【数据结构】栈
Yan-英杰的主页
悟已往之不谏 知来者之可追
C++程序员,2024届电子信息研究生
目录
1.栈的概念及结构
2.栈的实现
函数的定义:
函数的实现
3.栈的练习题
 1.栈的概念及结构
1.栈的概念及结构
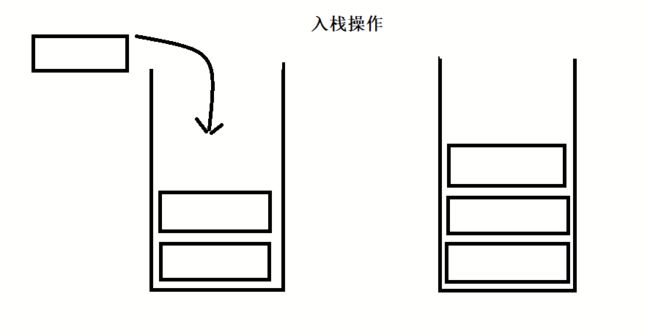
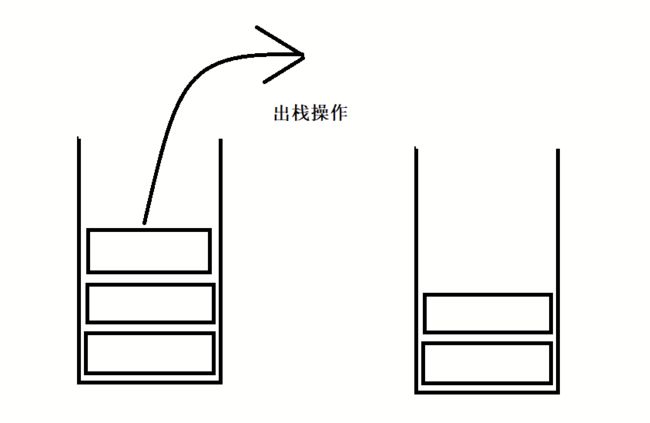
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作成为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(last in first Out)
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈同时也叫压栈/入栈。(数据存放在栈顶)。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。(先出栈的数据也在栈顶)
后入先出,先入后出
 2.栈的实现
2.栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小
函数的定义:
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
int* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* ps);
void STDestory(ST* ps);
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* ps);
int STSize(ST* ps);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
STDataType STTop(ST* ps); 函数的实现
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"stack.h"
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("fail:malloc");
return;
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;//top为0,说明栈顶空间在当前储存数据的位置
}
void STDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
//压栈
void STPush(ST* ps,STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("fail:realloc");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = ps->capacity * 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}栈的初始化,先暴力检查,开辟一块空间,存放栈数据,将栈的容量初试化为开辟好的空间
,栈顶为0(栈顶所在的位置)
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("fail:malloc");
return;
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;//top为0,说明栈顶空间在当前储存数据的位置
}栈的销毁,暴力检查栈是否为空,将栈空间的地址修改为空,容量修改为0,栈顶位置回到最初的位置
void STDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
判空,先暴力检查,当栈顶位置为0时,我们返回true,当其不为0时,返回false.
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
入栈/压栈,首先暴力检查,其次检查栈顶和栈的容量,当栈顶和栈空间的容量相等时,此时我们需要扩容,扩容完之后检查其是否为空,为空直接报错,将扩容完的地址赋给数组
//压栈
void STPush(ST* ps,STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("fail:realloc");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = ps->capacity * 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
} 3.栈的练习题
3.栈的练习题
有效的括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例 1:
输入:s = "()"
输出:true示例 2:
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true示例 3:
输入:s = "(]"
输出:false提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104s仅由括号'()[]{}'组成
代码实现:
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType * a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* ps);
void STDestory(ST* ps);
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* ps);
int STSize(ST* ps);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("fail:malloc");
return;
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;//top为0,说明栈顶空间在当前储存数据的位置
}
void STDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
//压栈
void STPush(ST* ps,STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("fail:realloc");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = ps->capacity * 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
bool isValid(char * s){
ST st;
STInit(&st);
while(*s)
{
if(*s == '('||*s=='['||*s == '{')
{
STPush(&st,*s);
}
else
{
if(STEmpty(&st))
{
STDestory(&st);
return false;
}
char top = STTop(&st);
STPop(&st);
if((*s == ')' && top != '(')||(*s == '}' && top != '{')||(*s == ']' && top != '['))
{
STDestory(&st);
return false;
}
}
++s;
}
bool ret = STEmpty(&st);
STDestory(&st);
return ret;
}代码思路:
1.在我们进行对比前,先创建一个栈空间,将其初始化
2.我们拿出该字符串对其进行循环
3.如果字符串中的某字符为([[我们对其进行压栈操作
4.否则进入非条件语句,栈空间为空,我们直接销毁栈空间,返回false,创建一个临时字符变量,对栈空间进行出栈操作,我们将出栈的字符与循环的字符进行对比,如果不同返回false,最后我们++字符串,进入到下一个字符5.如果栈空间与字符串均为空,则最后直接返回false