kNN分类器
文章目录
- 前言
- 一,kNN分类器的基本原理
- 二、kNN分类器
- 三、kNN分类器的实现
-
- 1.实现代码
- 2.运行结果
前言
KNN学习(K-Nearest Neighbor algorithm,K最邻近方法 )是一种统计分类器,对数据的特征变量的筛选尤其有效`
一,kNN分类器的基本原理
KNN的基本思想是:输入没有标签(标注数据的类别),即没有经过分类的新数据,首先提取新数据的特征并与測试集中的每一个数据特征进行比較;然后从測试集中提取K个最邻近(最类似)的数据特征标签,统计这K个最邻近数据中出现次数最多的分类,将其作为新的数据类别。
KNN的这样的基本思想有点类似于生活中的“物以类聚。人以群分”。
在KNN学习中,首先计算待分类数据特征与训练数据特征之间的距离并排序。 取出距离近期的K个训练数据特征。然后根据这K个相近训练数据特征所属类别来判定新样本类别:假设它们都属于一类,那么新的样本也属于这个类;否则,对每一个候选类别进行评分,依照某种规则确定新的样本的类别。
二、kNN分类器
通俗的讲,kNN就是一个简单粗暴的分类器(在下以为),以此图为例:
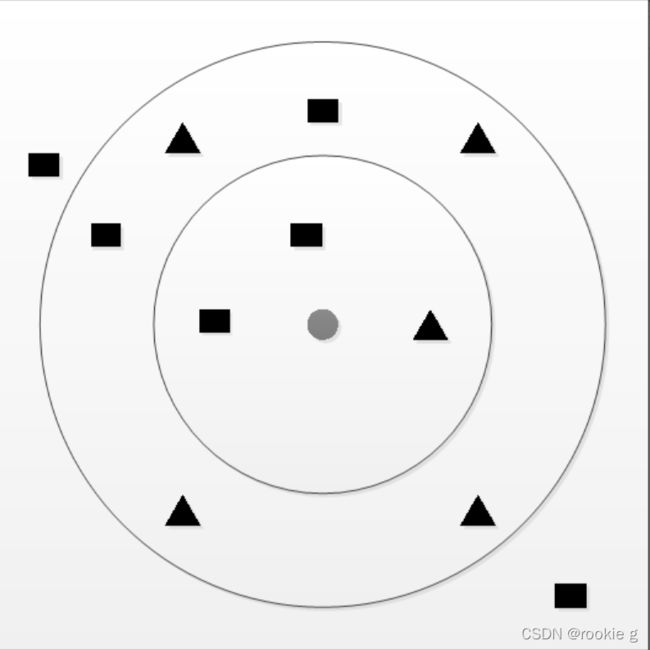
如上图,图中最小的那个圆圈代表新的待分类数据。三角形和矩形分别代表已知的类型,如今须要推断圆圈属于菱形那一类还是矩形那一类。
可是我该以什么样的根据来推断呢?
1.看离圆形近期(K=1)的那个类型是什么,由图可知,离圆形近期的是三角形,故将新数据判定为属于三角形这个类别。
2.看离圆形近期的3个数据(K=3)的类型是什么,由图可知离圆形近期的三个中间有两个是矩形,一个是三角形,故将新数据判定为属于矩形这个类别。
3.看离圆形近期的9个数据(K=9)的类型是什么,由图可知离圆形近期的9个数据中间,有五个是三角形。四个是矩形。故新数据判定为属于三角形这个类别。
上面所说的三种情况也能够说成是1-近邻方法、3-近邻方法、9-近邻方法。。。当然,K还能够取更大的值,当样本足够多,且样本类别的分布足够好的话,那么K值越大,划分的类别就越正确。而KNN中的K表示的就是划分数据时。所取类似样本的个数。
我们都知道,当K=1时,其抗干扰能力就较差。由于假如样本中出现了某种偶然的类别,那么新的数据非常有可能被分错。为了添加分类的可靠性,能够考察待測数据的K个近期邻样本 。统计这K个近邻样本中属于哪一类别的样本最多,就将样本X判属于该类。
当然。假设在样本有限的情况下,KNN算法的误判概率和距离的详细測度方法就有了直接关系。即用何种方式判定哪些数据与新数据近邻。不同的样本选择不同的距离測量函数,这能够提高分类的正确率。通常情况下,KNN能够采用Euclidean(欧几里得)、Manhattan(曼哈顿)、Mahalanobis(马氏距离)等距离用于计算。
三、kNN分类器的实现
1.实现代码
代码如下(示例):
package machinelearning.knn;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import weka.core.*;
/**
* kNN classification.
*
* @author goudiyuan.
*/
public class KnnClassification {
/**
* Manhattan distance.
*/
public static final int MANHATTAN = 0;
/**
* Euclidean distance.
*/
public static final int EUCLIDEAN = 1;
/**
* The distance measure.
*/
public int distanceMeasure = EUCLIDEAN;
/**
* A random instance;
*/
public static final Random random = new Random();
/**
* The number of neighbors.
*/
int numNeighbors = 7;
/**
* The whole dataset.
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* The training set. Represented by the indices of the data.
*/
int[] trainingSet;
/**
* The testing set. Represented by the indices of the data.
*/
int[] testingSet;
/**
* The predictions.
*/
int[] predictions;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename
* The arff filename.
*********************
*/
public KnnClassification(String paraFilename) {
try {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(fileReader);
// The last attribute is the decision class.
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
fileReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println("Error occurred while trying to read \'" + paraFilename
+ "\' in KnnClassification constructor.\r\n" + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
}// Of the first constructor
/**
*********************
* Get a random indices for data randomization.
*
* @param paraLength
* The length of the sequence.
* @return An array of indices, e.g., {4, 3, 1, 5, 0, 2} with length 6.
*********************
*/
public static int[] getRandomIndices(int paraLength) {
int[] resultIndices = new int[paraLength];
// Step 1. Initialize.
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
resultIndices[i] = i;
} // Of for i
// Step 2. Randomly swap.
int tempFirst, tempSecond, tempValue;
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
// Generate two random indices.
tempFirst = random.nextInt(paraLength);
tempSecond = random.nextInt(paraLength);
// Swap.
tempValue = resultIndices[tempFirst];
resultIndices[tempFirst] = resultIndices[tempSecond];
resultIndices[tempSecond] = tempValue;
} // Of for i
return resultIndices;
}// Of getRandomIndices
/**
*********************
* Split the data into training and testing parts.
*
* @param paraTrainingFraction
* The fraction of the training set.
*********************
*/
public void splitTrainingTesting(double paraTrainingFraction) {
int tempSize = dataset.numInstances();
int[] tempIndices = getRandomIndices(tempSize);
int tempTrainingSize = (int) (tempSize * paraTrainingFraction);
trainingSet = new int[tempTrainingSize];
testingSet = new int[tempSize - tempTrainingSize];
for (int i = 0; i < tempTrainingSize; i++) {
trainingSet[i] = tempIndices[i];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < tempSize - tempTrainingSize; i++) {
testingSet[i] = tempIndices[tempTrainingSize + i];
} // Of for i
}// Of splitTrainingTesting
/**
*********************
* Predict for the whole testing set. The results are stored in predictions.
* #see predictions.
*********************
*/
public void predict() {
predictions = new int[testingSet.length];
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
predictions[i] = predict(testingSet[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of predict
/**
*********************
* Predict for given instance.
*
* @return The prediction.
*********************
*/
public int predict(int paraIndex) {
int[] tempNeighbors = computeNearests(paraIndex);
int resultPrediction = simpleVoting(tempNeighbors);
return resultPrediction;
}// Of predict
/**
*********************
* The distance between two instances.
*
* @param paraI
* The index of the first instance.
* @param paraJ
* The index of the second instance.
* @return The distance.
*********************
*/
public double distance(int paraI, int paraJ) {
double resultDistance = 0;
double tempDifference;
switch (distanceMeasure) {
case MANHATTAN:
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - dataset.instance(paraJ).value(i);
if (tempDifference < 0) {
resultDistance -= tempDifference;
} else {
resultDistance += tempDifference;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
break;
case EUCLIDEAN:
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - dataset.instance(paraJ).value(i);
resultDistance += tempDifference * tempDifference;
} // Of for i
break;
default:
System.out.println("Unsupported distance measure: " + distanceMeasure);
}// Of switch
return resultDistance;
}// Of distance
/**
*********************
* Get the accuracy of the classifier.
*
* @return The accuracy.
*********************
*/
public double getAccuracy() {
// A double divides an int gets another double.
double tempCorrect = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
if (predictions[i] == dataset.instance(testingSet[i]).classValue()) {
tempCorrect++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return tempCorrect / testingSet.length;
}// Of getAccuracy
/**
************************************
* Compute the nearest k neighbors. Select one neighbor in each scan. In
* fact we can scan only once. You may implement it by yourself.
*
* @param paraK
* the k value for kNN.
* @param paraCurrent
* current instance. We are comparing it with all others.
* @return the indices of the nearest instances.
************************************
*/
public int[] computeNearests(int paraCurrent) {
int[] resultNearests = new int[numNeighbors];
boolean[] tempSelected = new boolean[trainingSet.length];
double tempDistance;
double tempMinimalDistance;
int tempMinimalIndex = 0;
// Select the nearest paraK indices.
for (int i = 0; i < numNeighbors; i++) {
tempMinimalDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < trainingSet.length; j++) {
if (tempSelected[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
tempDistance = distance(paraCurrent, trainingSet[j]);
if (tempDistance < tempMinimalDistance) {
tempMinimalDistance = tempDistance;
tempMinimalIndex = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
resultNearests[i] = trainingSet[tempMinimalIndex];
tempSelected[tempMinimalIndex] = true;
} // Of for i
System.out.println("The nearest of " + paraCurrent + " are: " + Arrays.toString(resultNearests));
return resultNearests;
}// Of computeNearests
/**
************************************
* Voting using the instances.
*
* @param paraNeighbors
* The indices of the neighbors.
* @return The predicted label.
************************************
*/
public int simpleVoting(int[] paraNeighbors) {
int[] tempVotes = new int[dataset.numClasses()];
for (int i = 0; i < paraNeighbors.length; i++) {
tempVotes[(int) dataset.instance(paraNeighbors[i]).classValue()]++;
} // Of for i
int tempMaximalVotingIndex = 0;
int tempMaximalVoting = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numClasses(); i++) {
if (tempVotes[i] > tempMaximalVoting) {
tempMaximalVoting = tempVotes[i];
tempMaximalVotingIndex = i;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return tempMaximalVotingIndex;
}// Of simpleVoting
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args
* Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
KnnClassification tempClassifier = new KnnClassification("D:/data/javasampledata-master/iris.arff");
tempClassifier.splitTrainingTesting(0.8);
tempClassifier.predict();
System.out.println("The accuracy of the classifier is: " + tempClassifier.getAccuracy());
}// Of main
}// Of class KnnClassification
2.运行结果
代码如下(示例):
The nearest of 15 are: [33, 14, 16, 5, 18, 32, 10]
The nearest of 113 are: [142, 121, 114, 83, 149, 123, 70]
The nearest of 122 are: [105, 118, 107, 135, 125, 117, 131]
The nearest of 110 are: [147, 115, 77, 145, 137, 141, 139]
The nearest of 101 are: [142, 121, 149, 83, 114, 123, 70]
The nearest of 55 are: [90, 96, 94, 78, 95, 99, 84]
The nearest of 126 are: [123, 83, 133, 63, 72, 149, 54]
The nearest of 127 are: [149, 70, 123, 83, 133, 56, 63]
The nearest of 128 are: [132, 104, 111, 137, 112, 147, 115]
The nearest of 129 are: [125, 107, 112, 139, 108, 124, 120]
The nearest of 138 are: [70, 149, 123, 78, 63, 91, 83]
The nearest of 103 are: [137, 111, 132, 147, 104, 134, 133]
The nearest of 59 are: [89, 94, 53, 80, 69, 64, 88]
The nearest of 24 are: [11, 29, 26, 7, 23, 39, 37]
The nearest of 71 are: [97, 82, 92, 99, 74, 67, 96]
The nearest of 66 are: [84, 96, 78, 95, 88, 94, 99]
The nearest of 25 are: [37, 34, 1, 12, 45, 49, 29]
The nearest of 61 are: [96, 78, 95, 99, 88, 97, 91]
The nearest of 116 are: [137, 147, 111, 112, 132, 104, 124]
The nearest of 9 are: [37, 34, 1, 12, 49, 29, 45]
The nearest of 140 are: [144, 120, 112, 104, 124, 139, 145]
The nearest of 58 are: [75, 54, 65, 76, 86, 74, 51]
The nearest of 8 are: [38, 3, 42, 47, 12, 45, 2]
The nearest of 143 are: [120, 124, 144, 104, 112, 100, 139]
The nearest of 119 are: [72, 83, 68, 123, 133, 142, 87]
The nearest of 13 are: [38, 42, 47, 2, 3, 12, 6]
The nearest of 146 are: [123, 111, 72, 83, 133, 142, 147]
The nearest of 130 are: [107, 125, 135, 105, 108, 120, 112]
The nearest of 102 are: [125, 120, 112, 124, 107, 139, 104]
The nearest of 30 are: [29, 37, 34, 3, 45, 12, 1]
The accuracy of the classifier is: 0.8666666666666667
链接: link.(大佬的搬运工)
