【leetcode-二叉树遍历】二叉树的前序遍历/后序遍历/中序遍历/层序遍历/迭代器/ N 叉树的前序遍历/后序遍历
文章目录
-
- 二叉树的前序遍历
-
- 递归
- 迭代
- Morris 遍历
- 二叉树的后序遍历
-
- 递归
- 迭代
- Morris 遍历
- 二叉树的中序遍历
-
- 递归法
- 迭代法
- 二叉树的层序遍历
-
- 广度优先搜索
- 二叉树的锯齿层序遍历
-
- 广度优先搜索
- 二叉搜索树迭代器
-
- 迭代
- 递归扁平化
- N 叉树的前序遍历
-
- 递归
- 迭代
- N 叉树的后序遍历
-
- 递归
- 迭代
二叉树的前序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
递归
class Solution {
private List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return new ArrayList<>();
result.add(root.val);
preorderTraversal(root.left);
preorderTraversal(root.right);
return result;
}
}
迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {
while (node != null) {
result.add(node.val);
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
node = node.right;
}
return result;
}
}
Morris 遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null)
return result;
TreeNode p1 = root, p2 = null;
while (p1 != null) {
p2 = p1.left;
if (p2 != null) {
while (p2.right != null && p2.right != p1)
p2 = p2.right;
if (p2.right == null) {
result.add(p1.val);
p2.right = p1;
p1 = p1.left;
continue;
} else {
p2.right = null;
}
} else {
result.add(p1.val);
}
p1 = p1.right;
}
return result;
}
}
二叉树的后序遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历。
递归
class Solution {
private List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return new ArrayList<>();
postorderTraversal(root.left);
postorderTraversal(root.right);
result.add(root.val);
return result;
}
}
迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while(root != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(root != null){
result.add(root.val);
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.left;
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
Morris 遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
TreeNode p1 = root, p2 = null;
while (p1 != null) {
p2 = p1.left;
if (p2 != null) {
while (p2.right != null && p2.right != p1)
p2 = p2.right;
if (p2.right == null) {
p2.right = p1;
p1 = p1.left;
continue;
} else {
p2.right = null;
addPath(result, p1.left);
}
}
p1 = p1.right;
}
addPath(result, root);
return result;
}
public void addPath(List<Integer> res, TreeNode node) {
int count = 0;
while (node != null) {
++count;
res.add(node.val);
node = node.right;
}
int left = res.size() - count, right = res.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
int temp = res.get(left);
res.set(left, res.get(right));
res.set(right, temp);
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
二叉树的中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
递归法
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
recursion(result, root);
return result;
}
private void recursion(List<Integer> result, TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
recursion(result, root.left);
result.add(root.val);
recursion(result, root.right);
}
}
迭代法
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
result.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return result;
}
}
二叉树的层序遍历
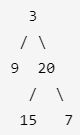
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例:
二叉树:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
返回其层序遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
广度优先搜索
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
while (size-- > 0) {
root = queue.poll();
level.add(root.val);
if (root.left != null)
queue.offer(root.left);
if (root.right != null)
queue.offer(root.right);
}
result.add(level);
}
return result;
}
}
二叉树的锯齿层序遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层序遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
返回锯齿形层序遍历如下:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
广度优先搜索
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean isOrderLeft = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
Deque<Integer> level = new LinkedList<>();
while (size-- > 0) {
root = queue.poll();
if (isOrderLeft)
level.offerLast(root.val);
else
level.offerFirst(root.val);
if (root.left != null)
queue.offer(root.left);
if (root.right != null)
queue.offer(root.right);
}
result.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(level));
isOrderLeft = !isOrderLeft;
}
return result;
}
}
二叉搜索树迭代器
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类BSTIterator ,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:
- BSTIterator(TreeNode root) 初始化 BSTIterator 类的一个对象。BST 的根节点 root 会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。
- boolean hasNext() 如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回 true ;否则返回 false 。
- int next()将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。
注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 next() 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字。
示例:
输入
[“BSTIterator”, “next”, “next”, “hasNext”, “next”, “hasNext”, “next”, “hasNext”, “next”, “hasNext”]
[[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]
输出
[null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false]
解释
BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False
迭代
class BSTIterator {
private TreeNode cur = null;
private Deque<TreeNode> stack;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
cur = root;
stack = new LinkedList<>();
}
public int next() {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
int res = cur.val;
cur = cur.right;
return res;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cur != null || !stack.isEmpty();
}
}
递归扁平化
class BSTIterator {
private int index;
private List<Integer> list;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
index = 0;
list = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, list);
}
public int next() {
return list.get(index++);
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < list.size();
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> arr) {
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left, arr);
arr.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, arr);
}
}
N 叉树的前序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的 前序遍历 。
N 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
进阶:
递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:[1,2,3,6,7,11,14,4,8,12,5,9,13,10]
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
preorder(root, result);
return result;
}
private void preorder(Node root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null)
return;
result.add(root.val);
for (Node child : root.children)
preorder(child, result);
}
}
迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
int size = cur.children.size();
while (size-- > 0)
stack.push(cur.children.get(size));
}
return result;
}
}
N 叉树的后序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
N 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
进阶:
递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:[2,6,14,11,7,3,12,8,4,13,9,10,5,1]
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, result);
return result;
}
private void postorder(Node root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null)
return;
for (Node child : root.children)
postorder(child, result);
result.add(root.val);
}
}
迭代
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
int size = cur.children.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
stack.push(cur.children.get(i));
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}