Linux Panic 机制解析
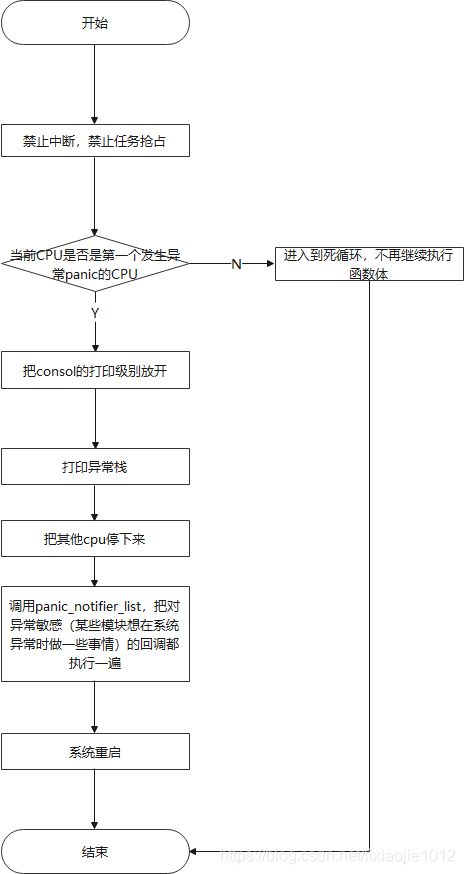
1.panic 操作
2.panic函数
主要功能:内核出现异常的时候输出异常信息,异常栈信息,挂起系统,代码主要流程和上面的流程图一致
/**
* panic - halt the system
* @fmt: The text string to print
*
* Display a message, then perform cleanups.
*
* This function never returns.
*/
void panic(const char *fmt, ...)
{
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(panic_lock);
static char buf[1024];
va_list args;
long i, i_next = 0;
int state = 0;
/*
* It's possible to come here directly from a panic-assertion and
* not have preempt disabled. Some functions called from here want
* preempt to be disabled. No point enabling it later though...
*
* Only one CPU is allowed to execute the panic code from here. For
* multiple parallel invocations of panic, all other CPUs either
* stop themself or will wait until they are stopped by the 1st CPU
* with smp_send_stop().
*/
if (!spin_trylock(&panic_lock))
panic_smp_self_stop(); /*同一时间只有一个核能执行panic代码,获取到锁的cpu先把自己stop掉,其他核要么自己stop自己 要么等待拿到锁的核执行smp_send_stop*/
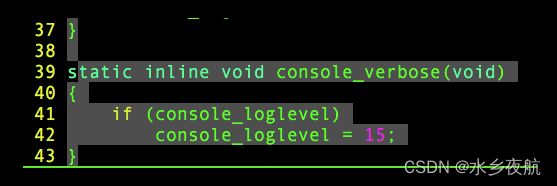
console_verbose();/* 提高打印等级 */
bust_spinlocks(1); /*bust_spinlocks()机制,用来避免系统crash以至于无法正常工作的时候还要进行不必要的等待spinlock操作*/
va_start(args, fmt);
/* 利用va_start指针遍历函数栈方式处理多参数
* 函数栈: (高地址)|-最后一个参数--... ...--第一个参数-|---返回地址---|---函数执行代码- --|(低地址)
*/
vsnprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), fmt, args);
va_end(args);
printk(KERN_EMERG "Kernel panic - not syncing: %s\n",buf);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_BUGVERBOSE /* 是否输出BUG行号和文件名 */
/*
* Avoid nested stack-dumping if a panic occurs during oops processing
*/
if (!test_taint(TAINT_DIE) && oops_in_progress <= 1)
dump_stack(); /*打印堆栈*/
#endif
/*
* If we have crashed and we have a crash kernel loaded let it handle
* everything else.
* Do we want to call this before we try to display a message?
*/
crash_kexec(NULL);/* 内核crash的操作 */
kmsg_dump(KMSG_DUMP_PANIC);/*kmsg日志保存到mtd设备去,需要提前分配好mtd存储*/
/*
* Note smp_send_stop is the usual smp shutdown function, which
* unfortunately means it may not be hardened to work in a panic
* situation.
*/
smp_send_stop(); /* 停止其他多核的工作 */
atomic_notifier_call_chain(&panic_notifier_list, 0, buf);/*注册了异常handle的函数都调用一次*/
bust_spinlocks(0);
if (!panic_blink)
panic_blink = no_blink;
if (panic_timeout > 0) {
/*
* Delay timeout seconds before rebooting the machine.
* We can't use the "normal" timers since we just panicked.
*/
printk(KERN_EMERG "Rebooting in %d seconds..", panic_timeout);
for (i = 0; i < panic_timeout * 1000; i += PANIC_TIMER_STEP) {
touch_nmi_watchdog();
if (i >= i_next) {
i += panic_blink(state ^= 1);
i_next = i + 3600 / PANIC_BLINK_SPD;
}
mdelay(PANIC_TIMER_STEP);
}
}
if (panic_timeout != 0) {
/*
* This will not be a clean reboot, with everything
* shutting down. But if there is a chance of
* rebooting the system it will be rebooted.
*/
emergency_restart();
}
/**
* panic_timeout = 0 进行死循环,抢占被禁止,CPU一直运行panic程序中运行。
*/
local_irq_enable();
for (i = 0; ; i += PANIC_TIMER_STEP) {
touch_softlockup_watchdog();
if (i >= i_next) {
i += panic_blink(state ^= 1);
i_next = i + 3600 / PANIC_BLINK_SPD;
}
mdelay(PANIC_TIMER_STEP);
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(panic);3. panic的打印和排查
![]()
① 内核代码可以放开 CONFIG_DEBUG_BUGVERBOSE宏,输出问题代码文件和位置,还可以了使用gdb打断点来排查
② 内核模块使用反汇编objdump -S XXX.o -g 可以将反汇编和代码放在一起比较
参考文章:
Kernel函数解析之panic_小小小小小小小小熊的博客-CSDN博客_kernel panic位置:panic()函数在panic.c文件中,该文件位于kernel/目录下;作用:该函数的主要作用是停止当前的系统运行,供系统监测到异常时调用。流程:【源码】:/** *panic - halt the system *@fmt: The text string to print * *Display a message, then perform cleanups. * *This function never returns. */void panic.https://blog.csdn.net/lixiaojie1012/article/details/119703588panic函数分析-xlzxlz2-ChinaUnix博客在阅读协议栈代码(内核版本2.6.38),在很多地方都看到panic调用,只是知道大体功能,从未具体分析过,也一直想把协议栈的分析过程写下来,很懒,就一有写,算今天是个开始吧。分析panic太艰难啦,涉及的东西太多啦。/** ![]() http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26377382-id-4913475.htmlkernel panic 分析解决方法_jerry_chg的博客-CSDN博客_kernel panickernel panic 表示Linux kernel走到了一个不知道该怎么走下一步的状况,一旦到这个情况,kernel就尽可能把它此时能获取的全部信息都打印出来,至于能打印出多少信息。 下面讲解几种用于查找出错函数定位的方法首先看一下出错的kernel panic 现象,下面是一个kernel panic的出错log:https://jerry-cheng.blog.csdn.net/article/details/19172725?spm=1001.2101.3001.6650.2&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7Edefault-2-19172725-blog-119703588.pc_relevant_default&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7Edefault-2-19172725-blog-119703588.pc_relevant_default&utm_relevant_index=5kernel crash 发生后的那些事(四)_shuai_wen的博客-CSDN博客
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26377382-id-4913475.htmlkernel panic 分析解决方法_jerry_chg的博客-CSDN博客_kernel panickernel panic 表示Linux kernel走到了一个不知道该怎么走下一步的状况,一旦到这个情况,kernel就尽可能把它此时能获取的全部信息都打印出来,至于能打印出多少信息。 下面讲解几种用于查找出错函数定位的方法首先看一下出错的kernel panic 现象,下面是一个kernel panic的出错log:https://jerry-cheng.blog.csdn.net/article/details/19172725?spm=1001.2101.3001.6650.2&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7Edefault-2-19172725-blog-119703588.pc_relevant_default&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7Edefault-2-19172725-blog-119703588.pc_relevant_default&utm_relevant_index=5kernel crash 发生后的那些事(四)_shuai_wen的博客-CSDN博客