spring-aop概述、aop面向切面编程
AOP,面向切面编程。面向切面编程是从动态角度考虑程序运行过程。
AOP 底层,就是采用动态代理模式实现的。采用了两种代理:JDK 的动态代理,与 CGLIB
的动态代理。
AOP 为 Aspect Oriented Programming 的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,可通过运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP 是 Spring 框架中的一个重要内容。利用 AOP
可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程
序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
面向切面编程,就是将交叉业务逻辑封装成切面,利用 AOP 容器的功能将切面织入到
主业务逻辑中。所谓交叉业务逻辑是指,通用的、与主业务逻辑无关的代码,如安全检查、
事务、日志、缓存等。
若不使用 AOP,则会出现代码纠缠,即交叉业务逻辑与主业务逻辑混合在一起。这样,
会使主业务逻辑变的混杂不清。
例如,转账,在真正转账业务逻辑前后,需要权限控制、日志记录、加载事务、结束事
务等交叉业务逻辑,而这些业务逻辑与主业务逻辑间并无直接关系。但,它们的代码量所占
比重能达到总代码量的一半甚至还多。它们的存在,不仅产生了大量的“冗余”代码,还大
大干扰了主业务逻辑---转账。
面向切面编程对有什么好处?
1.减少重复;
2.专注业务;
注意:面向切面编程只是面向对象编程的一种补充。
使用 AOP 减少重复代码,专注业务实现。

AOP 编程术语
接上一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/Sharpen__/article/details/109741343
(1) 切面(Aspect)
切面泛指交叉业务逻辑。上例中的事务处理、日志处理就可以理解为切面。常用的切面
是通知(Advice)。实际就是对主业务逻辑的一种增强。
(2) 连接点(JoinPoint)
连接点指可以被切面织入的具体方法。通常业务接口中的方法均为连接点。
(3) 切入点(Pointcut)
切入点指声明的一个或多个连接点的集合。通过切入点指定一组方法。
被标记为 final 的方法是不能作为连接点与切入点的。因为最终的是不能被修改的,不
能被增强的。
(4) 目标对象(Target)
目 标对象指将要被增强的对象 。即包含主业务逻辑的类的对象。上例中的StudentServiceImpl 的对象若被增强,则该类称为目标类,该类对象称为目标对象。当然,不被增强,也就无所谓目标不目标了。
(5) 通知(Advice)
通知表示切面的执行时间,Advice 也叫增强。上例中的 MyInvocationHandler 就可以理
解为是一种通知。换个角度来说,通知定义了增强代码切入到目标代码的时间点,是目标方
法执行之前执行,还是之后执行等。通知类型不同,切入时间不同。
切入点定义切入的位置,通知定义切入的时间。
AspectJ 对 AOP 的实现
对于 AOP 这种编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现。Spring 就是其中之一,可以完成面向
切面编程。然而,AspectJ 也实现了 AOP 的功能,且其实现方式更为简捷,使用更为方便,而且还支持注解式开发。所以,Spring 又将 AspectJ 的对于 AOP 的实现也引入到了自己的框架中。
在 Spring 中使用 AOP 开发时,一般使用 AspectJ 的实现方式。
aspectj框架实现aop的两种方式:
1.使用xml配置文件:配置全局事务
2.使用注解,我们在项目中要做aop功能,一般都使用注解,aspectj有5个注解。
AspectJ 简介:AspectJ 是一个优秀面向切面的框架,它扩展了 Java 语言,提供了强大的切面实现。
官网地址:http://www.eclipse.org/aspectj/
好处:1.(一种基于 Java 平台的面向切面编程的语言)
2.(兼容 Java 平台,可以无缝扩展)
3.(易学易用)
AspectJ 的通知类型
切面的执行时间,这个执行时间在规范中叫做Advice(通知、增强)
AspectJ 中常用的通知有五种类型:
(1)前置通知 @Before
(2)后置通知 @AfterReturning
(3)环绕通知 @Around
(4)异常通知 @AfterThrowing
(5)最终通知 @After
AspectJ 的切入点表达式
AspectJ 定义了专门的表达式用于指定切入点。表达式的原型是:
execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
解释:
modifiers-pattern] 访问权限类型
ret-type-pattern 返回值类型
declaring-type-pattern 包名类名
name-pattern(param-pattern) 方法名(参数类型和参数个数)
throws-pattern 抛出异常类型
?表示可选的部分以上表达式共 4 个部分。
execution(访问权限 方法返回值 方法声明(参数) 异常类型)
切入点表达式要匹配的对象就是目标方法的方法名。所以,execution 表达式中明显就
是方法的签名。注意,表达式中黑色文字表示可省略部分,各部分间用空格分开。在其中可
以使用以下符号。

举例:
execution(public * *(..))
指定切入点为:任意公共方法。
execution(* set*(..))
指定切入点为:任何一个以“set”开始的方法。
execution(* com.xyz.service.*.*(..))
指定切入点为:定义在 service 包里的任意类的任意方法。
execution(* com.xyz.service..*.*(..))
指定切入点为:定义在 service 包或者子包里的任意类的任意方法。“..”出现在类名中时,后
面必须跟“*”,表示包、子包下的所有类。
execution(* *..service.*.*(..))
指定所有包下的 serivce 子包下所有类(接口)中所有方法为切入点
execution(* *.service.*.*(..))
指定只有一级包下的 serivce 子包下所有类(接口)中所有方法为切入点
execution(* *.ISomeService.*(..))
指定只有一级包下的 ISomeSerivce 接口中所有方法为切入点
execution(* *..ISomeService.*(..))
指定所有包下的 ISomeSerivce 接口中所有方法为切入点
execution(* com.xyz.service.IAccountService.*(..))
指定切入点为:IAccountService 接口中的任意方法。
execution(* com.xyz.service.IAccountService+.*(..))
指定切入点为:IAccountService 若为接口,则为接口中的任意方法及其所有实现类中的任意
方法;若为类,则为该类及其子类中的任意方法。
execution(* joke(String,int)))
指定切入点为:所有的 joke(String,int)方法,且 joke()方法的第一个参数是 String,第二个参
数是 int。如果方法中的参数类型是 java.lang 包下的类,可以直接使用类名,否则必须使用
全限定类名,如 joke( java.util.List, int)。
execution(* joke(String,*)))
指定切入点为:所有的 joke()方法,该方法第一个参数为 String,第二个参数可以是任意类
型,如joke(String s1,String s2)和joke(String s1,double d2)都是,但joke(String s1,double d2,String
s3)不是。
execution(* joke(String,..)))
指定切入点为:所有的 joke()方法,该方法第一个参数为 String,后面可以有任意个参数且
参数类型不限,如 joke(String s1)、joke(String s1,String s2)和 joke(String s1,double d2,String s3)
都是。
execution(* joke(Object))
指定切入点为:所有的 joke()方法,方法拥有一个参数,且参数是 Object 类型。joke(Object ob)
是,但,joke(String s)与 joke(User u)均不是。
execution(* joke(Object+)))
指定切入点为:所有的 joke()方法,方法拥有一个参数,且参数是 Object 类型或该类的子类。
不仅 joke(Object ob)是,joke(String s)和 joke(User u)也是。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="someService" class="com.b204.ba01.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.b204.ba01.MyAspect"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
beans>
myAspect.java
/**
* @Aspect :是aspectj框架注解 作用:表示当前类是切面类 切面类:是用来给业务方法增加功能的类,在这个各类中
* 有切面的功能代码
* 位置:在类定义的上面
*/
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 定义方法,方法是实现切面功能的。
* 方法的定义要求:
* 1.公共方法public
* 2.方法没有返回值
* 3.方法名称自定义
* 4.方法可以有参数,也可以没有参数
* 如果有参数,参数不是自定义的,有几个参数类型都可以使用
*/
/**
* @Before:前置通知注解
* 属性:value,是切入点表达式,表示切面的功能执行的位置。
* 位置:在方法的上面
* 特点:
* 1.在目标方法之前先执行
* 2.不会改变目标方法的执行结果
* 3.不会影响目标方法的执行
*/
/*@Before(value = "execution(public void com.b204.ba01.SomeServiceImpl.doSome(String,Integer))")
public void myBefore(){
//切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("前置通知,切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+new Date());
}*/
/*@Before(value = "execution(void com.b204.ba01.SomeServiceImpl.doSome(String,Integer))")
public void myBefore(){
//切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("1=====前置通知,切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+new Date());
}*/
/*@Before(value = "execution(void *..SomeServiceImpl.doSome(String,Integer))")
public void myBefore(){
//切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("2===前置通知,切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+new Date());
}*/
@Before(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.do*(..))")
public void myBefore(){
//切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("3==前置通知,切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+new Date());
}
/*@Before(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.do*(..))")
public void myBefore02(){
//切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("3==前置通知,切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+new Date());
}*/
// 给所有的以ServiceImpl结尾的类加功能
@Before(value = "execution(* com.b204.ba01.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void myBefore03(){
//切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("3==前置通知,切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+new Date());
}
}
接口:
public interface SomeService {
void doSome(String name,Integer age);
}
接口实现类:
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doSome(String name,Integer age) {
//给doSome方法增加功能,在doSome()执行之前,输出方法的执行时间
System.out.println("目标方法doSome()======");
}
}
测试类;
public class MyTest01 {
@Test
public void test01(){
String config= "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeService proxy = (SomeService)ac.getBean("someService");
System.out.println(proxy.getClass().getName());
//通过我们的代理对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
proxy.doSome("Curry",24);
}
}
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 指定通知方法中的参数:JoinPoint
* JointPoint:业务方法,要加入切面功能的业务方法
*
* 作用:可以在通知方法中获取方法执行时的信息,例如方法名称,方法的实参
* 如果你的切面功能中需要用到方法的信息,就加入JoinPoint
* 这个JoinPoint参数的值由框架赋予,必须是第一个位置的参数
*/
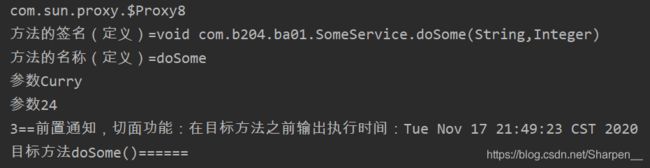
@Before(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.do*(..))")
public void myBefore(JoinPoint jp){
//获取方法的完整定义
System.out.println("方法的签名(定义)="+jp.getSignature());
System.out.println("方法的名称(定义)="+jp.getSignature().getName());
//获取方法的实参
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
for (Object tem:args){
System.out.println("参数"+tem);
}
//就是你切面要执行的功能代码
System.out.println("3==前置通知,切面功能:在目标方法之前输出执行时间:"+new Date());
}
}
测试文件:
String config= "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeService proxy = (SomeService)ac.getBean("someService");
System.out.println(proxy.getClass().getName());
//通过我们的代理对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
proxy.doSome("Curry",24);
结果:
AfterReturning:

MyAspect.java
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 后置通知定义方法,方法是实现切面功能的。
* 方法定义要求
* 1.公共方法public
* 2.方法没有返回值
* 3.方法名称自定义
* 4.方法可以有参数,也可以没有参数
* 如果有参数,参数不是自定义的,有几个参数类型可以使用
*/
/**
* @AfterReturning 后置通知
* 属性:1.value 切入点表达式
* 2.returning 自定义的变量 表示目标方法的返回值的
* 自定义变量名必须和通知方法的参数名一样
*
* 位置:在方法定义的上面
* 特点:
* 1.在目标方法之后执行的
* 2.能够获取到目标方法的返回值,可以根据返回值做不同的处理功能
* Object res=doOther()的调用返回
* 3.可以修改这个返回值
* @param res
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.doOther(..))",returning = "res")
public void myAfterReturning(Object res){
//Object res:目标方法执行后的返回值,根据返回值做你的切面的功能处理
System.out.println("后置通知:在目标方法之后执行的,回去的返回值是"+res);
if(res.equals("abcd")){
}else{
}
//修改目标方法的返回值,看一下是否会影响最后的方法的调用结果,结果不受影响,返回仍然是abcd
if(res!=null){
res="hello aspectj";
}
}
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.doOther2(..))",returning = "res")
public void myAfterReturning2(Object res){
//Object res:目标方法执行后的返回值,根据返回值做你的切面的功能处理
System.out.println("后置通知:在目标方法之后执行的,回去的返回值是"+res);
if(res.equals("abcd")){
}else{
}
//修改目标方法的返回值,看一下是否会影响最后的方法的调用结果
if(res!=null){
Student tem = (Student)res;
tem.setName("lebron");
tem.setAge(30);
}
}
}
接口:
public interface SomeService {
void doSome(String name, Integer age);
String doOther(String name,Integer age);
Student doOther2(String name,Integer age);
}
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doSome(String name,Integer age) {
//给doSome方法增加功能,在doSome()执行之前,输出方法的执行时间
System.out.println("目标方法doSome()======");
}
@Override
public String doOther(String name, Integer age) {
System.out.println("目标方法doOther()======");
return "abcd";
}
@Override
public Student doOther2(String name, Integer age) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("Curry");
student.setAge(25);
return student;
}
}
applicationContext.xml
<bean id="someService" class="com.b204.ba02.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.b204.ba02.MyAspect"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
beans>
测试文件:
@Test
public void test01(){
String config= "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeService proxy = (SomeService)ac.getBean("someService");
System.out.println(proxy.getClass().getName());
//通过我们的代理对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
String str= proxy.doOther("zhangsan",28);//结果是abcd
System.out.println("测试类的str="+str);
}
@Test
public void test02(){
String config= "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeService proxy = (SomeService)ac.getBean("someService");
System.out.println(proxy.getClass().getName());
//通过我们的代理对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
Student stu= proxy.doOther2("zhangsan",28);
System.out.println("测试类的stu="+stu);//结果受到影响
}
@Around 环绕通知-增强方法有 ProceedingJoinPoint参数
在目标方法执行之前之后执行。被注解为环绕增强的方法要有返回值,Object 类型。并且方法可以包含一个 ProceedingJoinPoint 类型的参数。接口 ProceedingJoinPoint 其有一个proceed()方法,用于执行目标方法。若目标方法有返回值,则该方法的返回值就是目标方法的返回值。最后,环绕增强方法将其返回值返回。该增强方法实际是拦截了目标方法的执行。
接口增加方法:
public interface SomeService {
String doFirst(String name,Integer age);
}
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public String doFirst(String name, Integer age) {
System.out.println("===doFirst()===");
return "doFirst";
}
}
MyAspect.java
/**
* @Aspect :是aspect框架中的注解
* 作用::表示当前类是切面类
* 切面类:是用来给业务方法增加功能的类,在这个类中有切面的功能代码
* 位置:在类定义的上面
*/
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 环绕通知方法的定义格式
* 1.public
* 2.必须有一个返回值,推荐使用object
* 3.方法名称自定义
* 4.方法有参数,固定的参数ProceedingJoinPoint
*/
/**
* @param pjp
* @return
* @Around 环绕通知
* 属性:value 切入点表达式
* 位置:在方法的定义什么
* 特点:1.它是功能最强的通知
* 2.在目标方法的前和后都能增强功能
* 3.控制目标方法是否被调用执行
* 4.修改原来的目标方法的执行结果,影响最后的调用结果
*
* 环绕通知,等同于jdk动态代理的,InvocationHandler接口
* 参数:ProceedingJoinPoint就等同于 jdk的 Method(用于执行目标方法)
* 返回值:就是目标方法的执行结果,可以被修改。
*
* 环绕通知:经常做事务,在目标方法之前开启事务,执行目标方法,在目标方法之后提交事务
*/
@Around(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.doFirst(..))")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//实现环绕通知的功能
String name="";
//获取第一个参数值
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
if (args != null && args.length > 1) {
Object arg = args[0];
name= (String) arg;
}
Object result = null;
System.out.println("环绕通知:在目标方法之前,输出时间:" + new Date());
//1.目标方法的调用
if("zhangsan".equals(name)){
//符合,调用目标方法
result = pjp.proceed();//method.invoke() Object result=doFirst();
}
System.out.println("环绕通知:在目标方法之后,输出时间:" + new Date());
//2.在目标方法的前或者后增加功能
//修改返回方法的执行结果
if(result!=null){
result = "hello world";
}
return result;
}
}
测试方法:
public void test01(){
String config= "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeService proxy = (SomeService)ac.getBean("someService");
//通过代理的对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
String first = proxy.doFirst("zhangsan", 20);
System.out.println(first);
}
public interface SomeService {
void doSecond();
}
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doSecond() {
System.out.println("执行方法doSecond"+(10/0));
}
}
MyAspect.java
/**
* @Aspect :是aspect框架中的注解
* 作用::表示当前类是切面类
* 切面类:是用来给业务方法增加功能的类,在这个类中有切面的功能代码
* 位置:在类定义的上面
*/
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 异常通知方法的定义格式
* 1.public
* 2.没有有一个返回值
* 3.方法名称自定义
* 4.方法有一个参数Exception,如果还有是JoinPoint
*/
/**
* @AfterThrowing :异常通知
* 属性:1.value 切入点表达式
* 2.throwing 自定义的变量 表示目标方法抛出的异常对象
* 变量名必须和方法的参数名一样
*
* 特点:1.在目标方法抛出异常时执行的
* 2.可以做异常的监控程序,监控目标方法执行时是不是有异常。
* 如果有异常,可以发送邮件,短信进行通知
*
* 执行的是:
* try{
* SomeServiceImpl.doSecond(..)
* }catch(Exception e){
* myAfterThrowing(e);
* }
*/
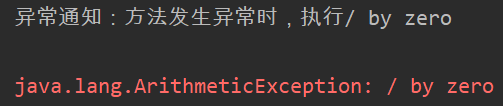
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.doSecond(..))",throwing = "ex")
public void myAfterThrowing(Exception ex){
System.out.println("异常通知:方法发生异常时,执行"+ex.getMessage());
//发送短信通知开发人员
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="someService" class="com.b204.ba04.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.b204.ba04.MyAspect"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
beans>
测试:
String config= "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeService proxy = (SomeService)ac.getBean("someService");
//通过代理的对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
proxy.doSecond();
public interface SomeService {
void doThird();
}
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doThird() {
System.out.println("执行方法doThird()");
}
}
MyAspect.java
/**
* @Aspect :是aspect框架中的注解
* 作用::表示当前类是切面类
* 切面类:是用来给业务方法增加功能的类,在这个类中有切面的功能代码
* 位置:在类定义的上面
*/
/**
* 最红通知方法的定义格式:
* 1.public
* 2.没有返回值
* 3.方法名称自定义
* 4.方法没有参数,如果有是JoinPoint
* 特点:
* 1.总是会执行
* 2.在目标方法之后执行
*
* try{
*
* }catch(Exception e){}finally{
* myAfter();
* }
*/
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@After(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.doThird(..))")
public void myAfter(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("最后通知:方法的执行总会被执行的代码");
//一般做资源清除工作的
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="someService" class="com.b204.ba05.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.b204.ba05.MyAspect"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
beans>
String config= "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeService proxy = (SomeService)ac.getBean("someService");
//通过代理的对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
proxy.doThird();
@Pointcut管理切入点
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@After(value = "mypt()")
public void myAfter(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("最后通知:方法的执行总会被执行的代码");
//一般做资源清除工作的
}
@Before(value = "mypt()")
public void myBefore(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("前置通知:目标方法之前先执行的");
}
/**
* @Pointcut: 定义和管理切入点,如果你的项目中有多个切入点表达式是重复的,可以复用的。
* 可以使用@Pointcut
*
* 属性:value 切入点表达式
* 位置:在自定义的方法上面
* 特点:当使用@Pointcut定义在一个方法的上面,此时这个方法的名称就是切入点表达式的别名。
* 其它的通知中,value属性就可以使用这个方法名称,代替切入点表达式了
*/
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.doThird(..))")
public void mypt(){
//mypt就是别名
}
}
如果把接口去掉,使用cglib的代理
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl{
public void doThird() {
System.out.println("执行方法doThird()");
}
}
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@After(value = "mypt()")
public void myAfter(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("最后通知:方法的执行总会被执行的代码");
//一般做资源清除工作的
}
@Before(value = "mypt()")
public void myBefore(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("前置通知:目标方法之前先执行的");
}
/**
* @Pointcut: 定义和管理切入点,如果你的项目中有多个切入点表达式是重复的,可以复用的。
* 可以使用@Pointcut
*
* 属性:value 切入点表达式
* 位置:在自定义的方法上面
* 特点:当使用@Pointcut定义在一个方法的上面,此时这个方法的名称就是切入点表达式的别名。
* 其它的通知中,value属性就可以使用这个方法名称,代替切入点表达式了
*/
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.doThird(..))")
public void mypt(){
//mypt就是别名
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="someService" class="com.b204.ba06.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.b204.ba06.MyAspect"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
beans>
测试:
String config= "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//从容器中获取目标对象
SomeServiceImpl proxy = (SomeServiceImpl)ac.getBean("someService");
System.out.println("proxy="+proxy.getClass().getName());
//通过代理的对象执行方法,实现目标方法执行时,增强了功能
proxy.doThird();
public interface SomeService {
void doThird();
}
//目标类
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doThird() {
System.out.println("执行方法doThird()");
}
}
MyAspect.java
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@After(value = "execution(* *..SomeServiceImpl.doThird(..))")
public void myAfter(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("最后通知:方法的执行总会被执行的代码");
//一般做资源清除工作的
}
}
配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="someService" class="com.b204.ba07.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.b204.ba07.MyAspect"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
beans>