蓝桥杯零基础冲国赛-第21天
文章目录
-
- 二叉排序树
-
- 二叉查找树的插入
- 二叉查找树的删除
-
- 删除叶子节点
- 删除出度为1的节点
- 删除出度为2的节点
- AVL树
-
- 调整树高
-
- 左旋
- 右旋
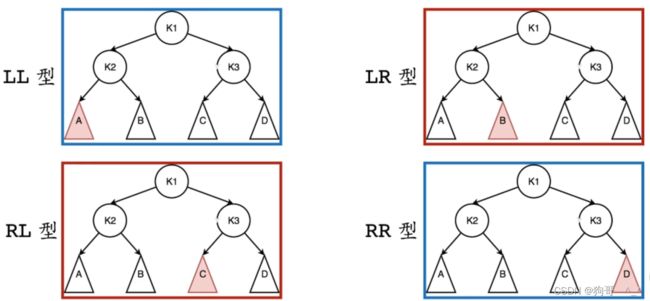
- AVL树-失衡类型
-
- AVL-LL型
- AVL-LR型
二叉排序树
名称:二叉排序树,二叉搜索树
性质:1、左子树 < 根节点(值)
2、右子树 > 根节点(值)
用途:解决与排名相关的检索需求
二叉查找树的插入
从根节点开始,根节点比较,如果小于根节点就跟左子树相比,如果小于根节点就跟左子树相比,如果要比的节点为空就在这个节点插入
//更新树高
void update_h(Node *root) {
root->h = max(root->left->h, root->right->h) + 1;
return ;
}
//插入
Node *insert(Node *root, int target) {
if (root == NIL) return getNewNode(target);
if (root->value == target) return root;
if (root->value > target) {//小于根节点放左节点
root->left = insert(root->left, target);
} else {//大于根节点放右子节点
root->right = insert(root->right, target);
}
update_h(root);
return root;
}
二叉查找树的删除
删除叶子节点
直接把要删除的这个节点置为空
删除出度为1的节点
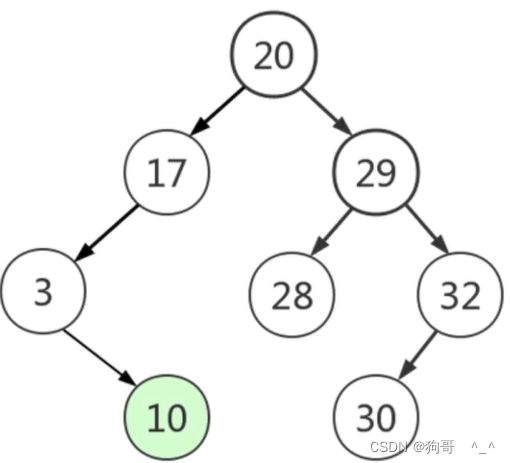
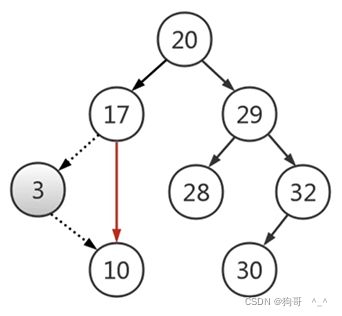
删除出度为1的节点。就提升要删除的这个节点的唯一子树。比如下面这个图,要删除3,那就提升10,10和3的父节点17比较,如果小于17就提升到左节点,大于就提升到右节点。

删除出度为2的节点
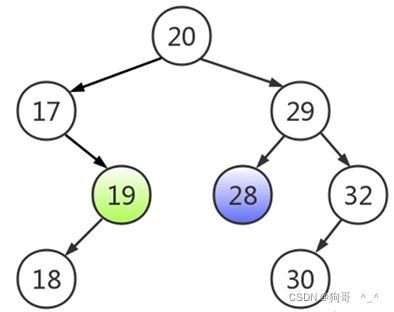
找到前驱或者后继替换后转换为度为1的节点。二叉排序树有这样一个性质,某个节点的前驱为左子树中的最大值,后继为右子树中的最小值,而又是二叉排序树的性质,左子树的最右侧的节点就是左子树的最大值,右子树的最左侧的节点就是右子树的最小值,所以只要分别循环,一直左节点或右节点循环直到到最后一个右节点或左节点。这样就找到了前驱或后继。找到前驱节点或后继节点后就把前驱节点或后继节点赋值给要删除的节点,然后删除前驱或后继就可以。替换为出度为1的节点后就可以按删除出度为1的节点的方式去操作.比如下面图删除的20这个节点
//删除
Node *erase(Node *root, int target) {
//找到要删除的节点
if (root == NIL) return root;
if (root->value > target) {
root->left = erase(root->left, target);
} else if (root->value <target) {
root->right = erase(root->right, target);
} else {
//出度为0的删除
if (root->left == NIL && root->right == NIL) {
free(root);
return NIL;
//出度为1的删除
} else if (root->left == NIL || root->right == NIL) {
//保存要删除节点的子节点
Node *tmp = (root->left != NIL ? root->left : root->right);
free(root);
return tmp;
//出度为2的删除
} else {
Node *tmp = get_pre(root->left);//得到入度为1的前驱节点/也可以找后继,不过这里用的是前驱
root->value = tmp->value;//替换前驱节点到要删除的节点
root->left = erase(root->left, tmp->value);//删除前驱节点
}
}
update_h(root);
return root;
}
AVL树
为什么有这个树:防止二叉查找树退化为链表
性质:1、左子树<根节点
2、右子树>根节点
3、| H(left) - H(right) | <= 1
优点:由于对每个节点的左右子树的树高做了限制,所以整颗树不会退化成一个链表
调整树高
左旋
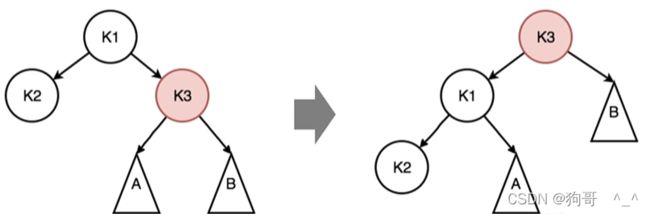
假设k2树高为1,A树高为2,B树高为2,k3树高就为3,那么k2和k3的树高就相差为2。所以要用左旋来减少树高差。
左选就是把树高比较大的那个子树(k3)作为树高比较小的那个子树(k2)的父节点,这时候树高比较大的那个节点(k3)可能会出现三个子节点,那么就把第二个子节点作为第一个子节点的子节点
代码演示:
//左旋,root为要旋转节点的父节点
Node *left_rotate(Node *root) {
Node *tmp = root->right;//保存要左旋节点为根节点的节点
root->right = tmp->left;//原先的根节点的右子节点存左旋节点的左节点,这样就不会出现三叉树了
tmp->left = root;//如果调整右旋节点为根节点
//更新树高
update_h(root);
update_h(tmp);
return tmp;
}
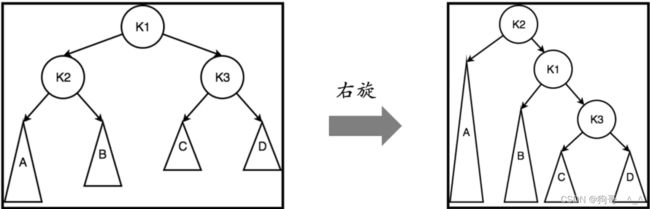
右旋
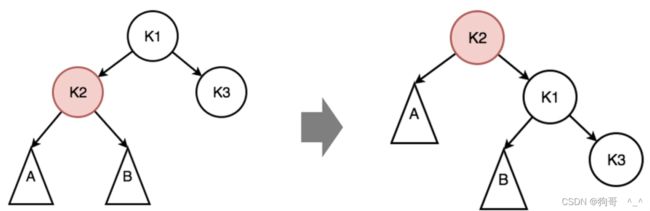
跟左旋差不多,只不过左旋是把右子节点调整为父节点,而右旋是把左子节点调整为父节点。
代码演示:
//右旋
Node *right_rotate(Node *root) {
Node *tmp = root->left;
root->left = tmp->right;
tmp->right = root;
update_h(root);
update_h(tmp);
return tmp;
}
那什么时候用左旋什么时候用右旋呢?我总结了四种失衡类型且给出了他们的旋转方式
AVL树-失衡类型
AVL-LL型
LL型就是一个根节点的左子树的左子树的树高最高且导致失衡。比如下面这张图,假设A的树高是3,B为2,C、D为1。
LL型的AVL调整方式:对一个根节点的左子树的左子树这个导致失衡的子节点的父节点进行一个右旋。(简称大左旋)
右旋正确性的数学推导:
//k2 k3 A B C D分别是以节点 k2 k3 A B C D作为根节点的树高
固定条件:
k2 = A + 1 ·······················①
k3 = max(C, D) + 1 ···············②
k2 = k3 + 2 ·····················③ //k2不可能等于 K3 + n(n>2), 因为在两子树的树高相差为2的时候就已经调整了。
A = B + 1 ························④
把①式和②式代入③式推得:
A + 1 = max(C, D) + 3 ············⑤
再把④式代入⑤式推得:
A = B + 1 = max(C, D) + 2
再看上面图形的右边这个图,A和k1、k1和A、K3和B都是平衡的
AVL-LR型
LR型就是一个根节点的左子树的右子树的树高最高且导致失衡。
LL型的AVL调整方式:对一个根节点的左子树的右子树这个导致失衡的节点先一个左旋再一个右旋。(简称小左旋再小右旋)
先进行左旋
再右旋
右旋正确性的数学推导:
//k2 k3 A B C D分别是以节点 k2 k3 A B C D作为根节点的树高
固定条件:
k3 = max(B, C) + 1 ············①
k3 = A + 1 ····················②
A = max(B, C) ················③
k2 = k3 + 1 ···················④
k2 = D + 2 ····················⑥
把②式代到④式得到
k2 = k3 + 1 = A + 2 ···········⑤
把⑥式代到⑤式得到
A = D
再看上面最后一个图,k2和k1平衡
RR、RL和LL、LR呈对称性
判断失衡类型代码演示:
Node *maitain(Node *root) {
if (abs(root->left->h - root->right->h) <= 1) return root;//不失衡
if (root->left->h > root->right->h) {//左子树更高,失衡条件是L
if (root->left->right->h > root->left->left->h) {
root->left = left_rotate(root->left);//LR
}
root = right_rotate(root);//LL,
} else {//右子树更高,失衡条件是R
if (root->right->left->h > root->right->right->h) {
root->right = right_rotate(root->right);//RL
}
root = left_rotate(root);//RR
}
return root;
}
二叉排序树更新为AVL树全部代码:
#include AVL题目练习:
leetcode:面试题04.06.后继者、450、1382、108、98、501、面试题04.09.、1008
预告:经典匹配算法:KMP、Sunday与shift-[And/or]