哈希
一、unordered系列关联式容器
set、map / unordered_set、unorder_map 区别:
- set、map底层结构是红黑树,unordered_set、unorder_map底层结构是哈希表
- unordered系列是:无序、单向迭代器、效率高( O(1) )
每个容器都自身提供swap成员函数,算法库也有swap,他们的区别是什么?
- s1.swap(s2) -----> 效率高,交换底层结构,比如树:交换根节点指针
- swap(s1,s2) -----> 效率低,利用第三个对象,深拷贝交换
二、底层结构
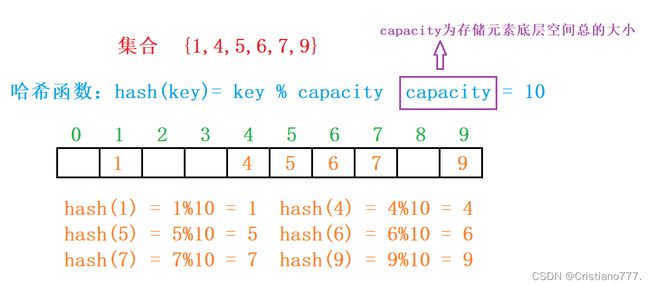
2.1 哈希概念
unordered系列的关联式容器之所以效率比较高,是因为其底层使用了哈希结构。
理想的搜索方法:可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中得到要搜索的元素。如果构造一种存储结构,通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立 一一映射的关系,那么在查找时通过该函数可以很快找到该元素当向该哈希结构中:1.插入:根据待插入元素的关键码,以此函数计算出该元素的存储位置并按此位置进行存放2.搜索:对元素的关键码进行同样的计算,把求得的函数值当做元素的存储位置,在结构中按此位置取元素比较,若关键码相等,则搜索成功该方式即为 哈希 (散列) 方法 ,哈希方法中使用的转换函数称为 哈希 (散列) 函数 ,构造出来的结构称为 哈希表 ( Hash Table )(或者称散列表)
2.2 哈希冲突解决
哈希冲突:不同关键字通过相同哈希哈数计算出相同的哈希地址。
引起哈希冲突的一个原因可能是:哈希函数设计不够合理。哈希函数设计原则:
解决哈希冲突两种常见的方法是:闭散列和开散列
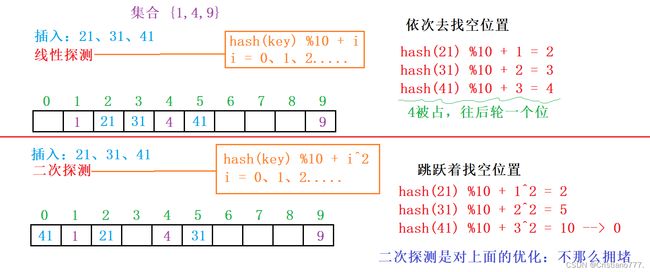
2.2.1 闭散列
又叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的“下一个” 空位置中去
1.线性探测
比如2.1中的场景,现在需要插入元素16,先通过哈希函数计算哈希地址,hashAddr为6,因此16理论上应该插在该位置,但是该位置已经放了值为6的元素,即发生哈希冲突。线性探测: 从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
优点: 实现简单
缺点:我占你的,你占他的,拥堵 (一旦发生哈希冲突,所有的冲突连在一起,容易产生数据“堆积”即:不同关键码占据了可利用的空位置,使得寻找某关键码的位置需要许多次比较,导致搜索效率降低)
注意:采用闭散列处理哈希冲突时,不能随便物理删除哈希表中已有的元素,若直接删除元素会影响其他元素的搜索。因此线性探测采用标记的伪删除法来删除一个元素。
模拟实现:
namespace Cris
{
enum State
{
EMPTY,
EXITS,
DELETE
};
template
struct HashData
{
pair _kv;
State _state;
};
template
struct DefalutHash
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//字符串特化后
template<>
struct DefalutHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
//131是验证过的随机数
hash = hash * 131 + ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
//HashFunc哈希函数,用来降低哈希冲突的概率,提高利用性
//哈希函数设计的越精妙,产生哈希冲突的可能性就越低
template >
class HashTable
{
typedef HashData Data;
public:
bool Insert(const pair& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
//负载因子到0.7以上就扩容
if (_tables.size() == 0 || _n * 10 / _tables.size() >= 7)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
//扩容之后需要重新映射
HashTable newHT;
for (auto& e : _tables)
{
if (e._state == EXITS)
{
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
}
}
newHT._tables.swap(_tables);
}
HashFunc hf;
//如果有kv.first为字符串,字符串转化为ASCII码值存储
size_t starti = hf(kv.first);
starti %= _tables.size();
size_t hashi = starti;
size_t i = 1;
// 线性探测/二次探测
while (_tables[hashi]._state == EXITS)
{
hashi = starti + i;
i++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._state = EXITS;
_n++;
return true;
}
Data* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
HashFunc hf;
size_t starti = hf(key);
starti %= _tables.size();
size_t hashi = starti;
size_t i = 1;
while (_tables[hash]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._state != DELETE && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
hashi = starti + i;
i++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Data* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = DELETE;
_n--;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
private:
vector _tables;
size_t _n = 0;//存储关键字数
};
}
2.二次探测
闭散列最大的缺陷就是空间利用率比较低,这也是哈希的缺陷。
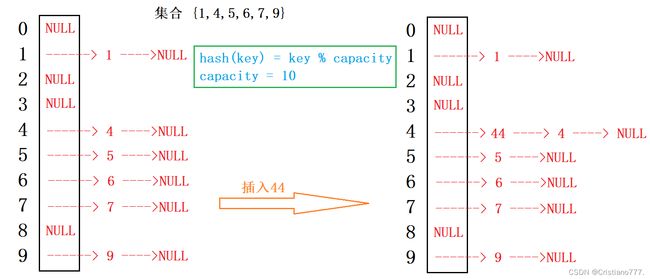
2.2.2 开散列
开散列法又叫链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。又称哈希桶。
数据不存在表中,表里面存储一个链表指针,冲突的数据链表形式挂起来
开散列(哈希桶的模拟实现):
template
struct DefaultHash
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
// key为字符串类型,需要将其转化为整形
template<>
struct DefaultHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
hash = hash * 131 + ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
namespace Bucket
{
template
struct HashNode
{
T _data;
HashNode* _next;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
template
class HashTable;
template
class __HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode Node;
typedef __HTIterator Self;
public:
Node* _node;
HashTable* _pht;
__HTIterator(Node* node, HashTable* pht)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
{}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
KeyOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data));
++hashi;
//找下一个不为空的桶
for (; hashi < _pht->_tables.size(); ++hashi)
{
if (_pht->_tables[hashi])
{
_node = _pht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
}
// 没有找到不为空的桶,用nullptr去做end标识
if (hashi == _pht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
// unordered_map ->HashTable, MapKeyOfT> _ht;
// unordered_set ->HashTable _ht;
template
class HashTable
{
template
friend class __HTIterator;
typedef HashNode Node;
public:
typedef __HTIterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
return iterator(cur, this);
}
}
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
//除留余数法,最好模一个素数
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
{
const int PRIMECOUNT = 28;
//每次快速取一个类似两倍关系的素数
static const size_t primeList[PRIMECOUNT] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
// 获取比prime大那一个素数
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < PRIMECOUNT; ++i)
{
if (primeList[i] > prime)
return primeList[i];
}
return primeList[i];
}
pair Insert(const T& data)
{
HashFunc hf;
KeyOfT kot;
iterator pos = Find(kot(data));
if (pos != end())
{
return make_pair(pos, false);
}
//负载因子 == 1时扩容
if (_tables.size() == _n)
{
//防止过多浪费
//size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
size_t newSize = GetNextPrime(_tables.size());
vector newTable;
newTable.resize(newSize, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newSize;
//头插
cur->_next = newTable[hashi];
newTable[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
newTable.swap(_tables);
}
size_t hashi = hf(kot(data));
hashi %= _tables.size();
// 头插到对应的桶即可
Node* newnode = new Node(data);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this), false);
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
KeyOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key);
hashi %= _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
{
return false;
}
HashFunc hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t hashi = hf(key);
hashi %= _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
};
} 开散列与闭散列比较 :开地址法必须保持大量的空闲空间以确保搜索效率,且表项所占空间又比指针大的多,所以使用 链地址法(哈希桶) 反而比 开地址法 节省存储空间。
三、模拟实现
3.1 unorder_map 、unorder_set改造
3.1.1 unorder_map模拟实现
#include "HashTable.h"
namespace Cris
{
template>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename Bucket::HashTable, MapKeyOfT, HashFunc>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair insert(const pair& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
Bucket::HashTable, MapKeyOfT, HashFunc> _ht;
}; 3.1.2 unorder_set模拟实现
namespace Cris
{
template>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename Bucket::HashTable::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
Bucket::HashTable _ht;
};
四、哈希的应用
4.1 位图
所谓位图,就是用每一位来存放某种状态,适用于海量数据,数据无重复的场景。通常是用来判断某个数据存不存在的。优点:节省空间、快
4.1.1位图的实现
namespace Cris
{
template
class Crisset
{
public:
Crisset()
{
// +1保证足够比特位,最多浪费8个
_bits.resize(N / 8 + 2, 0);
}
//x映射的位标记成1
void set(size_t x)
{
//x映射的比特位在第几个插入对象
size_t i = x / 8;
//x在插入第几个比特位
size_t j = x % 8;
_bits[i] |= (1 << j);
}
//x映射的位标记成0
void reset(size_t x)
{
//x映射的比特位在第几个char对象
size_t i = x / 8;
// x在char第几个比特位
size_t j = x % 8;
_bits[i] &= (~(1 << j));
}
//检测第x位是否为1
bool test(size_t x)
{
// x映射的比特位在第几个char对象
size_t i = x / 8;
// x在char第几个比特位
size_t j = x % 8;
return _bits[i] & (1 << j);
}
private:
std::vector _bits;
};
} 4.2 布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器:用多个哈希函数,将一个数据映射到位图结构中特点:高效地插入和查询,可以用来告诉你 “某样东西一定不存在或者可能存 在”位图一个key映射一个比特位,存在冲突,既误判。布隆过滤器一个key映射几个比特位,降低误判的概率,但还是在所难免
布隆过滤器的实现:
namespace bit
{
struct BKDRHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
// BKDR
size_t value = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
{
value *= 31;
value += ch;
}
return value;
}
};
struct APHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (long i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if ((i & 1) == 0)
{
hash ^= ((hash << 7) ^ s[i] ^ (hash >> 3));
}
else
{
hash ^= (~((hash << 11) ^ s[i] ^ (hash >> 5)));
}
}
return hash;
}
};
struct DJBHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 5381;
for (auto ch : s)
{
hash += (hash << 5) + ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
struct JSHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 1315423911;
for (auto ch : s)
{
hash ^= ((hash << 5) + ch + (hash >> 2));
}
return hash;
}
};
template
class BloomFilter
{
public:
void Set(const K& key)
{
size_t hash1 = HashFunc1()(key) % M;
size_t hash2 = HashFunc2()(key) % M;
size_t hash3 = HashFunc3()(key) % M;
size_t hash4 = HashFunc4()(key) % M;
//cout << hash1 << " " << hash2 << " " << hash3 << endl;
_bs.set(hash1);
_bs.set(hash2);
_bs.set(hash3);
_bs.set(hash4);
}
bool Test(const K& key)
{
size_t hash1 = HashFunc1()(key) % M;
if (_bs.test(hash1) == false)
{
return false;
}
size_t hash2 = HashFunc2()(key) % M;
if (_bs.test(hash2) == false)
{
return false;
}
size_t hash3 = HashFunc3()(key) % M;
if (_bs.test(hash3) == false)
{
return false;
}
size_t hash4 = HashFunc4()(key) % M;
if (_bs.test(hash4) == false)
{
return false;
}
// 可能存在误判
//不存在 绝对是真的,存在 可能是假的
return true;
}
//删除的话可能会影响别的值
//支持删除的话,布隆过滤器节约空间的特点就没了
//void Reset(const K& key);
private:
bitset _bs;
};