatching(test, child);
}
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error("Could not read package: " + packageName, ioe);
}
return this;
}
/**
* 判断一个类文件是否满足条件。如果满足则记录下来
* @param test 测试条件
* @param fqn 类文件全名
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void addIfMatching(Test test, String fqn) {
try {
// 转化为外部名称
String externalName = fqn.substring(0, fqn.indexOf('.')).replace('/', '.');
// 类加载器
ClassLoader loader = getClassLoader();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checking to see if class " + externalName + " matches criteria [" + test + "]");
}
// 加载类文件
Class<?> type = loader.loadClass(externalName);
if (test.matches(type)) { // 执行测试
// 测试通过则记录到matches属性中
matches.add((Class<T>) type);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.warn("Could not examine class '" + fqn + "'" + " due to a " +
t.getClass().getName() + " with message: " + t.getMessage());
}
}
}
- 我们可以看到通过我们配置的接口的信息:比如com.shu.mapper,的字符串包信息,通过VFS以及类加载器拿到对应的Mapper接口信息,添加到matches之中,并返回给调用者
MapperRegistry
// 已知的所有映射
// key:mapperInterface,即dao的数据库接口,不是方法
// value:MapperProxyFactory,即映射器代理工厂
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 要加入的肯定是接口,否则不添加
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 加入的是接口
if (hasMapper(type)) {
// 如果添加重复
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
- 通过ResolverUtil中的方法我们已经找到的我们写的接口信息并添加到knownMappers中,下面我们需要对
mapper.xml中的信息进行解析,因此调用了MapperAnnotationBuilder#parse()方法进行解析
MapperAnnotationBuilder
/**
* 解析包含注解的接口文档
*/
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
// 防止重复分析
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 寻找类名对应的resource路径下是否有xml配置,如果有则解析掉。这样就支持注解和xml混合使用
loadXmlResource();
// 记录资源路径
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 设置命名空间
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
// 处理缓存
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// 排除桥接方法
// JDK 1.5 引入泛型后,为了使Java的泛型方法生成的字节码和 1.5 版本前的字节码相兼容,由编译器自动生成的方法,这个就是桥接方法。
// 就是说一个子类在继承(或实现)一个父类(或接口)的泛型方法时,在子类中明确指定了泛型类型,那么在编译时编译器会自动生成桥接方法
if (!method.isBridge()) {
// 解析该方法
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 解析异常的方法暂存起来
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
// 处理解析异常的方法
parsePendingMethods();
}
// 加载对应的mapper.xml文件
private void loadXmlResource() {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we check a flag
// to prevent loading again a resource twice
// this flag is set at XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded("namespace:" + type.getName())) {
String xmlResource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";
// #1347
InputStream inputStream = type.getResourceAsStream("/" + xmlResource);
if (inputStream == null) {
// Search XML mapper that is not in the module but in the classpath.
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(type.getClassLoader(), xmlResource);
} catch (IOException e2) {
// ignore, resource is not required
}
}
if (inputStream != null) {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName());
xmlParser.parse();
}
}
}
/**
* 解析Mapper.xml文件
*/
public void parse() {
// 该节点是否被解析过,。或将加载过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 处理mapper节点
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 加入到已经解析的列表,防止重复解析
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 将mapper注册给Configuration
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 下面分别用来处理失败的、、SQL语句
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
- MapperAnnotationBuilder它的职责很简单,就是解析指定的mapper接口对应的Class对象中,包含的所有mybatis框架中定义的注解,并生成Cache、ResultMap、MappedStatement三种类型对象。
MapperAnnotationBuilder
public class MapperAnnotationBuilder {
// 语句注释类型
private static final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> statementAnnotationTypes = Stream
.of(Select.class, Update.class, Insert.class, Delete.class, SelectProvider.class, UpdateProvider.class,
InsertProvider.class, DeleteProvider.class)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
// 配置信息
private final Configuration configuration;
// MapperBuilder的辅助类
private final MapperBuilderAssistant assistant;
// 传入mapper接口类
private final Class<?> type;
// 构造方法
public MapperAnnotationBuilder(Configuration configuration, Class<?> type) {
// 把“.”换成“/”就从类名得到了Mapper的路径,当然,只是猜测。因为这是规范
String resource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".java (best guess)";
this.assistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.configuration = configuration;
this.type = type;
}
}
- 接下来我们来看看MapperBuilderAssistant这个类
MapperBuilderAssistant
public class MapperBuilderAssistant extends BaseBuilder {
// 当前Mapper接口的命名空间
private String currentNamespace;
// Mapper接口文件的路径
private final String resource;
// 当前Mapper的缓存
private Cache currentCache;
// 共享的其他命名空间缓存是否还没解析成功
private boolean unresolvedCacheRef; // issue #676
public MapperBuilderAssistant(Configuration configuration, String resource) {
super(configuration);
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
this.resource = resource;
}
}
- MapperBuilderAssistant作为MapperAnnotationBuilder的辅助类,十分重要,我们看看他的重要方法
MapperBuilderAssistant
/**
* 设置当前的namespace,只允许设置一次不允许修改
* @param currentNamespace 当前的namespace
*/
public void setCurrentNamespace(String currentNamespace) {
if (currentNamespace == null) {
throw new BuilderException("The mapper element requires a namespace attribute to be specified.");
}
if (this.currentNamespace != null && !this.currentNamespace.equals(currentNamespace)) {
throw new BuilderException("Wrong namespace. Expected '"
+ this.currentNamespace + "' but found '" + currentNamespace + "'.");
}
this.currentNamespace = currentNamespace;
}
/**
* 使用当前的命名空间来确定base的命名空间
* @param base 一个路径
* @param isReference 是否参考当前命名空间
* @return 在当前命名空间基础上的路径
*/
public String applyCurrentNamespace(String base, boolean isReference) {
if (base == null) {
return null;
}
if (isReference) {
// is it qualified with any namespace yet?
if (base.contains(".")) {
return base;
}
} else {
// is it qualified with this namespace yet?
if (base.startsWith(currentNamespace + ".")) {
return base;
}
if (base.contains(".")) {
throw new BuilderException("Dots are not allowed in element names, please remove it from " + base);
}
}
return currentNamespace + "." + base;
}
/**
* 使用其他namespace的缓存
* @param namespace 其他的namespace
* @return 其他namespace的缓存
*/
public Cache useCacheRef(String namespace) {
if (namespace == null) {
throw new BuilderException("cache-ref element requires a namespace attribute.");
}
try {
unresolvedCacheRef = true;
// 获取其他namespace的缓存
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace);
if (cache == null) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.");
}
// 修改当前缓存为其他namespace的缓存,从而实现缓存共享
currentCache = cache;
unresolvedCacheRef = false;
return cache;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.", e);
}
}
/**
* 创建一个新的缓存
* @param typeClass 缓存的实现类
* @param evictionClass 缓存的清理类,即使用哪种包装类来清理缓存
* @param flushInterval 缓存清理时间间隔
* @param size 缓存大小
* @param readWrite 缓存是否支持读写
* @param blocking 缓存是否支持阻塞
* @param props 缓存配置属性
* @return 缓存
*/
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
/**
* 创建一个详细的参数映射
* 相关入参请参照ParameterMapping的属性注释
* @return 参数映射
*/
public ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(
Class<?> parameterType,
String property,
Class<?> javaType,
JdbcType jdbcType,
String resultMap,
ParameterMode parameterMode,
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandler,
Integer numericScale) {
resultMap = applyCurrentNamespace(resultMap, true);
// Class parameterType = parameterMapBuilder.type();
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveParameterJavaType(parameterType, property, javaType, jdbcType);
TypeHandler<?> typeHandlerInstance = resolveTypeHandler(javaTypeClass, typeHandler);
return new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, javaTypeClass)
.jdbcType(jdbcType)
.resultMapId(resultMap)
.mode(parameterMode)
.numericScale(numericScale)
.typeHandler(typeHandlerInstance)
.build();
}
/**
* 创建结果映射对象
* 入参参照ResultMap属性
* @return ResultMap对象
*/
public ResultMap addResultMap(
String id,
Class<?> type,
String extend,
Discriminator discriminator,
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings,
Boolean autoMapping) {
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true);
// 解析ResultMap的继承关系
if (extend != null) { // 如果存在ResultMap的继承
if (!configuration.hasResultMap(extend)) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Could not find a parent resultmap with id '" + extend + "'");
}
// 获取父级的ResultMap
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(extend);
// 获取父级的属性映射
List<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappings = new ArrayList<>(resultMap.getResultMappings());
// 删除当前ResultMap中已有的父级属性映射,为当前属性映射覆盖父级属性属性创造条件
extendedResultMappings.removeAll(resultMappings);
// 如果当前ResultMap设置有构建器,则移除父级构建器
boolean declaresConstructor = false;
for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMappings) {
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
declaresConstructor = true;
break;
}
}
if (declaresConstructor) {
extendedResultMappings.removeIf(resultMapping -> resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR));
}
// 最终从父级继承而来的所有属性映射
resultMappings.addAll(extendedResultMappings);
}
// 创建当前的ResultMap
ResultMap resultMap = new ResultMap.Builder(configuration, id, type, resultMappings, autoMapping)
.discriminator(discriminator)
.build();
// 将当期的ResultMap加入到Configuration
configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);
return resultMap;
}
- 接下来我们继续看MapperAnnotationBuilder#parse()方法
MapperAnnotationBuilder
/**
* 解析包含注解的接口文档
*/
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
// 防止重复分析
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 寻找类名对应的resource路径下是否有xml配置,如果有则解析掉。这样就支持注解和xml混合使用
loadXmlResource();
// 记录资源路径
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 设置命名空间
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
// 处理缓存
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// 排除桥接方法
// JDK 1.5 引入泛型后,为了使Java的泛型方法生成的字节码和 1.5 版本前的字节码相兼容,由编译器自动生成的方法,这个就是桥接方法。
// 就是说一个子类在继承(或实现)一个父类(或接口)的泛型方法时,在子类中明确指定了泛型类型,那么在编译时编译器会自动生成桥接方法
if (!method.isBridge()) {
// 解析该方法
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 解析异常的方法暂存起来
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
// 处理解析异常的方法
parsePendingMethods();
}
- 下面调用loadXmlResource()方法,调用Resources类的方法来加载我们写的Mapper.xml文件交给XMLMapperBuilder进行解析
private void loadXmlResource() {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we check a flag
// to prevent loading again a resource twice
// this flag is set at XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded("namespace:" + type.getName())) {
String xmlResource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";
// #1347
InputStream inputStream = type.getResourceAsStream("/" + xmlResource);
if (inputStream == null) {
// Search XML mapper that is not in the module but in the classpath.
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(type.getClassLoader(), xmlResource);
} catch (IOException e2) {
// ignore, resource is not required
}
}
if (inputStream != null) {
// 构建XMLMapperBuilder
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName());
// 调用解析方法
xmlParser.parse();
}
}
}
我们回顾一下之前的知识:
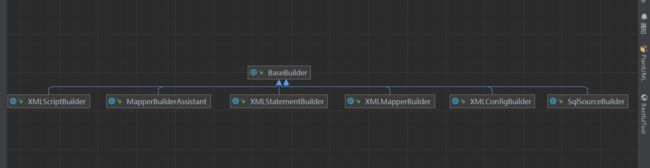
●XMLConfigBuilder:解析mybatis配置文件
●XMLMapperBuilder:解析mybatis映射文件
●MapperBuilderAssistant:XMLMapperBuilder的帮助类
●XMLStatementBuilder:解析映射文件中的sql语句标签insert|update|delete|select
●XMLScriptBuilder: SQL语句在XML文件中,处理动态SQL语句标签
●SQLSourceBuilder:在RawSqlSource使用
- 我们来看看XMLMapperBuilder的构造方法
XMLMapperBuilder
public XMLMapperBuilder(InputStream inputStream, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments, String namespace) {
this(inputStream, configuration, resource, sqlFragments);
// 设置当前命名空间,不可修改
this.builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
}
// 调用重载方法
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
this.resource = resource;
}
/**
* 解析Mapper文件
*/
public void parse() {
// 该节点是否被解析过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 处理mapper节点
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 加入到已经解析的列表,防止重复解析
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 将mapper注册给Configuration
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 下面分别用来处理失败的、、SQL语句
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
- 接下来与前面一样解析Xml文件中的节点信息,填充给configuration,方便系统后面使用
XMLMapperBuilder
/**
* 解析Mapper文件的下层节点
* @param context Mapper文件的根节点
*/
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 读取当前Mapper文件的命名空间mapper.EmployeeMapper
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// 绑定当前命名空间
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// mapper文件中其他配置节点的解析
// 解析cache-ref节点
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// 解析cache节点
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
// 解析parameterMap节点
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
// 解析resultMap节点
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析sql
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 处理各个数据库操作语句
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- 接下里我们依次来看看如何解析节点信息,关于缓存的那一块,后面会文章详细介绍Cache
三 解析cache-ref节点
参考官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | XML 映射器
对某一命名空间的语句,只会使用该命名空间的缓存进行缓存或刷新。 但你可能会想要在多个命名空间中共享相同的缓存配置和实例。要实现这种需求,你可以使用 cache-ref 元素来引用另一个缓存。
<cache-ref namespace="com.someone.application.data.SomeMapper"/>
XMLMapperBuilder
private void cacheRefElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
// 传入当前命令空间,配置的namespace属性:eg: com.shu.UserMapper
configuration.addCacheRef(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
// 缓存引用解析器
CacheRefResolver cacheRefResolver = new CacheRefResolver(builderAssistant, context.getStringAttribute("namespace"));
try {
//解析缓存引用
cacheRefResolver.resolveCacheRef();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteCacheRef(cacheRefResolver);
}
}
}
- 创建缓存解析器,来解析缓存引用,实际上调用了MapperBuilderAssistant#useCacheRef()方法来达到缓存的共享
MapperBuilderAssistant
/**
* 使用其他namespace的缓存
* @param namespace 其他的namespace
* @return 其他namespace的缓存
*/
public Cache useCacheRef(String namespace) {
if (namespace == null) {
throw new BuilderException("cache-ref element requires a namespace attribute.");
}
try {
unresolvedCacheRef = true;
// 获取其他namespace的缓存
Cache cache = configuration.getCache(namespace);
if (cache == null) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.");
}
// 修改当前缓存为其他namespace的缓存,从而实现缓存共享
currentCache = cache;
unresolvedCacheRef = false;
return cache;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("No cache for namespace '" + namespace + "' could be found.", e);
}
}
具体是实现细节我们后面在一级缓存,二级缓存中文字会详细介绍
四 解析Cache节点
官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | XML 映射器
MyBatis 内置了一个强大的事务性查询缓存机制,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。 为了使它更加强大而且易于配置,我们对 MyBatis 3 中的缓存实现进行了许多改进。
默认情况下,只启用了本地的会话缓存,它仅仅对一个会话中的数据进行缓存。 要启用全局的二级缓存,只需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行:
<cache/>
这个简单语句的效果如下:
- 映射语句文件中的所有 select 语句的结果将会被缓存。
- 映射语句文件中的所有 insert、update 和 delete 语句会刷新缓存。
- 缓存会使用最近最少使用算法(LRU, Least Recently Used)算法来清除不需要的缓存。
- 缓存不会定时进行刷新(也就是说,没有刷新间隔)。
- 缓存会保存列表或对象(无论查询方法返回哪种)的 1024 个引用。
- 缓存会被视为读/写缓存,这意味着获取到的对象并不是共享的,可以安全地被调用者修改,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。
也可以使用第三方缓存
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.redis.RedisCache"/>
其中有一些属性可以选择
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
- 根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”
- 缓存的容量为 512 个对象引用
- 缓存每隔60秒刷新一次
- 缓存返回的对象是写安全的,即在外部修改对象不会影响到缓存内部存储对象
eviction可用的清除策略有:
- LRU – 最近最少使用:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
- FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
- SOFT – 软引用:基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则移除对象。
- WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则移除对象。
默认的清除策略是 LRU。
flushInterval(刷新间隔)属性可以被设置为任意的正整数,设置的值应该是一个以毫秒为单位的合理时间量。 默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅会在调用语句时刷新。
size(引用数目)属性可以被设置为任意正整数,要注意欲缓存对象的大小和运行环境中可用的内存资源。默认值是 1024。
readOnly(只读)属性可以被设置为 true 或 false。只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。 因此这些对象不能被修改。这就提供了可观的性能提升。而可读写的缓存会(通过序列化)返回缓存对象的拷贝。 速度上会慢一些,但是更安全,因此默认值是 false。
XMLMapperBuilder
//
// eviction="FIFO"
// flushInterval="60000"
// size="512"
// readOnly="true"/>
//
// select * from `user` where id = #{id}
//
//
// 这里处理其中的节点
private void cacheElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
// 获取type属性,如果type没有指定就用默认的PERPETUAL(早已经注册过的别名的PerpetualCache)
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
根据type从早已经注册的别名中获取对应的Class,PERPETUAL对应的Class是PerpetualCache.class
// 如果我们写了type属性,如type="org.mybatis.caches.redis.RedisCache",这里将会得到RedisCache.class
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
// //获取淘汰方式,默认为LRU(早已经注册过的别名的LruCache),最近最少使用到的先淘汰
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
// 解析刷新间隔
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
// 大小
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
// 是否只读
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
// 获取子节点配置
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 构建缓存对象
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
- 从上面我们需要在配置文件中读取常见缓存的必要条件,从而创建一个新的缓存对象,我们首先来看看他是如何在typeAliasRegistry中获取在注册的对象?
registerAlias("map", Map.class);
// 通过注册的别名来获取在typeAliasRegistry注册的对象
public <T> Class<T> resolveAlias(String string) {
try {
if (string == null) {
return null;
}
// issue #748
String key = string.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
Class<T> value;
// 是否注册过
if (typeAliases.containsKey(key)) {
value = (Class<T>) typeAliases.get(key);
}
// 没有的话交给Resources来查找
else {
value = (Class<T>) Resources.classForName(string);
}
return value;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not resolve type alias '" + string + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- 通过typeAliasRegistry#resolveAlias()方法 ,我们拿到了构建先缓存的必要条件
MapperBuilderAssistant
/**
* 创建一个新的缓存
* @param typeClass 缓存的实现类
* @param evictionClass 缓存的清理类,即使用哪种包装类来清理缓存
* @param flushInterval 缓存清理时间间隔
* @param size 缓存大小
* @param readWrite 缓存是否支持读写
* @param blocking 缓存是否支持阻塞
* @param props 缓存配置属性
* @return 缓存
*/
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
// 当前命令空间
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
- 上面使用了建造模式构建 Cache 实例?
CacheBuilder
public class CacheBuilder {
// Cache的编号
private final String id;
// Cache的实现类
private Class<? extends Cache> implementation;
// Cache的装饰器列表
private final List<Class<? extends Cache>> decorators;
// Cache的大小
private Integer size;
// Cache的清理间隔
private Long clearInterval;
// Cache是否可读写
private boolean readWrite;
// Cache的配置信息
private Properties properties;
// Cache是否阻塞
private boolean blocking;
/**
* 组建缓存
* @return 缓存对象
*/
public Cache build() {
// 设置缓存的默认实现、默认装饰器(仅设置,并未装配)PerpetualCache
setDefaultImplementations();
// 创建默认的缓存
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
// 设置缓存的属性
setCacheProperties(cache);
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) { // 缓存实现是PerpetualCache,即不是用户自定义的缓存实现
// 为缓存逐级嵌套自定义的装饰器
for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) {
// 生成装饰器实例,并装配。入参依次是装饰器类、被装饰的缓存
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
// 为装饰器设置属性
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
// 为缓存增加标准的装饰器
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
// 增加日志装饰器
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
// 返回被包装好的缓存
return cache;
}
private void setDefaultImplementations() {
if (this.implementation == null) {
//设置默认缓存类型为PerpetualCache
this.implementation = PerpetualCache.class;
if (this.decorators.isEmpty()) {
this.decorators.add(LruCache.class);
}
}
}
private Cache newBaseCacheInstance(Class<? extends Cache> cacheClass, String id) {
//获取构造器
Constructor cacheConstructor = this.getBaseCacheConstructor(cacheClass);
try {
//通过构造器实例化Cache
return (Cache)cacheConstructor.newInstance(id);
} catch (Exception var5) {
throw new CacheException("Could not instantiate cache implementation (" + cacheClass + "). Cause: " + var5, var5);
}
}
}
- 如上就创建好了一个Cache的实例,然后把它添加到Configuration中,并且设置到currentCache属性中,这个属性后面还要使用,也就是Cache实例后面还要使用,我们后面再看。
五 解析ParameterMap节点
ParameterMap和resultMap类似,表示将查询结果集中列值的类型一一映射到java对象属性的类型上,在开发过程中不推荐这种方式。
一般使用parameterType直接将查询结果列值类型自动对应到java对象属性类型上,不再配置映射关系一一对应,例如上述代码中下划线部分表示将查询结果类型自动对应到hdu.terence.bean.Message的Bean对象属性类型。(这里我们就 不解析了,我们重点来看看ResultMap)
<parameterMap class="java.util.Map" id="query_some_param">
<parameter property="firstName" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<parameter property="lastName" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
</parameterMap>
六 解析ResultMap节点
参考官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | XML 映射器
resultMap 元素是 MyBatis 中最重要最强大的元素。它可以让你从 90% 的 JDBC ResultSets 数据提取代码中解放出来,并在一些情形下允许你进行一些 JDBC 不支持的操作。实际上,在为一些比如连接的复杂语句编写映射代码的时候,一份 resultMap 能够代替实现同等功能的数千行代码。ResultMap 的设计思想是,对简单的语句做到零配置,对于复杂一点的语句,只需要描述语句之间的关系就行了。
<resultMap type="com.sundancersystem.model.SysRole" id="SysRoleMap">
<id column="ROLE_ID" property="roleId"/>
<result property="roleId" column="ROLE_ID" jdbcType="TINYINT"/>
<result property="roleName" column="ROLE_NAME" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="roleValue" column="ROLE_VALUE" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="roleCreatTime" column="ROLE_CREAT_TIME" jdbcType="DATE"/>
<result property="roleDelete" column="ROLE_DELETE" jdbcType="TINYINT"/>
</resultMap>
resultMap 主要用于映射结果。通过 resultMap 和自动映射,可以让 MyBatis 帮助我们完成 ResultSet → Object 的映射。
XMLMapperBuilder
private void resultMapElements(List<XNode> list) throws Exception {
// 遍历节点信息
for (XNode resultMapNode : list) {
try {
// 解析resultMap元素
resultMapElement(resultMapNode);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// ignore, it will be retried
}
}
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode) throws Exception {
return resultMapElement(resultMapNode, Collections.emptyList(), null);
}
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings, Class<?> enclosingType) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// 获取type属性
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
// 找到获取 type 属性对应的类型,就是我们的实体类对象
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
if (typeClass == null) {
typeClass = inheritEnclosingType(resultMapNode, enclosingType);
}
Discriminator discriminator = null;
// 创建ResultMapping集合,对应resultMap子节点的id和result节点
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
// 获取并遍历 的子节点列表
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
// 用于在实例化类时,注入结果到构造方法中
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
}
// 使用结果值来决定使用哪个 resultMap
else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 添加 ID 到 flags 集合中
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
// 解析 id 和 result 节点,将id或result节点生成相应的 ResultMapping,将ResultMapping添加到resultMappings集合中
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
// 获取id
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
// 创建ResultMapResolver对象
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
// 根据前面获取到的信息构建 ResultMap 对象
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}
- 我们来看看XMLMapperBuilder#buildResultMappingFromContext()解析过程
XMLMapperBuilder
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags) throws Exception {
String property;
// 根据节点类型获取 name 或 property 属性
if (flags.contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
// 构造方法形参的名字
property = context.getStringAttribute("name");
} else {
// 映射到列结果的字段或属性
property = context.getStringAttribute("property");
}
// 获取其他各种属性
// 数据库中的列名
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
// 一个 Java 类的完全限定名,或一个类型别名(关于内置的类型别名,可以参考上面的表格)
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
// JDBC 类型,所支持的 JDBC 类型参见这个表格之前的“支持的 JDBC 类型”。
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
// 用于加载复杂类型属性的映射语句的 ID,它会从 column 属性指定的列中检索数据,作为参数传递给目标 select 语句。
String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select");
/*
* 解析 resultMap 属性,该属性出现在 和 节点中。
* 若这两个节点不包含 resultMap 属性,则调用 processNestedResultMappings 方法,递归调用resultMapElement解析 和 的嵌套节点,生成resultMap,并返回resultMap.getId();
* 如果包含resultMap属性,则直接获取其属性值,这个属性值对应一个resultMap节点
*/
String nestedResultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap", processNestedResultMappings(context, Collections.<ResultMapping>emptyList()));
// 默认情况下,在至少一个被映射到属性的列不为空时,子对象才会被创建。
String notNullColumn = context.getStringAttribute("notNullColumn");
// 当连接多个表时,你可能会不得不使用列别名来避免在 ResultSet 中产生重复的列名。
String columnPrefix = context.getStringAttribute("columnPrefix");
// 我们在前面讨论过默认的类型处理器。
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
// 指定用于加载复杂类型的结果集名字。
String resultSet = context.getStringAttribute("resultSet");
// 指定外键对应的列名,指定的列将与父类型中 column 的给出的列进行匹配。
String foreignColumn = context.getStringAttribute("foreignColumn");
// 可选的。有效值为 lazy 和 eager。 指定属性后,将在映射中忽略全局配置参数 lazyLoadingEnabled,使用属性的值。
boolean lazy = "lazy".equals(context.getStringAttribute("fetchType", configuration.isLazyLoadingEnabled() ? "lazy" : "eager"));
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
// 构建 ResultMapping 对象
return builderAssistant.buildResultMapping(resultType, property, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, nestedSelect,
nestedResultMap, notNullColumn, columnPrefix, typeHandlerClass, flags, resultSet, foreignColumn, lazy);
}
- 在上面的解析中我们需要重点关注一下复杂结构的嵌套过程,processNestedResultMappings()方法
XMLMapperBuilder
private String processNestedResultMappings(XNode context, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception {
if (("association".equals(context.getName()) || "collection".equals(context.getName()) || "case".equals(context.getName())) && context.getStringAttribute("select") == null) {
ResultMap resultMap = this.resultMapElement(context, resultMappings);
return resultMap.getId();
} else {
return null;
}
}
只要此节点是(association或者collection)并且select为空,就说明是嵌套查询,那如果select不为空呢?那说明是延迟加载此节点的信息,并不属于嵌套查询,但是有可能有多个association或者collection,有一个设置为延迟加载也就是select属性不为空,有一个没有设置延迟加载,那说明resultMap中有嵌套查询的ResultMapping,也有延迟加载的ResultMapping,这个在后面结果集映射时会用到。
- 下面分析 ResultMapping 的构建过程,我们依照官网来看看这些属性
| property | 映射到列结果的字段或属性。如果 JavaBean 有这个名字的属性(property),会先使用该属性。否则 MyBatis 将会寻找给定名称的字段(field)。 无论是哪一种情形,你都可以使用常见的点式分隔形式进行复杂属性导航。 比如,你可以这样映射一些简单的东西:“username”,或者映射到一些复杂的东西上:“address.street.number”。 |
| — | — |
| column | 数据库中的列名,或者是列的别名。一般情况下,这和传递给 resultSet.getString(columnName) 方法的参数一样。 |
| javaType | 一个 Java 类的全限定名,或一个类型别名(关于内置的类型别名,可以参考上面的表格)。 如果你映射到一个 JavaBean,MyBatis 通常可以推断类型。然而,如果你映射到的是 HashMap,那么你应该明确地指定 javaType 来保证行为与期望的相一致。 |
| jdbcType | JDBC 类型,所支持的 JDBC 类型参见这个表格之后的“支持的 JDBC 类型”。 只需要在可能执行插入、更新和删除的且允许空值的列上指定 JDBC 类型。这是 JDBC 的要求而非 MyBatis 的要求。如果你直接面向 JDBC 编程,你需要对可以为空值的列指定这个类型。 |
| typeHandler | 我们在前面讨论过默认的类型处理器。使用这个属性,你可以覆盖默认的类型处理器。 这个属性值是一个类型处理器实现类的全限定名,或者是类型别名。 |
MapperBuilderAssistant
public ResultMapping buildResultMapping(
Class<?> resultType, // 当前隐射实例对象
String property, // 实例字段名称
String column, // 数据库字段名称
Class<?> javaType, // Java 类的全限定名
JdbcType jdbcType, // JDBC 类型,所支持的 JDBC 类型参见这个表格之后的“支持的 JDBC 类型”。
String nestedSelect, // 复杂查询嵌套的选择
String nestedResultMap, // 复杂查询嵌套的结果隐射
String notNullColumn, // 非空列
String columnPrefix,
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandler, // 类型处理器,不同的类型对应着不同的类型处理器
List<ResultFlag> flags, // 结果标识
String resultSet, // 指定用于加载复杂类型的结果集名字。
String foreignColumn, // 指定外键对应的列名,指定的列将与父类型中 column 的给出的列进行匹配。
boolean lazy) { // 是否懒加载
// 解析Java类型
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveResultJavaType(resultType, property, javaType);
// 类型处理器
TypeHandler<?> typeHandlerInstance = resolveTypeHandler(javaTypeClass, typeHandler);
List<ResultMapping> composites;
if ((nestedSelect == null || nestedSelect.isEmpty()) && (foreignColumn == null || foreignColumn.isEmpty())) {
composites = Collections.emptyList();
} else {
composites = parseCompositeColumnName(column);
}
// 通过建造模式构建 ResultMapping
return new ResultMapping.Builder(configuration, property, column, javaTypeClass)
.jdbcType(jdbcType)
.nestedQueryId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedSelect, true))
.nestedResultMapId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedResultMap, true))
.resultSet(resultSet)
.typeHandler(typeHandlerInstance)
.flags(flags == null ? new ArrayList<>() : flags)
.composites(composites)
.notNullColumns(parseMultipleColumnNames(notNullColumn))
.columnPrefix(columnPrefix)
.foreignColumn(foreignColumn)
.lazy(lazy)
.build();
}
//略
}
- 通过buildResultMappingFromContext方法的解析我们已经拿到构建ResultMapping的必要条件,我们来看看resolveResultJavaType()方法与resolveTypeHandler方法
private Class<?> resolveResultJavaType(Class<?> resultType, String property, Class<?> javaType) {
if (javaType == null && property != null) {
try {
MetaClass metaResultType = MetaClass.forClass(resultType, configuration.getReflectorFactory());
javaType = metaResultType.getSetterType(property);
} catch (Exception e) {
//ignore, following null check statement will deal with the situation
}
}
if (javaType == null) {
javaType = Object.class;
}
return javaType;
}
- 这个方法其实也很简单就是获取我们创建的实体类的字段的类型,如果没有的话,就返回一个Object的类型,为下面常见类型处理器提供构造参数,那我们首先来看看TypeHandler接口,采用模板模式来实现不同的类型不同的处理接口。
TypeHandler
![]()
public interface TypeHandler<T> {
/**
* 设置参数
* @param ps
* @param i
* @param parameter
* @param jdbcType
* @throws SQLException
*/
void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
/**
* 获取结果
* @param rs
* @param columnName
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
在接口中它只是定义了他的方法,而实现在他的基类中
BaseTypeHandler
public abstract class BaseTypeHandler<T> extends TypeReference<T> implements TypeHandler<T>{
/**
* 设置参数
* @param ps
* @param i
* @param parameter
* @param jdbcType SQL 参数类型
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
if (parameter == null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
throw new TypeException("JDBC requires that the JdbcType must be specified for all nullable parameters.");
}
try {
ps.setNull(i, jdbcType.TYPE_CODE);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . "
+ "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different jdbcTypeForNull configuration property. "
+ "Cause: " + e, e);
}
} else {
try {
setNonNullParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting non null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . "
+ "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different configuration property. "
+ "Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
/**
* 从结果集中读出一个结果
* @param rs 结果集
* @param columnName 要读取的结果的列名称
* @return 结果值
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(rs, columnName);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column '" + columnName + "' from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(rs, columnIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column #" + columnIndex + " from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
@Override
public T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(cs, columnIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column #" + columnIndex + " from callable statement. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
/**
* 向PreparedStatement对象中的指定变量位置写入一个不为 null的值;
* @param ps
* @param i
* @param parameter
* @param jdbcType
* @throws SQLException
*/
public abstract void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
/**
* 从 ResultSet 中按照字段名读出一个可能为null的数据;
* @param rs
* @param columnName
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public abstract T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
/**
* 从 ResultSet 中按照字段编号读出一个可能为null的数据;
* @param rs
* @param columnIndex
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public abstract T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
/**
* 从 CallableStatement中按照字段编号读出一个可能为 null的数据。
* @param cs
* @param columnIndex
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public abstract T getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
这些类型处理器在对配置文件解析的时候已经注册到了TypeHandlerRegistry()中,我们只需要通过不同的类型在TypeHandlerRegistry中拿到对应的类型处理器就可以了
BaseBuilder
protected TypeHandler<?> resolveTypeHandler(Class<?> javaType, Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerType) {
if (typeHandlerType == null) {
return null;
}
// javaType ignored for injected handlers see issue #746 for full detail
// 注意,这一次查询的地方变了,是去typeHandlerRegistry,里面存的是 key为typeHandler.getClass() value为typeHandler
TypeHandler<?> handler = typeHandlerRegistry.getMappingTypeHandler(typeHandlerType);
if (handler == null) {
// not in registry, create a new one
handler = typeHandlerRegistry.getInstance(javaType, typeHandlerType);
}
return handler;
}
- 构建ResultMap对象,调用Builder()方法
MapperBuilderAssistant
return new ResultMapping.Builder(configuration, property, column, javaTypeClass)
.jdbcType(jdbcType)
.nestedQueryId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedSelect, true))
.nestedResultMapId(applyCurrentNamespace(nestedResultMap, true))
.resultSet(resultSet)
.typeHandler(typeHandlerInstance)
.flags(flags == null ? new ArrayList<>() : flags)
.composites(composites)
.notNullColumns(parseMultipleColumnNames(notNullColumn))
.columnPrefix(columnPrefix)
.foreignColumn(foreignColumn)
.lazy(lazy)
.build();
- 构建完成返回一个ResultMapping对象,我们他看看ResultMapping的成员变量
ResultMapping
private Configuration configuration;
private String property;
private String column;
private Class<?> javaType;
private JdbcType jdbcType;
private TypeHandler<?> typeHandler;
private String nestedResultMapId;
private String nestedQueryId;
private Set<String> notNullColumns;
private String columnPrefix;
private List<ResultFlag> flags;
private List<ResultMapping> composites;
private String resultSet;
private String foreignColumn;
private boolean lazy;
- 解析完成后我们回到resultMapElement()方法中
XMLMapperBuilder
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings, Class<?> enclosingType) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
if (typeClass == null) {
typeClass = inheritEnclosingType(resultMapNode, enclosingType);
}
Discriminator discriminator = null;
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
// 用于在实例化类时,注入结果到构造方法中
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
}
else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
// 创建ResultMapResolver解析器
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}
接着上面代码我们可以发现:调用了ResultMapResolver#resolve()
ResultMapResolver
public class ResultMapResolver {
// Mapper建造者辅助类
private final MapperBuilderAssistant assistant;
// ResultMap的id
private final String id;
// ResultMap的type属性,即目标对象类型
private final Class<?> type;
// ResultMap的extends属性,即继承属性
private final String extend;
// ResultMap中的Discriminator节点,即鉴别器
private final Discriminator discriminator;
// ResultMap中的属性映射列表
private final List<ResultMapping> resultMappings;
// ResultMap的autoMapping属性,即是否开启自动映射
private final Boolean autoMapping;
public ResultMapResolver(MapperBuilderAssistant assistant, String id, Class<?> type, String extend, Discriminator discriminator, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings, Boolean autoMapping) {
this.assistant = assistant;
this.id = id;
this.type = type;
this.extend = extend;
this.discriminator = discriminator;
this.resultMappings = resultMappings;
this.autoMapping = autoMapping;
}
public ResultMap resolve() {
return assistant.addResultMap(this.id, this.type, this.extend, this.discriminator, this.resultMappings, this.autoMapping);
}
}
MapperBuilderAssistant
/**
* 创建结果映射对象
* 入参参照ResultMap属性
* @return ResultMap对象
*/
public ResultMap addResultMap(
String id,
Class<?> type,
String extend,
Discriminator discriminator,
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings,
Boolean autoMapping) {
// 验证当前命名空间
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true);
// 解析ResultMap的继承关系
if (extend != null) { // 如果存在ResultMap的继承
if (!configuration.hasResultMap(extend)) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Could not find a parent resultmap with id '" + extend + "'");
}
// 获取父级的ResultMap
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(extend);
// 获取父级的属性映射
List<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappings = new ArrayList<>(resultMap.getResultMappings());
// 删除当前ResultMap中已有的父级属性映射,为当前属性映射覆盖父级属性属性创造条件
extendedResultMappings.removeAll(resultMappings);
// 如果当前ResultMap设置有构建器,则移除父级构建器
boolean declaresConstructor = false;
for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMappings) {
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
declaresConstructor = true;
break;
}
}
if (declaresConstructor) {
extendedResultMappings.removeIf(resultMapping -> resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR));
}
// 最终从父级继承而来的所有属性映射
resultMappings.addAll(extendedResultMappings);
}
// 创建当前的ResultMap
ResultMap resultMap = new ResultMap.Builder(configuration, id, type, resultMappings, autoMapping)
.discriminator(discriminator)
.build();
// 将当期的ResultMap加入到Configuration
configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);
return resultMap;
}
/**
* 使用当前的命名空间来确定base的命名空间
* @param base 一个路径
* @param isReference 是否参考当前命名空间
* @return 在当前命名空间基础上的路径
*/
public String applyCurrentNamespace(String base, boolean isReference) {
if (base == null) {
return null;
}
if (isReference) {
// is it qualified with any namespace yet?
if (base.contains(".")) {
return base;
}
} else {
// is it qualified with this namespace yet?
if (base.startsWith(currentNamespace + ".")) {
return base;
}
if (base.contains(".")) {
throw new BuilderException("Dots are not allowed in element names, please remove it from " + base);
}
}
return currentNamespace + "." + base;
}
- 到了方法的后面调用了ResultMap#Builder()方法来创建ResultMap对象,我们首先来看看ResultMap的成员方法。
// 全局配置信息
private Configuration configuration;
// resultMap的编号
private String id;
// 最终输出结果对应的Java类
private Class<?> type;
// XML中的的列表,即ResultMapping列表
private List<ResultMapping> resultMappings;
// XML中的的列表
private List<ResultMapping> idResultMappings;
// XML中的中各个属性的列表
private List<ResultMapping> constructorResultMappings;
// XML中非相关的属性列表
private List<ResultMapping> propertyResultMappings;
// 所有参与映射的数据库中字段的集合
private Set<String> mappedColumns;
// 所有参与映射的Java对象属性集合
private Set<String> mappedProperties;
// 鉴别器
private Discriminator discriminator;
// 是否存在嵌套映射
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
// 是否存在嵌套查询
private boolean hasNestedQueries;
// 是否启动自动映射
private Boolean autoMapping;
- 最后将返回的ResultMap对象设置到Configuration中,并返回ResultMap,我们对ResultMap的解析就完成了
MapperBuilderAssistant
// 将当期的ResultMap加入到Configuration
configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);
return resultMap;
七 解析Sql节点
参考官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | XML 映射器
节点用来定义一些可重用的 SQL 语句片段,比如表名,或表的列名等。在映射文件中,我们可以通过 节点引用 节点定义的内容。
<!-- 通过用户id查询具有的角色信息数据 -->
<select id="queryByUserId" resultMap="SysRoleMap">
select
s1.ROLE_ID,s1.ROLE_NAME,s1.ROLE_VALUE
from sys_role s1 inner join sys_user_role s2 on s2.ROLE_ID=s1.ROLE_ID
where s2.USER_ID = #{userId} and s1.ROLE_DELETE=0
</select>
XMLMapperBuilder
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list) throws Exception {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
// 调用 sqlElement 解析 节点
sqlElement(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
// 再次调用 sqlElement,不同的是,这次调用,该方法的第二个参数为 null
sqlElement(list, null);
}
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) throws Exception {
for (XNode context : list) {
// 获取 id 和 databaseId 属性
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
// id = currentNamespace + "." + id
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
// 检测当前 databaseId 和 requiredDatabaseId 是否一致
if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) {
// 将 键值对缓存到XMLMapperBuilder对象的 sqlFragments 属性中,以供后面的sql语句使用
sqlFragments.put(id, context);
}
}
}
八 处理各个数据库操作语句
参考官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | XML 映射器
、、 以及 等节点统称为 SQL 语句节点。
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| id | 在命名空间中唯一的标识符,可以被用来引用这条语句。 |
| parameterType | 将会传入这条语句的参数的类全限定名或别名。这个属性是可选的,因为 MyBatis 可以通过类型处理器(TypeHandler)推断出具体传入语句的参数,默认值为未设置(unset)。 |
| flushCache | 将其设置为 true 后,只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存被清空,默认值:(对 insert、update 和 delete 语句)true。 |
| timeout | 这个设置是在抛出异常之前,驱动程序等待数据库返回请求结果的秒数。默认值为未设置(unset)(依赖数据库驱动)。 |
| statementType | 可选 STATEMENT,PREPARED 或 CALLABLE。这会让 MyBatis 分别使用 Statement,PreparedStatement 或 CallableStatement,默认值:PREPARED。 |
| useGeneratedKeys | (仅适用于 insert 和 update)这会令 MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键(比如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系型数据库管理系统的自动递增字段),默认值:false。 |
| keyProperty | (仅适用于 insert 和 update)指定能够唯一识别对象的属性,MyBatis 会使用 getGeneratedKeys 的返回值或 insert 语句的 selectKey 子元素设置它的值,默认值:未设置(unset)。如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。 |
| keyColumn | (仅适用于 insert 和 update)设置生成键值在表中的列名,在某些数据库(像 PostgreSQL)中,当主键列不是表中的第一列的时候,是必须设置的。如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。 |
| databaseId | 如果配置了数据库厂商标识(databaseIdProvider),MyBatis 会加载所有不带 databaseId 或匹配当前 databaseId 的语句;如果带和不带的语句都有,则不带的会被忽略。 |
<insert
id="insertAuthor"
parameterType="domain.blog.Author"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
keyProperty=""
keyColumn=""
useGeneratedKeys=""
timeout="20">
<update
id="updateAuthor"
parameterType="domain.blog.Author"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
timeout="20">
<delete
id="deleteAuthor"
parameterType="domain.blog.Author"
flushCache="true"
statementType="PREPARED"
timeout="20">
<insert id="insertAuthor">
insert into Author (id,username,password,email,bio)
values (#{id},#{username},#{password},#{email},#{bio})
</insert>
<update id="updateAuthor">
update Author set
username = #{username},
password = #{password},
email = #{email},
bio = #{bio}
where id = #{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteAuthor">
delete from Author where id = #{id}
</delete>
XMLMapperBuilder
// 处理sq语句
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
// 解析语句
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
// 单条语句的解析器,解析类似:
//
// select * from `user` where id = #{id}
//
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
从这我们我们可以看到XMLStatementBuilder对象:来帮助解析SQL语句,我们来仔细看看XMLStatementBuilder的创建
XMLStatementBuilder
public XMLStatementBuilder(Configuration configuration, MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, XNode context, String databaseId) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant;
this.context = context;
this.requiredDatabaseId = databaseId;
}
- 我们可以发现他先调用父类的方法, super(configuration),完成对TypeAliasRegistry和TypeHandlerRegistry的初始化
BaseBuilder
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
}
- 对象创建完毕,接着调用XMLStatementBuilder#parseStatementNode()方法来进行解析
/**
* 解析select、insert、update、delete这四类节点
*/
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 读取当前节点的id与databaseId
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
// 验证id与databaseId是否匹配。MyBatis允许多数据库配置,因此有些语句只对特定数据库生效
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
// 读取节点名
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 读取和判断语句类型
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// 处理语句中的Include节点
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// 参数类型
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
// 语句类型
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// 处理SelectKey节点,在这里会将KeyGenerator加入到Configuration.keyGenerators中
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// 此时, 和 节点均已被解析完毕并被删除,开始进行SQL解析
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
// 判断是否已经有解析好的KeyGenerator
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
// 全局或者本语句只要启用自动key生成,则使用key生成
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
// 读取各个配置属性
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
// 在MapperBuilderAssistant的帮助下创建MappedStatement对象,并写入到Configuration中
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
我们来重点关注几个方法:
- 判断语句类型
- 处理语句中的Include节点
- SqlSource的创建
- 他是判断是啥语句类型?
- 我们可以看到解析Node 解析的时候就获取他的语句类型,需要详细的过程需要自己去Bebug,下面我们看看他是怎样处理Include节点信息
XMLIncludeTransformer
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
/**
* 解析数据库操作节点中的include节点
* @param source 数据库操作节点,即select、insert、update、delete这四类节点
*/
public void applyIncludes(Node source) {
Properties variablesContext = new Properties();
// 读取全局属性信息
Properties configurationVariables = configuration.getVariables();
Optional.ofNullable(configurationVariables).ifPresent(variablesContext::putAll);
applyIncludes(source, variablesContext, false);
}
/**
* Recursively apply includes through all SQL fragments.
* @param source Include node in DOM tree
* @param variablesContext Current context for static variables with values
*/
/**
* 解析数据库操作节点中的include节点
* @param source 数据库操作节点或其子节点
* @param variablesContext 全局属性信息
* @param included 是否嵌套
*/
private void applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included) {
if (source.getNodeName().equals("include")) { // 当前节点是include节点
// 找出被应用的节点
Node toInclude = findSqlFragment(getStringAttribute(source, "refid"), variablesContext);
Properties toIncludeContext = getVariablesContext(source, variablesContext);
// 递归处理被引用节点中的include节点
applyIncludes(toInclude, toIncludeContext, true);
if (toInclude.getOwnerDocument() != source.getOwnerDocument()) {
toInclude = source.getOwnerDocument().importNode(toInclude, true);
}
// 完成include节点的替换
source.getParentNode().replaceChild(toInclude, source);
while (toInclude.hasChildNodes()) {
toInclude.getParentNode().insertBefore(toInclude.getFirstChild(), toInclude);
}
toInclude.getParentNode().removeChild(toInclude);
} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // 元素节点
if (included && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// 用属性值替代变量
NamedNodeMap attributes = source.getAttributes();
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
Node attr = attributes.item(i);
attr.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(attr.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
// 循环到下层节点递归处理下层的include节点
NodeList children = source.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext, included);
}
} else if (included && source.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE
&& !variablesContext.isEmpty()) { // 文本节点
// 用属性值替代变量
source.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
-
我们可以看到对Included的解析主要是对Sql片段的加载Configuration.getSqlFragments()
-
接下来使用语言驱动来创建sqlSource,这个是否重要,这决定了后面BoundSql的处理,我们首先来看看LanguageDriver接口
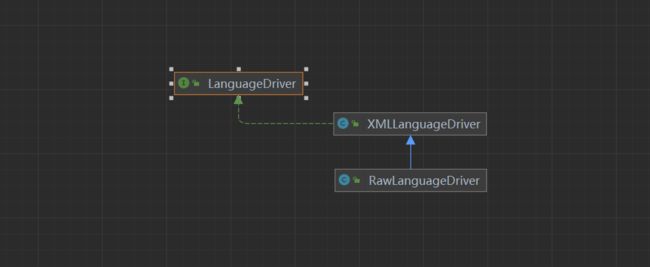
LanguageDriver
// 脚本语言解释器
// 在接口上注解的SQL语句,就是由它进行解析的
// @Select("select * from `user` where id = #{id}")
//User queryUserById(Integer id);
public interface LanguageDriver {
/**
* 创建参数处理器。参数处理器能将实参传递给JDBC statement。
* @param mappedStatement 完整的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @param boundSql 数据库操作语句转化的BoundSql对象
* @return 参数处理器
*/
ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql);
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于映射文件的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 映射文件中的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象
*/
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType);
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于注解的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 注解中的SQL字符串
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象,具体来说是DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource中的一种
*/
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType);
}
public class XMLLanguageDriver implements LanguageDriver {
@Override
public ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
return new DefaultParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
}
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于映射文件的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 映射文件中的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象
*/
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
// 创建SQL源码(注解方式)
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) {
if (script.startsWith("