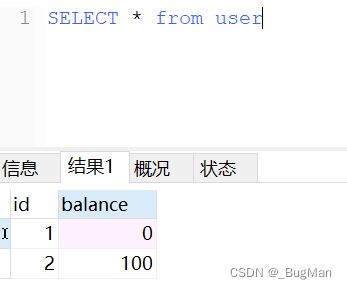
- Long类型前后端数据不一致
igotyback
前端
响应给前端的数据浏览器控制台中response中看到的Long类型的数据是正常的到前端数据不一致前后端数据类型不匹配是一个常见问题,尤其是当后端使用Java的Long类型(64位)与前端JavaScript的Number类型(最大安全整数为2^53-1,即16位)进行数据交互时,很容易出现精度丢失的问题。这是因为JavaScript中的Number类型无法安全地表示超过16位的整数。为了解决这个问
- LocalDateTime 转 String
igotyback
java开发语言
importjava.time.LocalDateTime;importjava.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;publicclassMain{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//获取当前时间LocalDateTimenow=LocalDateTime.now();//定义日期格式化器DateTimeFormatterformat
- mysql禁用远程登录
igotyback
mysql
去mysql库中的user表里,将host都改成localhost之后刷新权限FLUSHPRIVILEGES;
- Linux下QT开发的动态库界面弹出操作(SDL2)
13jjyao
QT类qt开发语言sdl2linux
需求:操作系统为linux,开发框架为qt,做成需带界面的qt动态库,调用方为java等非qt程序难点:调用方为java等非qt程序,也就是说调用方肯定不带QApplication::exec(),缺少了这个,QTimer等事件和QT创建的窗口将不能弹出(包括opencv也是不能弹出);这与qt调用本身qt库是有本质的区别的思路:1.调用方缺QApplication::exec(),那么我们在接口
- DIV+CSS+JavaScript技术制作网页(旅游主题网页设计与制作)云南大理
STU学生网页设计
网页设计期末网页作业html静态网页html5期末大作业网页设计web大作业
️精彩专栏推荐作者主页:【进入主页—获取更多源码】web前端期末大作业:【HTML5网页期末作业(1000套)】程序员有趣的告白方式:【HTML七夕情人节表白网页制作(110套)】文章目录二、网站介绍三、网站效果▶️1.视频演示2.图片演示四、网站代码HTML结构代码CSS样式代码五、更多源码二、网站介绍网站布局方面:计划采用目前主流的、能兼容各大主流浏览器、显示效果稳定的浮动网页布局结构。网站程
- 【华为OD机试真题2023B卷 JAVA&JS】We Are A Team
若博豆
java算法华为javascript
华为OD2023(B卷)机试题库全覆盖,刷题指南点这里WeAreATeam时间限制:1秒|内存限制:32768K|语言限制:不限题目描述:总共有n个人在机房,每个人有一个标号(1<=标号<=n),他们分成了多个团队,需要你根据收到的m条消息判定指定的两个人是否在一个团队中,具体的:1、消息构成为:abc,整数a、b分别代
- 关于城市旅游的HTML网页设计——(旅游风景云南 5页)HTML+CSS+JavaScript
二挡起步
web前端期末大作业javascripthtmlcss旅游风景
⛵源码获取文末联系✈Web前端开发技术描述网页设计题材,DIV+CSS布局制作,HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业|游景点介绍|旅游风景区|家乡介绍|等网站的设计与制作|HTML期末大学生网页设计作业,Web大学生网页HTML:结构CSS:样式在操作方面上运用了html5和css3,采用了div+css结构、表单、超链接、浮动、绝对定位、相对定位、字体样式、引用视频等基础知识JavaScrip
- HTML网页设计制作大作业(div+css) 云南我的家乡旅游景点 带文字滚动
二挡起步
web前端期末大作业web设计网页规划与设计htmlcssjavascriptdreamweaver前端
Web前端开发技术描述网页设计题材,DIV+CSS布局制作,HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业游景点介绍|旅游风景区|家乡介绍|等网站的设计与制作HTML期末大学生网页设计作业HTML:结构CSS:样式在操作方面上运用了html5和css3,采用了div+css结构、表单、超链接、浮动、绝对定位、相对定位、字体样式、引用视频等基础知识JavaScript:做与用户的交互行为文章目录前端学习路线
- MYSQL面试系列-04
king01299
面试mysql面试
MYSQL面试系列-0417.关于redolog和binlog的刷盘机制、redolog、undolog作用、GTID是做什么的?innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit及sync_binlog参数意义双117.1innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit该变量定义了InnoDB在每次事务提交时,如何处理未刷入(flush)的重做日志信息(redolog)。它
- node.js学习
小猿L
node.jsnode.js学习vim
node.js学习实操及笔记温故node.js,node.js学习实操过程及笔记~node.js学习视频node.js官网node.js中文网实操笔记githubcsdn笔记为什么学node.js可以让别人访问我们编写的网页为后续的框架学习打下基础,三大框架vuereactangular离不开node.jsnode.js是什么官网:node.js是一个开源的、跨平台的运行JavaScript的运行
- SpringBlade dict-biz/list 接口 SQL 注入漏洞
文章永久免费只为良心
oracle数据库
SpringBladedict-biz/list接口SQL注入漏洞POC:构造请求包查看返回包你的网址/api/blade-system/dict-biz/list?updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,md5(1),0x7e),1)=1漏洞概述在SpringBlade框架中,如果dict-biz/list接口的后台处理逻辑没有正确地对用户输入进行过滤或参数化查询(PreparedSta
- Java 重写(Override)与重载(Overload)
叨唧唧的
Java重写(Override)与重载(Overload)重写(Override)重写是子类对父类的允许访问的方法的实现过程进行重新编写,返回值和形参都不能改变。即外壳不变,核心重写!重写的好处在于子类可以根据需要,定义特定于自己的行为。也就是说子类能够根据需要实现父类的方法。重写方法不能抛出新的检查异常或者比被重写方法申明更加宽泛的异常。例如:父类的一个方法申明了一个检查异常IOExceptio
- 简单了解 JVM
记得开心一点啊
jvm
目录♫什么是JVM♫JVM的运行流程♫JVM运行时数据区♪虚拟机栈♪本地方法栈♪堆♪程序计数器♪方法区/元数据区♫类加载的过程♫双亲委派模型♫垃圾回收机制♫什么是JVMJVM是JavaVirtualMachine的简称,意为Java虚拟机。虚拟机是指通过软件模拟的具有完整硬件功能的、运行在一个完全隔离的环境中的完整计算机系统(如:JVM、VMwave、VirtualBox)。JVM和其他两个虚拟机
- 关于Mysql 中 Row size too large (> 8126) 错误的解决和理解
秋刀prince
mysqlmysql数据库
提示:啰嗦一嘴,数据库的任何操作和验证前,一定要记得先备份!!!不会有错;文章目录问题发现一、问题导致的可能原因1、页大小2、行格式2.1compact格式2.2Redundant格式2.3Dynamic格式2.4Compressed格式3、BLOB和TEXT列二、解决办法1、修改页大小(不推荐)2、修改行格式3、修改数据类型为BLOB和TEXT列4、其他优化方式(可以参考使用)4.1合理设置数据
- 1分钟解决 -bash: mvn: command not found,在Centos 7中安装Maven
Energet!c
开发语言
1分钟解决-bash:mvn:commandnotfound,在Centos7中安装Maven检查Java环境1下载Maven2解压Maven3配置环境变量4验证安装5常见问题与注意事项6总结检查Java环境Maven依赖Java环境,请确保系统已经安装了Java并配置了环境变量。可以通过以下命令检查:java-version如果未安装,请先安装Java。1下载Maven从官网下载:前往Apach
- Java企业面试题3
马龙强_
java
1.break和continue的作用(智*图)break:用于完全退出一个循环(如for,while)或一个switch语句。当在循环体内遇到break语句时,程序会立即跳出当前循环体,继续执行循环之后的代码。continue:用于跳过当前循环体中剩余的部分,并开始下一次循环。如果是在for循环中使用continue,则会直接进行条件判断以决定是否执行下一轮循环。2.if分支语句和switch分
- JVM、JRE和 JDK:理解Java开发的三大核心组件
Y雨何时停T
Javajava
Java是一门跨平台的编程语言,它的成功离不开背后强大的运行环境与开发工具的支持。在Java的生态中,JVM(Java虚拟机)、JRE(Java运行时环境)和JDK(Java开发工具包)是三个至关重要的核心组件。本文将探讨JVM、JDK和JRE的区别,帮助你更好地理解Java的运行机制。1.JVM:Java虚拟机(JavaVirtualMachine)什么是JVM?JVM,即Java虚拟机,是Ja
- Java面试题精选:消息队列(二)
芒果不是芒
Java面试题精选javakafka
一、Kafka的特性1.消息持久化:消息存储在磁盘,所以消息不会丢失2.高吞吐量:可以轻松实现单机百万级别的并发3.扩展性:扩展性强,还是动态扩展4.多客户端支持:支持多种语言(Java、C、C++、GO、)5.KafkaStreams(一个天生的流处理):在双十一或者销售大屏就会用到这种流处理。使用KafkaStreams可以快速的把销售额统计出来6.安全机制:Kafka进行生产或者消费的时候会
- 白骑士的Java教学基础篇 2.5 控制流语句
白骑士所长
Java教学java开发语言
欢迎继续学习Java编程的基础篇!在前面的章节中,我们了解了Java的变量、数据类型和运算符。接下来,我们将探讨Java中的控制流语句。控制流语句用于控制程序的执行顺序,使我们能够根据特定条件执行不同的代码块,或重复执行某段代码。这是编写复杂程序的基础。通过学习这一节内容,你将掌握如何使用条件语句和循环语句来编写更加灵活和高效的代码。条件语句条件语句用于根据条件的真假来执行不同的代码块。if语句‘
- python语法——三目运算符
HappyRocking
pythonpython三目运算符
在java中,有三目运算符,如:intc=(a>b)?a:b表示c取两者中的较大值。但是在python,不能直接这样使用,估计是因为冒号在python有分行的关键作用。那么在python中,如何实现类似功能呢?可以使用ifelse语句,也是一行可以完成,格式为:aifbelsec表示如果b为True,则表达式等于a,否则等于c。如:c=(aif(a>b)elseb)同样是完成了取最大值的功能。
- spring如何整合druid连接池?
惜.己
springspringjunit数据库javaidea后端xml
目录spring整合druid连接池1.新建maven项目2.新建mavenModule3.导入相关依赖4.配置log4j2.xml5.配置druid.xml1)xml中如何引入properties2)下面是配置文件6.准备jdbc.propertiesJDBC配置项解释7.配置druid8.测试spring整合druid连接池1.新建maven项目打开IDE(比如IntelliJIDEA,Ecl
- ArrayList 源码解析
程序猿进阶
Java基础ArrayListListjava面试性能优化架构设计idea
ArrayList是Java集合框架中的一个动态数组实现,提供了可变大小的数组功能。它继承自AbstractList并实现了List接口,是顺序容器,即元素存放的数据与放进去的顺序相同,允许放入null元素,底层通过数组实现。除该类未实现同步外,其余跟Vector大致相同。每个ArrayList都有一个容量capacity,表示底层数组的实际大小,容器内存储元素的个数不能多于当前容量。当向容器中添
- Java爬虫框架(一)--架构设计
狼图腾-狼之传说
java框架java任务html解析器存储电子商务
一、架构图那里搜网络爬虫框架主要针对电子商务网站进行数据爬取,分析,存储,索引。爬虫:爬虫负责爬取,解析,处理电子商务网站的网页的内容数据库:存储商品信息索引:商品的全文搜索索引Task队列:需要爬取的网页列表Visited表:已经爬取过的网页列表爬虫监控平台:web平台可以启动,停止爬虫,管理爬虫,task队列,visited表。二、爬虫1.流程1)Scheduler启动爬虫器,TaskMast
- Java:爬虫框架
dingcho
Javajava爬虫
一、ApacheNutch2【参考地址】Nutch是一个开源Java实现的搜索引擎。它提供了我们运行自己的搜索引擎所需的全部工具。包括全文搜索和Web爬虫。Nutch致力于让每个人能很容易,同时花费很少就可以配置世界一流的Web搜索引擎.为了完成这一宏伟的目标,Nutch必须能够做到:每个月取几十亿网页为这些网页维护一个索引对索引文件进行每秒上千次的搜索提供高质量的搜索结果简单来说Nutch支持分
- MongoDB知识概括
GeorgeLin98
持久层mongodb
MongoDB知识概括MongoDB相关概念单机部署基本常用命令索引-IndexSpirngDataMongoDB集成副本集分片集群安全认证MongoDB相关概念业务应用场景:传统的关系型数据库(如MySQL),在数据操作的“三高”需求以及应对Web2.0的网站需求面前,显得力不从心。解释:“三高”需求:①Highperformance-对数据库高并发读写的需求。②HugeStorage-对海量数
- python怎么将png转为tif_png转tif
weixin_39977276
发国外的文章要求图片是tif,cmyk色彩空间的。大小尺寸还有要求。比如网上大神多,找到了一段代码,感谢!https://www.jianshu.com/p/ec2af4311f56https://github.com/KevinZc007/image2Tifimportjava.awt.image.BufferedImage;importjava.io.File;importjava.io.Fi
- SpringCloudAlibaba—Sentinel(限流)
菜鸟爪哇
前言:自己在学习过程的记录,借鉴别人文章,记录自己实现的步骤。借鉴文章:https://blog.csdn.net/u014494148/article/details/105484410Sentinel介绍Sentinel诞生于阿里巴巴,其主要目标是流量控制和服务熔断。Sentinel是通过限制并发线程的数量(即信号隔离)来减少不稳定资源的影响,而不是使用线程池,省去了线程切换的性能开销。当资源
- springboot+vue项目实战一-创建SpringBoot简单项目
苹果酱0567
面试题汇总与解析springboot后端java中间件开发语言
这段时间抽空给女朋友搭建一个个人博客,想着记录一下建站的过程,就当做笔记吧。虽然复制zjblog只要一个小时就可以搞定一个网站,或者用cms系统,三四个小时就可以做出一个前后台都有的网站,而且想做成啥样也都行。但是就是要从新做,自己做的意义不一样,更何况,俺就是专门干这个的,嘿嘿嘿要做一个网站,而且从零开始,首先呢就是技术选型了,经过一番思量决定选择-SpringBoot做后端,前端使用Vue做一
- JavaScript 中,深拷贝(Deep Copy)和浅拷贝(Shallow Copy)
跳房子的前端
前端面试javascript开发语言ecmascript
在JavaScript中,深拷贝(DeepCopy)和浅拷贝(ShallowCopy)是用于复制对象或数组的两种不同方法。了解它们的区别和应用场景对于避免潜在的bugs和高效地处理数据非常重要。以下是对深拷贝和浅拷贝的详细解释,包括它们的概念、用途、优缺点以及实现方式。1.浅拷贝(ShallowCopy)概念定义:浅拷贝是指创建一个新的对象或数组,其中包含了原对象或数组的基本数据类型的值和对引用数
- JAVA·一个简单的登录窗口
MortalTom
java开发语言学习
文章目录概要整体架构流程技术名词解释技术细节资源概要JavaSwing是Java基础类库的一部分,主要用于开发图形用户界面(GUI)程序整体架构流程新建项目,导入sql.jar包(链接放在了文末),编译项目并运行技术名词解释一、特点丰富的组件提供了多种可视化组件,如按钮(JButton)、文本框(JTextField)、标签(JLabel)、下拉列表(JComboBox)等,可以满足不同的界面设计
- ztree设置禁用节点
3213213333332132
JavaScriptztreejsonsetDisabledNodeAjax
ztree设置禁用节点的时候注意,当使用ajax后台请求数据,必须要设置为同步获取数据,否者会获取不到节点对象,导致设置禁用没有效果。
$(function(){
showTree();
setDisabledNode();
});
- JVM patch by Taobao
bookjovi
javaHotSpot
在网上无意中看到淘宝提交的hotspot patch,共四个,有意思,记录一下。
7050685:jsdbproc64.sh has a typo in the package name
7058036:FieldsAllocationStyle=2 does not work in 32-bit VM
7060619:C1 should respect inline and
- 将session存储到数据库中
dcj3sjt126com
sqlPHPsession
CREATE TABLE sessions (
id CHAR(32) NOT NULL,
data TEXT,
last_accessed TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
<?php
/**
* Created by PhpStorm.
* User: michaeldu
* Date
- Vector
171815164
vector
public Vector<CartProduct> delCart(Vector<CartProduct> cart, String id) {
for (int i = 0; i < cart.size(); i++) {
if (cart.get(i).getId().equals(id)) {
cart.remove(i);
- 各连接池配置参数比较
g21121
连接池
排版真心费劲,大家凑合看下吧,见谅~
Druid
DBCP
C3P0
Proxool
数据库用户名称 Username Username User
数据库密码 Password Password Password
驱动名
- [简单]mybatis insert语句添加动态字段
53873039oycg
mybatis
mysql数据库,id自增,配置如下:
<insert id="saveTestTb" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"
parameterType=&
- struts2拦截器配置
云端月影
struts2拦截器
struts2拦截器interceptor的三种配置方法
方法1. 普通配置法
<struts>
<package name="struts2" extends="struts-default">
&
- IE中页面不居中,火狐谷歌等正常
aijuans
IE中页面不居中
问题是首页在火狐、谷歌、所有IE中正常显示,列表页的页面在火狐谷歌中正常,在IE6、7、8中都不中,觉得可能那个地方设置的让IE系列都不认识,仔细查看后发现,列表页中没写HTML模板部分没有添加DTD定义,就是<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3
- String,int,Integer,char 几个类型常见转换
antonyup_2006
htmlsql.net
如何将字串 String 转换成整数 int?
int i = Integer.valueOf(my_str).intValue();
int i=Integer.parseInt(str);
如何将字串 String 转换成Integer ?
Integer integer=Integer.valueOf(str);
如何将整数 int 转换成字串 String ?
1.
- PL/SQL的游标类型
百合不是茶
显示游标(静态游标)隐式游标游标的更新和删除%rowtyperef游标(动态游标)
游标是oracle中的一个结果集,用于存放查询的结果;
PL/SQL中游标的声明;
1,声明游标
2,打开游标(默认是关闭的);
3,提取数据
4,关闭游标
注意的要点:游标必须声明在declare中,使用open打开游标,fetch取游标中的数据,close关闭游标
隐式游标:主要是对DML数据的操作隐
- JUnit4中@AfterClass @BeforeClass @after @before的区别对比
bijian1013
JUnit4单元测试
一.基础知识
JUnit4使用Java5中的注解(annotation),以下是JUnit4常用的几个annotation: @Before:初始化方法 对于每一个测试方法都要执行一次(注意与BeforeClass区别,后者是对于所有方法执行一次)@After:释放资源 对于每一个测试方法都要执行一次(注意与AfterClass区别,后者是对于所有方法执行一次
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(12)开发包
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*开发包
*包用于逻辑组合相关的PL/SQL类型(例如TABLE类型和RECORD类型)、PL/SQL项(例如游标和游标变量)和PL/SQL子程序(例如过程和函数)
*/
--包用于逻辑组合相关的PL/SQL类型、项和子程序,它由包规范和包体两部分组成
--建立包规范:包规范实际是包与应用程序之间的接口,它用于定义包的公用组件,包括常量、变量、游标、过程和函数等
--在包规
- 【EhCache二】ehcache.xml配置详解
bit1129
ehcache.xml
在ehcache官网上找了多次,终于找到ehcache.xml配置元素和属性的含义说明文档了,这个文档包含在ehcache.xml的注释中!
ehcache.xml : http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xml
ehcache.xsd : http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd
ehcache配置文件的根元素是ehcahe
ehcac
- java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderL
白糖_
javaeclipsespringtomcatWeb
今天学习spring+cxf的时候遇到一个问题:在web.xml中配置了spring的上下文监听器:
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
随后启动
- angular.element
boyitech
AngularJSAngularJS APIangular.element
angular.element
描述: 包裹着一部分DOM element或者是HTML字符串,把它作为一个jQuery元素来处理。(类似于jQuery的选择器啦) 如果jQuery被引入了,则angular.element就可以看作是jQuery选择器,选择的对象可以使用jQuery的函数;如果jQuery不可用,angular.e
- java-给定两个已排序序列,找出共同的元素。
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class CommonItemInTwoSortedArray {
/**
* 题目:给定两个已排序序列,找出共同的元素。
* 1.定义两个指针分别指向序列的开始。
* 如果指向的两个元素
- sftp 异常,有遇到的吗?求解
Chen.H
javajcraftauthjschjschexception
com.jcraft.jsch.JSchException: Auth cancel
at com.jcraft.jsch.Session.connect(Session.java:460)
at com.jcraft.jsch.Session.connect(Session.java:154)
at cn.vivame.util.ftp.SftpServerAccess.connec
- [生物智能与人工智能]神经元中的电化学结构代表什么?
comsci
人工智能
我这里做一个大胆的猜想,生物神经网络中的神经元中包含着一些化学和类似电路的结构,这些结构通常用来扮演类似我们在拓扑分析系统中的节点嵌入方程一样,使得我们的神经网络产生智能判断的能力,而这些嵌入到节点中的方程同时也扮演着"经验"的角色....
我们可以尝试一下...在某些神经
- 通过LAC和CID获取经纬度信息
dai_lm
laccid
方法1:
用浏览器打开http://www.minigps.net/cellsearch.html,然后输入lac和cid信息(mcc和mnc可以填0),如果数据正确就可以获得相应的经纬度
方法2:
发送HTTP请求到http://www.open-electronics.org/celltrack/cell.php?hex=0&lac=<lac>&cid=&
- JAVA的困难分析
datamachine
java
前段时间转了一篇SQL的文章(http://datamachine.iteye.com/blog/1971896),文章不复杂,但思想深刻,就顺便思考了一下java的不足,当砖头丢出来,希望引点和田玉。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- 小学5年级英语单词背诵第二课
dcj3sjt126com
englishword
money 钱
paper 纸
speak 讲,说
tell 告诉
remember 记得,想起
knock 敲,击,打
question 问题
number 数字,号码
learn 学会,学习
street 街道
carry 搬运,携带
send 发送,邮寄,发射
must 必须
light 灯,光线,轻的
front
- linux下面没有tree命令
dcj3sjt126com
linux
centos p安装
yum -y install tree
mac os安装
brew install tree
首先来看tree的用法
tree 中文解释:tree
功能说明:以树状图列出目录的内容。
语 法:tree [-aACdDfFgilnNpqstux][-I <范本样式>][-P <范本样式
- Map迭代方式,Map迭代,Map循环
蕃薯耀
Map循环Map迭代Map迭代方式
Map迭代方式,Map迭代,Map循环
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
蕃薯耀 2015年
- Spring Cache注解+Redis
hanqunfeng
spring
Spring3.1 Cache注解
依赖jar包:
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
- Guava中针对集合的 filter和过滤功能
jackyrong
filter
在guava库中,自带了过滤器(filter)的功能,可以用来对collection 进行过滤,先看例子:
@Test
public void whenFilterWithIterables_thenFiltered() {
List<String> names = Lists.newArrayList("John"
- 学习编程那点事
lampcy
编程androidPHPhtml5
一年前的夏天,我还在纠结要不要改行,要不要去学php?能学到真本事吗?改行能成功吗?太多的问题,我终于不顾一切,下定决心,辞去了工作,来到传说中的帝都。老师给的乘车方式还算有效,很顺利的就到了学校,赶巧了,正好学校搬到了新校区。先安顿了下来,过了个轻松的周末,第一次到帝都,逛逛吧!
接下来的周一,是我噩梦的开始,学习内容对我这个零基础的人来说,除了勉强完成老师布置的作业外,我已经没有时间和精力去
- 架构师之流处理---------bytebuffer的mark,limit和flip
nannan408
ByteBuffer
1.前言。
如题,limit其实就是可以读取的字节长度的意思,flip是清空的意思,mark是标记的意思 。
2.例子.
例子代码:
String str = "helloWorld";
ByteBuffer buff = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
Sy
- org.apache.el.parser.ParseException: Encountered " ":" ": "" at line 1, column 1
Everyday都不同
$转义el表达式
最近在做Highcharts的过程中,在写js时,出现了以下异常:
严重: Servlet.service() for servlet jsp threw exception
org.apache.el.parser.ParseException: Encountered " ":" ": "" at line 1,
- 用Java实现发送邮件到163
tntxia
java实现
/*
在java版经常看到有人问如何用javamail发送邮件?如何接收邮件?如何访问多个文件夹等。问题零散,而历史的回复早已经淹没在问题的海洋之中。
本人之前所做过一个java项目,其中包含有WebMail功能,当初为用java实现而对javamail摸索了一段时间,总算有点收获。看到论坛中的经常有此方面的问题,因此把我的一些经验帖出来,希望对大家有些帮助。
此篇仅介绍用
- 探索实体类存在的真正意义
java小叶檀
POJO
一. 实体类简述
实体类其实就是俗称的POJO,这种类一般不实现特殊框架下的接口,在程序中仅作为数据容器用来持久化存储数据用的
POJO(Plain Old Java Objects)简单的Java对象
它的一般格式就是
public class A{
private String id;
public Str