词云生成库wordcloud详解(三):IntegralOccupancyMap类——词云布局机制
当前wordcloud版本:1.81
词云绘制需求
在绘制词云时大概有以下需求:
- 词与词之间相互不重叠。
- 尽可能填充满整个空间,词与词之间间隙比较小。
- 空间可能按照某张图片布局,即所有词要布局在图片的轮廓内。
- 词绘制时可能要求随机位置、随机颜色。
- 词的绘制的尺寸可能跟词的一些特征相关。
根据词的特征控制词绘制位置、颜色、尺寸比较容易实现。
有效利用布局空间,避免词重叠可能需要图像处理的一些知识。
wordcloud词云布局机制——积分图
根据wordcloud源码可知,wordcloud模块中的IntegralOccupancyMap类负责根据文本词频和背景图对整个词云图进行布局。
理解该类就需要了解图像处理中的重要方法积分图(Integral Image),也叫做Summed Area Table,通常用于加速图像计算速度。在这里积分图主要用于检测重叠。下面通过一个案例方便理解。
对于原始图像(下图1),我们可以认为没有内容的像素值为0,有内的像素值为1,这样就构造了简易的像素图(下图2)。下图3为积分图,积分顾名思义就是求和。积分图中,每个单元的值,等于原图此位置左上角所有像素值之和(图3橙框的值 = 图2蓝框中所有值之和)。这个性质,能够帮助我们快速判断一个区域内有没有内容。
 如果一个矩形区域内没有内容,说明这个区域内所有像素值之和为零。根据积分图的特征,可以进行如下计算:用大矩形所有像素值之和,减去上方和左侧两个矩形像素值之和,再加上左上角小矩形像素值之和,就得到了所求区域内像素值之和。
如果一个矩形区域内没有内容,说明这个区域内所有像素值之和为零。根据积分图的特征,可以进行如下计算:用大矩形所有像素值之和,减去上方和左侧两个矩形像素值之和,再加上左上角小矩形像素值之和,就得到了所求区域内像素值之和。
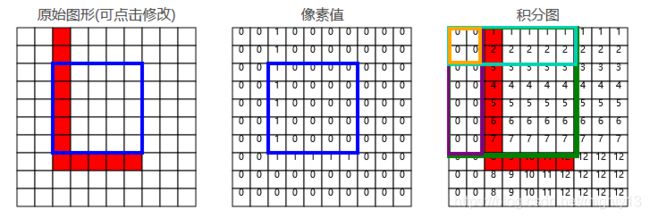
大矩形(绿色): 7
左侧矩形(紫色): 0
上方矩形(青色): 2
左上矩形(橙色): 0
目标矩形(蓝色): 7 - 0 - 2 + 0 = 5
这样,只需要进行四次取值和一次运算就能够判断某区域是否为空,比逐个像素检测快很多。
每个词都可以简便的计算出所占据的矩形区域(根据词的位置,字符内容、字体类型、字体大小、旋转度等),我们只需要对词云图整体的每个位置 (x,y) 进行计算,如果(x,y) 到(x + w - 1, y + h - 1) 这个矩形区域内没有内容,就能够放置这个词。
IntegralOccupancyMap类
IntegralOccupancyMap类负责根据文本词频和背景图对整个词云图进行布局。
与该类相关的模块为query_integral_image.cp37-win_amd64.pyd。
IntegralOccupancyMap类有三个方法:构造方法__init__、sample_position、update。
__init__方法
方法签名为def __init__(self, height, width, mask)。
该方法有3个参数:
height,width:词云图整体的高度和宽度,单位为像素。mask:蒙版图像。类型为numpy数组。
该方法会检测mask的值:
如果为None,即没有蒙版图像,则以(height,width)为形状构造二维全零数组integral。
如果不为None,即有蒙版图像,则构造蒙版图像的积分图数组integral。
sample_position方法
方法签名为def sample_position(self, size_x, size_y, random_state)
该方法有3个参数:
size_x,size_y:词所占的矩形区域范围。random_state:随机对象。
返回值为二元组。
该方法最终调用query_integral_image.cp37-win_amd64.pyd模块中的query_integral_image函数,由于.pyd文件无法反编译,因此看不到源码。但功能为随机生成词位置。
update方法
该方法的功能为根据蒙版图像和词的位置重新计算并更新积分图。
方法签名为def update(self, img_array, pos_x, pos_y)
该方法有3个参数:
img_array:图像数组。pos_x,pos_y:词区域的位置。
源码
class IntegralOccupancyMap(object):
def __init__(self, height, width, mask):
self.height = height
self.width = width
if mask is not None:
# the order of the cumsum's is important for speed ?!
self.integral = np.cumsum(np.cumsum(255 * mask, axis=1),
axis=0).astype(np.uint32)
else:
self.integral = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint32)
def sample_position(self, size_x, size_y, random_state):
return query_integral_image(self.integral, size_x, size_y,
random_state)
def update(self, img_array, pos_x, pos_y):
partial_integral = np.cumsum(np.cumsum(img_array[pos_x:, pos_y:],
axis=1), axis=0)
# paste recomputed part into old image
# if x or y is zero it is a bit annoying
if pos_x > 0:
if pos_y > 0:
partial_integral += (self.integral[pos_x - 1, pos_y:]
- self.integral[pos_x - 1, pos_y - 1])
else:
partial_integral += self.integral[pos_x - 1, pos_y:]
if pos_y > 0:
partial_integral += self.integral[pos_x:, pos_y - 1][:, np.newaxis]
self.integral[pos_x:, pos_y:] = partial_integral
参考文献
积分图部分内容,参考文章《你不知道的词云》https://python123.io/tutorials/word_cloud