C++STL详解(七)哈希封装模拟实现unordered_set&unordered_map
前言
在模拟实现unordered_set&unordered_map,我们还需要对之前的哈希表进行一定的改造。
1.unordered_set 模拟实现
哈希表模板参数控制
我们知道 unordered_set 是 K 模型的容器,而 unordered_map 是 KV 模型的容器。
而我们希望的是用一份哈希表代码就能同时封装出K模型和KV模型,因此哈希表接受的参数就得需要根据情况变化。
如果上层使用的是unordered_set容器,那么传入哈希表的模板参数就是key和key。
template<class K>
class unordered_set
{
public:
//...
private:
HashBucket<K, K> _hb; //传入底层哈希桶的是K和K
};
但如果上层使用的是unordered_map容器,那么传入哈希表的模板参数就是key以及key和value构成的键值对。
template<class K, class V>
class unordered_map
{
public:
//...
private:
HashTable<K, pair<K, V>> _ht; //传入底层哈希桶的是K以及K和V构成的键值对
};
因此,哈希表接受的模板的参数是T,T可以是K,也可以是pair
对于哈希表来说,不知道T具体是是吗,因此也就需要一个仿函数KeyOfT来获取T类型中的键值
template<class K, class V>
class unordered_map
{
//仿函数
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv) //返回键值对当中的键值key
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
//...
private:
HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _ht;
};
template<class K>
class unordered_set
{
//仿函数
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key) //返回键值key
{
return key;
}
};
public:
//...
private:
HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _ht;
};
此时哈希模板参数变成了
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class HashBucket
{
// ...
}
此外,哈希最重要的映射问题我们还没有解决,由于我们采用的是取模求余法来解决哈希冲突的。
这就需要获取将数组转化为对应的整数,而对哈希本身来说,接收到任何数据都是有可能的,因此哈希函数就不能固定,也得由参数来决定。
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
class HashTable
{
//...
}
默认成员函数
哈希表中有两个成员变量,当我们实例化一个对象时:
_tables会自动调用vector的默认构造函数完成初始化。_n会根据我们所给的缺省值被设置为0。
vector<Node*> _tables; //哈希表
size_t _n = 0; //哈希表中的有效元素个数
因此就不需要再写构造函数,使用默认生成的构造函数就足够了,但是由于我们后面需要写拷贝构造函数,写了拷贝构造函数后,默认的构造函数就不会生成了,而此时由于不存在默认构造函数,编译会通不过。因此,我们要么就写一个空的默认构造,或者default关键字显示指定生成默认构造函数。
//构造函数
HashTable() = default; //显示指定生成默认构造函数
拷贝构造函数:
由于我们实现的其实是哈希桶,也就是vector中是一个一个的节点。因此在拷贝时需要进行深拷贝,否则拷贝出来的哈希表和原哈希表中存储的都是同一批结点,析构时就会发生析构2次的问题。
拷贝也就是将原来表中的节点,一个个创建出来,并头插到新表中。
HashTable(const HashTable& ht)
{
KeyOfT kot;
_tables.resize(ht._tables.size());
for (int i = 0; i < ht._tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(kot(cur->_data));
tmp->_next = _tables[i];
_tables[i] = tmp;
_n++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
赋值重载:
实现赋值重载时,可以借助现代写法。
传参的时候会产生一次拷贝构造,然后将当前和ht的数据交换即可,完成的是深拷贝。
当赋值运算符重载函数调用结束后,拷贝构造出来的哈希表会因为出了作用域而被自动析构,此时原哈希表之前的数据也就顺势被释放了。
// 传参的时候有一次拷贝构造了
HashTable& operator=(HashTable ht)
{
if (this != &ht)
{
swap(_tables, ht._tables);
swap(_n, ht._n);
}
return *this;
}
析构函数:
vector虽然能自己调用其析构函数完成析构,但是vector里面的节点是手动new出来,因此也必须手动delete。
// vector free itself,but the node in the vector need free mannually
// these nodes are pointer , built-in type
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
// delete every bucket
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
迭代器
迭代器其实只是一个 HashNode 的封装。
注意,迭代器的封装中用到了哈希表的指针,因此需要对 HashTable 进行前置声明。
operator++ :
迭代器++的逻辑很简单,就是一个一个桶去遍历,当前节点的 next 不为空,就去下一个节点,为空就说明当前桶走完了,就去下一个桶。
// forward declaration __HTIterator__ use a pointer of HashTable
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
class __HTIterator__
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef __HTIterator__<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc> Self;
Node* _node;
HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc>* _pht;
public:
__HTIterator__() {} // deault construction
__HTIterator__(Node* node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc>* pht)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
{}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next != nullptr)
_node = _node->_next;
else // bucket is empty
{
KeyOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_tables.size();
hashi++;
// go to next not-empty bucket
for (; hashi < _pht->_tables.size(); ++hashi)
{
if (_pht->_tables[hashi] != nullptr) // find it
{
_node = _pht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
}
if (hashi == _pht->_tables.size()) // find not
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this; // return object itself
}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
HashTable 中,begin 返回的是第一个不为空的桶中的第一个节点。
迭代器需要用当前节点指针和哈希表指针去构造,也就是 this 指针。
typedef __HTIterator__<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc> iterator;
iterator begin()
{
// find the not-empty bucket
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
return iterator(cur, this); // convert the pointer of HashTable
}
// all empty bucket
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
注意:
由于正向迭代器中++运算符重载函数在寻找下一个结点时,会访问哈希表中的成员变量_table,而_table成员变量是哈希表的私有成员,因此我们需要将正向迭代器类声明为哈希表类的友元。
素数表
素数只能被 1 和它自己整除,这样再去计算 hashi 的时候,取模哈希表的大小,一定程度上能减少哈希冲突。
因此,有人搞了素数表出来,HashTable 的扩容已素数表中的大小来扩容。
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
{
const int PRIMECOUNT = 28;
static const size_t primeList[PRIMECOUNT] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
// get the primeNum larger than prime
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < PRIMECOUNT; ++i)
{
if (primeList[i] > prime)
return primeList[i];
}
return primeList[i];
}
HashTable 源代码
注意:
- 将哈希表中查找函数返回的结点指针,改为返回由结点指针和哈希表地址构成的迭代器。
- 将哈希表中插入函数的返回值类型,改为由正向迭代器类型和布尔类型所构成的键值对。
// unordered_map -> HashTable, MapKeyOfT, HashFunc> _ht;
// unordered_set -> HashTable _ht;
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
friend class __HTIterator__;
public:
typedef __HTIterator__<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc> iterator;
iterator begin()
{
// find the not-empty bucket
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
return iterator(cur, this); // convert the pointer of HashTable
}
// all empty bucket
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
// vector free itself,but the node in the vector need free mannually
// these nodes are pointer , built-in type
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
// delete every bucket
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
/*HashTable()
:_tables(0, nullptr)
, _n(0)
{}*/
// 也可以直接
HashTable() = default;
HashTable(const HashTable& ht)
{
KeyOfT kot;
_tables.resize(ht._tables.size());
for (int i = 0; i < ht._tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(kot(cur->_data));
tmp->_next = _tables[i];
_tables[i] = tmp;
_n++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
// 传参的时候有一次拷贝构造了
HashTable& operator=(HashTable ht)
{
if (this != &ht)
{
swap(_tables, ht._tables);
swap(_n, ht._n);
}
return *this;
}
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
{
const int PRIMECOUNT = 28;
static const size_t primeList[PRIMECOUNT] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
// get the primeNum larger than prime
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < PRIMECOUNT; ++i)
{
if (primeList[i] > prime)
return primeList[i];
}
return primeList[i];
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
HashFunc hf;
KeyOfT kot;
iterator pos = Find(kot(data)); // find the same
if (pos != end()) // not find --> insert
return make_pair(pos, false);
// load factor == 1,expand capacity.
// that is,one node per bucket on average
if (_tables.size() == _n)
{
//size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
size_t newSize = GetNextPrime(_tables.size());
if (newSize != _tables.size()) // avert surpass 4294967291ul
{
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(newSize, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur) // head-insert
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newSize;
cur->_next = newTables[hashi];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next; // update cur
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
newTables.swap(_tables);
}
}
size_t hashi = hf(kot(data));
hashi %= _tables.size();
// head-insert to the bucket counterpart
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
newNode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newNode;
++_n; // increase size
return make_pair(iterator(newNode, this), true);
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return iterator(nullptr, this);
KeyOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key);
// size_t hashi = HashFunc()(key); // anonymous object
hashi %= _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
return iterator(cur, this);
cur = cur->_next;
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return false;
HashFunc hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t hashi = hf(key);
hashi %= _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
// prev cur cur->next
if (prev == nullptr)
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
else
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
--_n;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
unordered_set源码
namespace yzq
{
template<class K, class HashFunc = HashBucketForSetMap::DefaultHash<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashBucketForSetMap::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, HashFunc>::iterator iterator;
public:
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
private:
HashBucketForSetMap::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, HashFunc> _ht;
};
struct Date
{
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator==(const Date& d) const
{
return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;
}
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
struct DateHashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const Date& d)
{
size_t hashi = 0;
hashi += d._year;
hashi *= 131;
hashi += d._month;
hashi *= 112;
hashi += d._day;
return hashi;
}
};
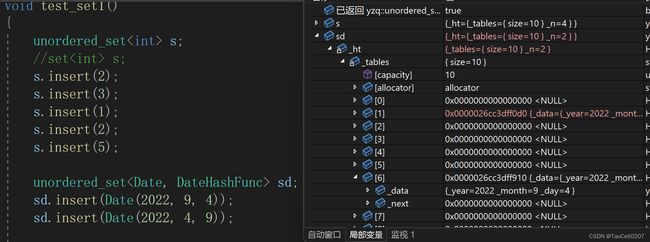
void test_set1()
{
unordered_set<int> s;
//set s;
s.insert(2);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(12);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(5);
unordered_set<Date, DateHashFunc> sd;
sd.insert(Date(2022, 9, 4));
sd.insert(Date(2022, 4, 9));
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
//auto it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl; // 1 12 2 3 5
//for (auto e : s)
//{
// cout << e << " ";
//}
//cout << endl; // 2 3 1 5
}
}
2.unordered_map 模拟实现
unordered_map源码
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"
namespace yzq
{
template<class K, class V, class HashFunc = HashBucketForSetMap::DefaultHash<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashBucketForSetMap::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT, HashFunc>::iterator iterator;
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
iterator erase(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Erase(kv);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
HashBucketForSetMap::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT, HashFunc> _ht;
};
void test_map1()
{
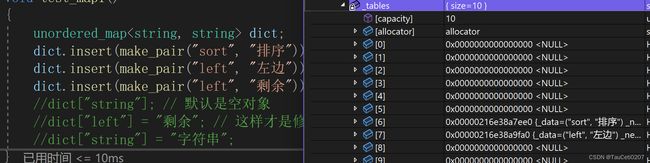
unordered_map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
dict.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
dict.insert(make_pair("left", "剩余")); // 已经有了left,不能再插进去
dict["string"]; // 默认是空对象
dict["left"] = "剩余"; // 这样才是修改
dict["string"] = "字符串";
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end()) // actually is HashNode*
{
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
for (const auto& kv : dict)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
}
}
尾声
写文不易,如果有帮助烦请点个赞~
Thanks♪(・ω・)ノ
由于笔者水平有限,在今后的博文中难免会出现错误之处,本人非常希望您如果发现错误,恳请留言批评斧正,希望和大家一起学习,一起进步ヽ( ̄ω ̄( ̄ω ̄〃)ゝ,期待您的留言评论。
附GitHub仓库链接