跳板(trampoline)实现原理
1.基础知识
1.1.虚拟内存
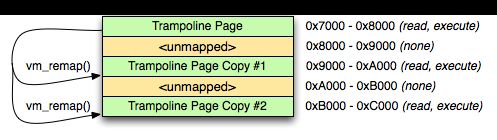
虚拟内存到物理内存之间的映射
从上面的图中可以得出一些结论:
- 无论是物理内存还是虚拟内存的管理都是以页为单位来进行管理的,并且一般情况下二者的尺寸保持一致。
- 操作系统为每个进程建立一张进程页表mmu,页表记录着虚拟内存页到物理内存页的映射关系以及相关的权限。并且页表是保存在物理内存页中的。因此所谓的虚拟内存分配其本质就是在页表中建立一个从虚拟内存页到物理内存页的映射关系而已。而所谓的remap就是将不同的虚拟页号映射到同一个物理页号而已。就如例子中进程1的第1页和第4页都是映射在同一个6号物理页中。
- 不同进程之间的不同虚拟页号可以映射到相同的物理页号。
- 操作系统还会维持一个全局物理页空闲信息表,用来记录当前未被分配的物理内存。这样一旦有进程需要分配虚拟内存空间时就从这个表中查找空闲的区域进行快速分配。
iOS的内核系统中有一层Mach子系统,Mach子系统是内核中的内核,它是一种微内核。Mach子系统中将进程(task)、线程、内存的管理都称之为一个对象,并且为每个对象都会分配一个被称之为port的端口号,所有对象之间的通信和功能调用都是通过port为标识的mach message来进行通信的。
1.2vm_remap
做到可以将动态分配出来的内存页具备可执行权限,就需要利用 vm_remap。 它的定义是这样的:
On Darwin, vm_remap() provides support for mapping an existing code page at new address, while retaining the existing page protections; using vm_remap(), we can create multiple copies of existing, executable code, placed at arbitrary addresses.
从定义中我们可以知道两点信息:
- vm_remap 可以让内存页具备被 map 的页的特性,如果是可执行页被 map,那新创建的页自然而然页具备了这个权限。
- vm_remap 也不是肆无忌惮的创建任何可执行的页,通俗理解,它只是一个 copy 映射。
上述图片引用自Implementing imp_implementationWithBlock()
因此,我们可以通过在编写代码的过程中,精心构造、预留在程序二进制的代码页,在运行时不断“复制映射”,来完成特殊的使命。
tramplion实现步骤
1.struct定义dataPage和textPage数据结构 构造textPage页函数实现(汇编或者c实现等等),使用数据结构来进行相关操作
2.vm_remap构造页:vm_allocate分配两页虚拟内存 dataPage数据页 textPage代码页 初始都是读写权限 vm_remap使textPage指向构造好的函数(可以是c实现,汇编实现等等)
3.textPage汇编实现:
• 取出原方法的 IMP A,保存起来
• 替换原方法 IMP 为一个新地址 B
• 当执行到该方法时,会跳转到新地址 B
• 在 B 中做一些自定义的操作
• 获取原先的 A,跳转过去
源码解析:
IMP imp_implementationWithBlock(id block)
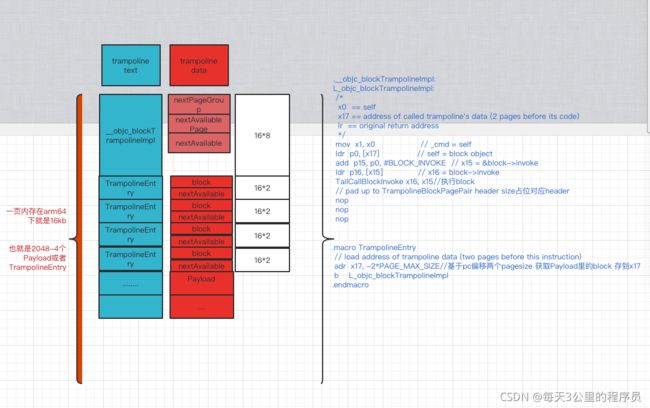
datapage和textpage内存结构
union Payload {
id block;
uintptr_t nextAvailable; // free list
};
一个data页的Payload对应一个TrampolineEntry
关键代码解析:
#pragma mark Public API
IMP imp_implementationWithBlock(id block)
{
// Block object must be copied outside runtimeLock
// because it performs arbitrary work.
//因为可以执行任意的工作 所以Block_copy必须在runtimeLock之外
block = Block_copy(block);
// Trampolines must be initialized outside runtimeLock
// because it calls dlopen().
//Trampolines是类TrampolinePointerWrapper的别名 Trampolines 初始化
Trampolines.Initialize();
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
return _imp_implementationWithBlockNoCopy(block);
}
TrampolineBlockPageGroup的初始化
TrampolineBlockPageGroup就是包含textpage和datapage的类
#pragma mark Trampoline Management Functions
static TrampolineBlockPageGroup *_allocateTrampolinesAndData()
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
vm_address_t dataAddress;
TrampolineBlockPageGroup::check();
//我们的最终映射大致如下所示:
//r/w数据
//从libobjc-trampolines.dylib映射的r/o可执行代码 (包含修正的从执行代码到数据之间的偏移值)
//
//更准确地说,它将如下所示:
//1页r/w数据
//1页libobjc-trampolines.dylib Mach-O标题
//N页蹦床代码,每个Argument模式一页
//libobjc trampolines代码段的其余部分为M页。
//内核要求我们每次重新remap整个可执行代码段。
//我们假设我们的代码从第二个可执行代码页开始,但是非常健壮针对可执行代码段末尾的其他添加。
ASSERT(HeadPageGroup == nil || HeadPageGroup->nextAvailablePage == nil);
auto textSource = Trampolines.textSegment();
auto textSourceSize = Trampolines.textSegmentSize();
auto dataSize = Trampolines.dataSize();
// Allocate a single contiguous region big enough to hold data+text.
//分配一个足够大的连续区域来容纳数据+可执行代码
kern_return_t result;
result = vm_allocate(mach_task_self(), &dataAddress,
dataSize + textSourceSize,
VM_FLAGS_ANYWHERE | VM_MAKE_TAG(VM_MEMORY_FOUNDATION));
if (result != KERN_SUCCESS) {
_objc_fatal("vm_allocate trampolines failed (%d)", result);
}
// Remap libobjc-trampolines' TEXT segment atop all
// but the first of the pages we just allocated:
//将libobjc trampolines的文本段重新映射到我们刚才分配的所有页面上,但第一个页除外:
//也就是dataSize那块区域除外 只remap textSourceSize那块内存(可执行代码)
vm_address_t textDest = dataAddress + dataSize;
vm_prot_t currentProtection, maxProtection;
result = vm_remap(mach_task_self(), &textDest,
textSourceSize,
0, VM_FLAGS_FIXED | VM_FLAGS_OVERWRITE,
mach_task_self(), textSource, TRUE,
¤tProtection, &maxProtection, VM_INHERIT_SHARE);
if (result != KERN_SUCCESS) {
_objc_fatal("vm_remap trampolines failed (%d)", result);
}
//把以dataAddress为起点的dataSize + textSourceSize长度的内存区域强转成TrampolineBlockPageGroup实例对象
auto *pageGroup = new ((void*)dataAddress) TrampolineBlockPageGroup;
//类似链表的数据结构 执行add操作
if (HeadPageGroup) {//如果已经存在一个头pageGroup,
TrampolineBlockPageGroup *lastPageGroup = HeadPageGroup;
while(lastPageGroup->nextPageGroup) {//取到链表的最后一个元素
lastPageGroup = lastPageGroup->nextPageGroup;
}
lastPageGroup->nextPageGroup = pageGroup;
//nextAvailablePage指针方便快速取到可操作的pageGroup
HeadPageGroup->nextAvailablePage = pageGroup;
} else {//如果不存在一个头pageGroup就自己当头pageGroup,
HeadPageGroup = pageGroup;
}
return pageGroup;
}
//主要逻辑
IMP _imp_implementationWithBlockNoCopy(id block)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
TrampolineBlockPageGroup *pageGroup =
getOrAllocatePageGroupWithNextAvailable();
//找到数据取可以存block的index
uintptr_t index = pageGroup->nextAvailable;
ASSERT(index >= pageGroup->startIndex() && index < pageGroup->endIndex());
TrampolineBlockPageGroup::Payload *payload = pageGroup->payload(index);//用于存储原来的block
uintptr_t nextAvailableIndex = payload->nextAvailable;
if (nextAvailableIndex == 0) {//第一次进入
// First time through (unused slots are zero). Fill sequentially.
// If the page is now full this will now be endIndex(), handled below.
nextAvailableIndex = index + 1;
}
pageGroup->nextAvailable = nextAvailableIndex;
if (nextAvailableIndex == pageGroup->endIndex()) {//页满
// PageGroup is now full (free list or wilderness exhausted)
// Remove from available page linked list
TrampolineBlockPageGroup *iterator = HeadPageGroup;
while(iterator && (iterator->nextAvailablePage != pageGroup)) {
iterator = iterator->nextAvailablePage;
}
if (iterator) {
iterator->nextAvailablePage = pageGroup->nextAvailablePage;
pageGroup->nextAvailablePage = nil;
}
}
payload->block = block;
return pageGroup->trampoline(argumentModeForBlock(block), index);
}