数据结构与算法题目集(中文)编程题
文章目录
-
- 7-1 最大子列和问题
- 7-2 一元多项式的乘法与加法运算
- 7-3 树的同构
- 7-4 是否同一棵二叉搜索树
- 7-5 堆中的路径
- 7-6 列出连通集
- 7-7 六度空间
- 7-8 哈利·波特的考试
- 7-9 旅游规划
- 7-10 公路村村通
- 7-11 关键活动
- 7-12 排序
- 7-11 关键活动
- 7-13 统计工龄
- 7-14 电话聊天狂人
- 总结
7-1 最大子列和问题
const和static的用法没搞清楚!!!
#include 7-2 一元多项式的乘法与加法运算
在用结构体数组和链表间考虑了一下,配套慕课是用的链表,那就也试试链表,写完看看比数组方便在哪里。
按理来说传入函数后,是个新的作用域了,不传出去,值是不会改变的。改变传入指针的值!!!?
#include 感觉用两种结构体都差不多,因为每次加法和乘法都是开辟新的空间。
7-3 树的同构
完全没思路,连这棵树是怎么读取去构成都不知道。老师讲解视频
两棵树如果是同构的,他们对应节点的儿子是一样的,左右位置可以不同。
解题关键:
1、二叉树表示
一般用链表表示,或者看作完全二叉树用数组表示。这里用一种新的结构去表示。
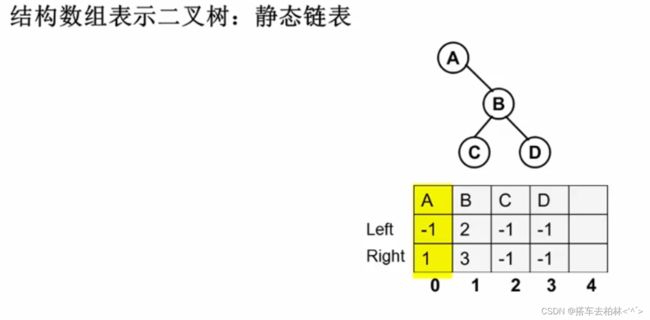
2、建二叉树
可以发现Left和Right都是存的左右孩子结点,那么根结点就是没有被存储的那个结点啦,泪目。用.和->去指向结构体某个属性到底是啥区别呢?! 而且为啥输入会不能读取呢?cpp的cin>>用法又是什么
3、同构判别
先写出递归出口,然后分情况讨论递归。
#include 7-4 是否同一棵二叉搜索树
按理来说 有不用把所有树都构造出来的方法。 之后找视频看看吧。
#include 7-5 堆中的路径
堆是按照完全二叉树的结构存储的,图解建立最大堆
#include 7-6 列出连通集
#include 7-7 六度空间
因为结点很多,所以用链表去存储,矩阵存储的话稀疏就很浪费空间和遍历的时间。然后用BFS去入栈连同他自己这个结点,一共入栈7次。但是还是用矩阵写的快,而且难点是判断第几层
有一个原因造成部分错误,就是0.2f是四舍五入,如果写截断反而会报错 printf("%d: %0.2f%%\n", i, ((int)(percentage*100))/100.0);。
算百分比不能double = int/int,int/int得到的就是int,只不过变成double单纯加了个小数点再赋值的。这也是容易错误的地方。
#include 7-8 哈利·波特的考试
无向图的多元最短路径算法;如果图不连通,就直接输出0.小白专场
弗洛伊德算法模板:
bool Floyd_Standard(MGraph Graph, WeightType D[][Max], Vertex path[][Max])
{
Vertex i, j, k;
//初始化
for(i=0; i<Graph->Nv; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<Graph->Nv; j++)
{
D[i][j] = Graph->G[i][j];
path[i][j] = -1;
}
}
for(k=0; k<Graph->Nv; k++)
{
for(i=0; i<Graph->Nv; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<Graph->Nv; j++)
{
if(D[i][k]+D[k][j] < D[i][j])
{
D[i][j] = D[i][k] + D[k][j];
if(i==j && D[i][j]<0) //负值圈要不得
{
return false;
}
path[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
学习数据结构的定义,也正是因为这些数据结构代码很长。Floyed到底怎么回事?!!
#include 7-9 旅游规划
单源最短路径咯,那就迪杰斯特拉算法?但是为啥会保留两条最短的路径?,那么贪心的时候就还要考虑价格少。其实用弗洛伊德也能算,修改的也不多,但是先练习一下迪杰斯特拉算法。
#include 我只能说核心代码要反复看,跟着思路走,不然很容易忘!
7-10 公路村村通
这是一个最小生成树问题,特点是:1、无回路;2、n个顶点就有n-1条边;3、包含全部图里的点;4、生成树的所有边都在图里的;5、边的权重和最小。
最小生成树存在<-------->连通图
贪心算法,每次都找权重最小的边,但是约束有:1.只能用图中有的边;2.只能正好用掉顶点数减一条边;3.不能有回路。
Prim算法与Dijkstra算法具有相似的地方。稠密图更加划算。这篇讲的真不错,特别是后面那张图

这个要多复习呀,不然就忘啦
#include 当顶点和边同一数量级可以用Kruskal算法贪心。直接从最小权重的边在不构成回路情况下贪心每个边,最后由森林组成树。

7-11 关键活动
7-12 排序
三种语言写的快排模板
7-11 关键活动
没通过的案例和这位同学一样
懒猫老师数据结构
#include
i--;
}
}
}
ALGraph::~ALGraph()
{
ArcNode *p, *pre;
for(int i=0; i<vertexNum; i++)
{
p = adjList[i].firstEdge;
adjList[i].firstEdge = NULL;
while(p)
{
pre = p;
p = p->next;
delete pre;
}
}
delete [] adjList;
delete [] ve;
delete [] vl;
}
bool ALGraph::TopologicalSort(int result[], int &count)
{
int stack[MAX_VERTEX]; //把顶点对应下标压入栈
int top = -1;
int inVex;
int outVex;
ArcNode *p;
for(int i=0; i<vertexNum; i++)
{
ve[i] = 0; //最早发生时间初始化为0
}
//遍历顶点表,把入度为0的压入堆栈
for(int i=0; i<vertexNum; i++)
{
if(adjList[i].in == 0)
{
stack[++top] = i;
}
}
count = 0; //处理过的顶点
while(top != -1)
{
inVex = stack[top--];
result[count] = inVex; //拓扑排序的序列
count++;
p = adjList[inVex].firstEdge;
while(p)
{
outVex = p->adjvex;
adjList[outVex].in--;
if(adjList[outVex].in == 0)
{
stack[++top] = outVex;
}
if(ve[inVex]+p->weight > ve[outVex])
{
ve[outVex] = ve[inVex] + p->weight;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
if(count == vertexNum)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool ALGraph::GriticalPath()
{
int resultStack[MAX_VERTEX];
int resultTop;
ArcNode *p;
int i, count;
int inVex, outVex;
if(!TopologicalSort(resultStack, count))
{
return false;
}
// cout << "拓扑排序处理顺序为:";
// for(i=0; i
// cout << resultStack[i] << " ";
// cout << endl;
// cout << "ve数组值为:" << endl;
// for(i=0; i
// cout<<"ve[" << i << "]=" << ve[i] << endl;
resultTop = count - 1;
inVex = resultStack[resultTop--];
for(i=0; i<vertexNum; i++)
{
vl[i] = ve[inVex];
}
while(resultTop != -1)
{
inVex = resultStack[resultTop--];
p = adjList[inVex].firstEdge;
while(p)
{
outVex = p->adjvex;
if(vl[inVex]>vl[outVex] - p->weight)
{
vl[inVex] = vl[outVex] - p->weight;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
//输出关键路径
int sum = 0;
queue< int > q;
int head, tail;
bool flag = true;
for(inVex = 0; inVex<vertexNum; inVex++)
{
p = adjList[inVex].firstEdge;
while(p)
{
outVex = p->adjvex;
int weight = p->weight;
int ee = ve[inVex];
int el = vl[outVex]-weight;
if(ee == el)
{//当存在多条路径时
if(flag)
{
flag = false;
head = inVex+1;
tail = outVex+1;
sum += weight;
}
if(head == outVex+1)
{
head = inVex+1;
sum += weight; //有多条路径时会算错
}
if(tail == inVex+1)
{
tail = outVex+1;
sum += weight; //有多条路径时会算错
}
q.push(inVex+1);
q.push(outVex+1);
//cout << "<" << inVex+1 << ","<< outVex+1 << ">" << weight << " "; //因为是从0开始存,所以得+1再输出
}
p = p->next;
}
}
printf("%d\n", sum);
while(!q.empty())
{
printf("%d->", q.front());
q.pop();
printf("%d\n", q.front());
q.pop();
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int vertex[MAX_VERTEX];
int num, edge;
cin>>num>>edge;
for(int i=0; i<num; i++)
{
vertex[i] = i+1;
}
ALGraph graph(vertex, num, edge);
graph.inputEdges();
//graph.displayData();
if(!graph.GriticalPath())
{
cout << 0;
}
return 0;
}
7-13 统计工龄
傻了,开始还准备排个序,直接只有0到50的工龄开个数组去记录不就好了。
7-14 电话聊天狂人
陈越姥姥讲聊天狂人
总结
因为实习和毕设的原因刷题就暂停了,之后大概率不会使用Java做题了