力扣刷题笔记23—— 二叉树中和为某一值的路径/DFS和BFS/push_back和emplace_back的差异/移动构造函数
二叉树中和为某一值的路径/DFS和BFS/push_back和emplace_back的差异/移动构造函数
- 问题
- 示例代码
-
- 方法一深度优先搜索
- 方法二广度优先搜索
- push_back和emplace_back
- 移动构造函数
问题
来自力扣:
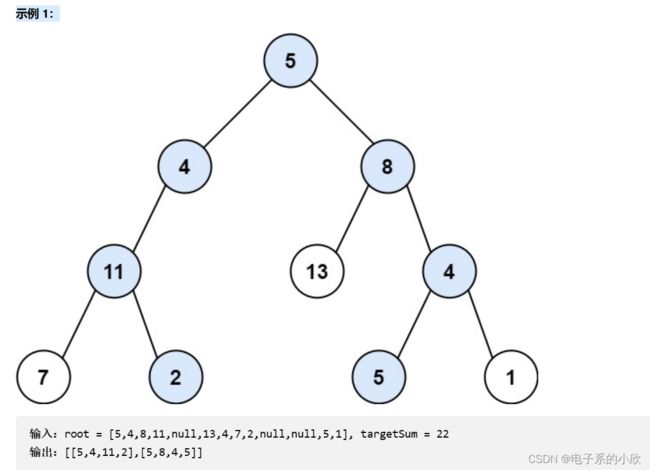
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例代码
最近的状态:简单的题不想记笔记,繁琐的题不想自己码代码。
这其实就是一个遍历的代码,遍历所有节点。
方法一深度优先搜索
采用深度优先搜索的方式,枚举每一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径。当我们遍历到叶子节点,且此时路径和恰为目标和时,我们就找到了一条满足条件的路径。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int target) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return;
}
path.emplace_back(root->val);
target -= root->val;
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && target == 0) {
ret.emplace_back(path);
}
dfs(root->left, target);
dfs(root->right, target);
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int target) {
dfs(root, target);
return ret;
}
};
方法二广度优先搜索
采用广度优先搜索的方式,遍历这棵树。当我们遍历到叶子节点,且此时路径和恰为目标和时,我们就找到了一条满足条件的路径.
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
unordered_map<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> parent;
void getPath(TreeNode* node) {
vector<int> tmp;
while (node != nullptr) {
tmp.emplace_back(node->val);
node = parent[node];
}
reverse(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
ret.emplace_back(tmp);
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int target) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return ret;
}
queue<TreeNode*> que_node;
queue<int> que_sum;
que_node.emplace(root);
que_sum.emplace(0);
while (!que_node.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = que_node.front();
que_node.pop();
int rec = que_sum.front() + node->val;
que_sum.pop();
if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) {
if (rec == target) {
getPath(node);
}
} else {
if (node->left != nullptr) {
parent[node->left] = node;
que_node.emplace(node->left);
que_sum.emplace(rec);
}
if (node->right != nullptr) {
parent[node->right] = node;
que_node.emplace(node->right);
que_sum.emplace(rec);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
关于广度优先和深度优先搜索的原理,可以看看我的另一个专栏。人工智能算法中的盲目搜索
push_back和emplace_back
参考文章
这两个的功能都是向vector容器的尾部添加元素。区别是前者需要先创建,然后再拷贝进vector。后者则是直接在vector的尾部创建元素。所以emplace_back的执行效率更高,但它是C++11标准新加的,所以如果考虑兼容性,就得用push_back。
代码:
#include 结果:
emplace_back:
调用构造函数
push_back:
调用构造函数
调用移动构造函数
移动构造函数
参考文章
在上面的代码中,出现了移动构造函数。印象中没学过,所以也查了下。
当我们利用拷贝构造函数进行深拷贝时,实际上会多出一次深拷贝操作,因为需要想创建一个,然后拷贝过来,在销毁那个用来拷贝的。为了提高效率,C++11就多了移动构造函数。当进行深拷贝时,不会再去让新指针指向新的空间,而是将新指针指向临时指针的空间,然后把临时指针指向NULL。这样就减少了一次拷贝。
这个是参考文章里的代码:
#include