数据结构与算法题目集(中文)函数题
PTA数据结构与算法题目集(中文)的函数题部分。本身底子就差,还有好多语法知识都快忘了,这里写出来相当于一个查漏补缺了。不能一蹴而就。
文章目录
-
- 6-1 单链表逆转
- 6-2 顺序表操作集
- 6-3 求链式表的表长
- 6-4 链式表的按序号查找
- 6-5 链式表操作集
- 6-6 带头结点的链式表操作集
- 6-7 在一个数组中实现两个堆栈
- 6-8 求二叉树高度
- 6-9 二叉树的遍历
- 6-10 二分查找
- 6-11 先序输出叶结点
- 6-12 二叉搜索树的操作集
- 总结
6-1 单链表逆转
图解

用头插法去做,1->3中,1被取出作为头,接着3被取出放在1的前面作为新头。但是要注意顺序,这个容易出错!!!
另外就是结构体链表的创建和输出。
#include 6-2 顺序表操作集
顺序表有些小小的特征,都在注释里
#include 6-3 求链式表的表长
读到-1时停止输入
#include 6-4 链式表的按序号查找
#include 6-5 链式表操作集
#include 6-6 带头结点的链式表操作集
#include 6-7 在一个数组中实现两个堆栈
必须检查Stack是否为NULL,要不然一个测试案例都过不了
Stack CreateStack( int MaxSize )
{
Stack s = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
s->MaxSize = MaxSize;
//动态开辟一个数组
s->Data = (ElementType*)malloc(MaxSize*sizeof(ElementType));
//栈底就是数组的两个边界
s->Top1 = -1;
s->Top2 = MaxSize;
return s;
}
bool Push( Stack S, ElementType X, int Tag )
{
if (!S) return false;
if(S->Top1+1 == S->Top2)
{
printf("Stack Full\n");
return false;
}
if(Tag == 1)
{
S->Data[++S->Top1] = X;
}
else
{
S->Data[--S->Top2] = X;
}
return true;
}
ElementType Pop( Stack S, int Tag )
{
if (!S) return ERROR;
if(Tag == 1)
{
if(S->Top1 == -1)
{
printf("Stack 1 Empty\n");
return ERROR;
}
return S->Data[S->Top1--];
}
else
{
if(S->Top2 == S->MaxSize)
{
printf("Stack 2 Empty\n");
return ERROR;
}
return S->Data[S->Top2++];
}
}
6-8 求二叉树高度
我们一定要考虑几个条件:
- 二叉树空 return 0
- 只有一个节点的情况
- 一般情况
if (ch=='#')
{//没孩子
BT=NULL;
}
else
{
BT=(BinTree)malloc(sizeof(BinTree));
BT->Data=ch;
CreatBinTree(BT->Left);
CreatBinTree(BT->Right);
}
当用先序创造一棵树时,可以画出递归函数的前进:
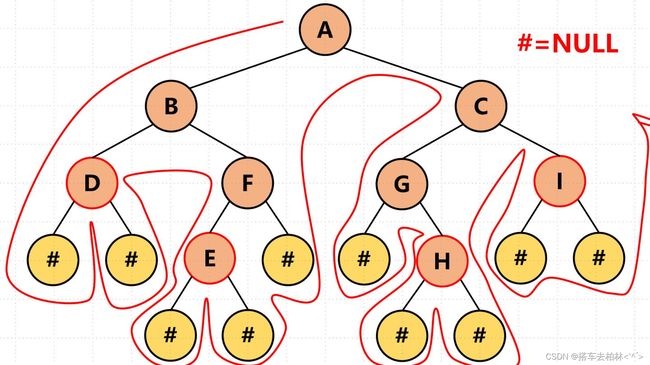
计算树的高度,每次左右节点递归完,到中间节点处要做个比较。
int GetHeight( BinTree BT )
{
if (!BT) return 0;
else
{
int left = GetHeight( BT->Left )+1;
int right = GetHeight( BT->Right )+1;
return (left>right) ? left : right;
}
}
6-9 二叉树的遍历
//前中后序遍历都是有规律的
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT )
{//中序
if(!BT)
{
return;
}
InorderTraversal( BT->Left );
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
InorderTraversal( BT->Right );
}
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT )
{//前序
if(!BT)
{
return;
}
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
PreorderTraversal( BT->Left );
PreorderTraversal( BT->Right );
}
void PostorderTraversal( BinTree BT )
{//后序
if(!BT)
{
return;
}
PostorderTraversal( BT->Left );
PostorderTraversal( BT->Right );
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
}
void LevelorderTraversal( BinTree BT )
{
// 所以说队列还是很好写的
if(BT == NULL)
{
return;
}
BinTree queen[100];
int front=0,rear=0;
//queen[0] = BT; //不能这么写,要不然进不了循环
queen[rear++] = BT;
while(front != rear)
{
BT = queen[front++];//段错误?因为没写而这句话
if(BT->Left)
queen[rear++] = BT->Left;
if(BT->Right)
queen[rear++] = BT->Right;
printf(" %c", BT->Data);
}
}
所以要换到cpp里运行检查错误
void CreatBinTree(BinTree &BT)
{//CreatBinTree(BT);这样写BT是个空的
char ch;
scanf("%c", &ch);
if (ch=='#')
{
//没孩子
BT=NULL;
}
else
{
BT = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(BinTree));
BT->Data = ch;
CreatBinTree(BT->Left);
CreatBinTree(BT->Right);
}
}
6-10 二分查找
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X )
{
//元素从下标1开始存储
if(!L){return NotFound;}
Position min = 1;
Position max = L->Last;
Position now;
while(min <= max)
{
now = (min+max)/2;
if(L->Data[now] > X)
{
max = now-1;
}
else if(L->Data[now] < X)
{
min = now+1;
}
else
{
return now;
}
}
return NotFound;
}
6-11 先序输出叶结点
void PreorderPrintLeaves( BinTree BT )
{
if(!BT){return;}
if(!BT->Left && !BT->Right)
{
printf(" %c", BT->Data);
return;
}
PreorderPrintLeaves(BT->Left);
PreorderPrintLeaves(BT->Right);
}
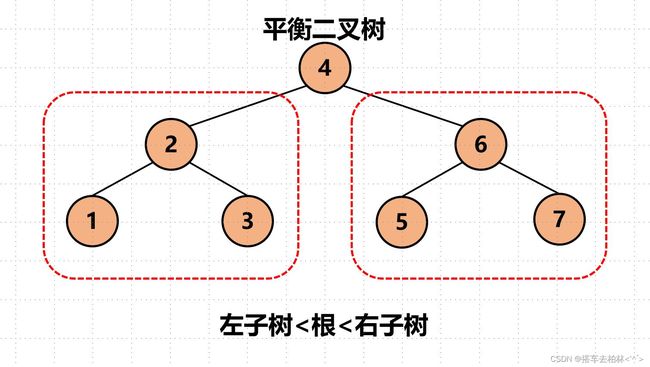
6-12 二叉搜索树的操作集
二叉搜索树又叫「平衡二叉树」。
它的特点:左子树<根<右子树。
先放除了删除部分的代码:
#include 解决了为啥不能随便删的疑惑以及有两个子节点,用左儿子或者右儿子的值替换改节点的值,然后删除那个叶子节点。注意用节点的值替换不必用节点替换。
进一步简化:有两个子节点,将右子树最小值替换当前root值,或者左子树最大值去替换,然后删掉那个最小值叶节点。
BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X )
{
//查找,正是因为递归才能保留双亲节点
//如果用Find查找返回一个新指针,是没法改变值的
if (!BST)
{
//当递归找到空节点或者本身为空时就退出
printf("Not Found\n");
return NULL;
}
else if (X > BST->Data)
{
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right, X);
}
else if (X < BST->Data)
{
BST->Left = Delete(BST->Left, X);
}
//找到了
else if(X == BST->Data)
{
Position tmp;
if (BST->Left && BST->Right)
{//左右双亲都有
tmp = FindMin(BST->Right);
BST->Data = tmp->Data;
//替换掉值之后的任务就是,把用来替换那个删掉(但是递归你不用考虑是怎么被删掉的)
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right, BST->Data);
}
else
{
if (BST->Left == NULL)
BST = BST->Right;
else if (BST->Right == NULL)
BST = BST->Left;
else
free(BST);
}
}
return BST;
}
如果不用递归去做,那么删除的时候不能用Find函数之类的了,因为你的拿到双亲节点,也就不能只是替换节点的值那么简单了。
BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X )
{
if(!BST)
{
//空的直接不找了
printf("Not Found\n");
return BST;
}
//由于删除的时候要保留前一个节点,寻找就不能调用那个寻找函数了
BinTree p = BST;
BinTree parent = NULL;
while(1)
{
//找节点,按照道理找不到就退出循环
if (X > p->Data)
{
if(p->Right != NULL)
{
parent = p;
p = p->Right;
}
else
break;
}
else if (X < p->Data)
{
if(p->Left != NULL)
{
parent = p;
p = p->Left;
}
else
break;
}
//找到了节点,分情况删除
else if (X == p->Data)
{
//当为叶结点时
if(p->Left == NULL && p->Right == NULL)
{
if(parent->Left == p)
{
parent->Left = NULL;
}
else if(parent->Right == p)
{
parent->Right = NULL;
}
else //没有双亲,是个单独的节点
return NULL;
}
//当为一个子结点时
else if(p->Left == NULL)
{
if(parent == NULL)
{
return p->Right;
}
else if(parent->Left == p)
{
parent->Left = p->Right;
}
else
{
parent->Right = p->Right;
}
}
else if(p->Right == NULL)
{
if(parent == NULL)
{
return p->Left;
}
else if(parent->Left == p)
{
parent->Left = p->Left;
}
else
{
parent->Right = p->Left;
}
}
else
{
//非递归的方法就得额外保存双亲,不是仅仅替换值就可以了。
BinTree tmp = FindMin(p->Right);
p->Data = tmp->Data;
//tmp = NULL; //这样是错的
//去置空孩子节点
p = p->Right;
while (p->Left != tmp)
{
p = p->Left;
}
//此时被删除的点p->Left一定是没有左孩子的,但可能有右孩子
if(p->Left->Right != NULL)
{
p->Left = p->Left->Right;
}
else
p->Left = NULL;
}
return BST;
}
}
printf("Not Found\n");
return BST;
}
这道题的一些测试数据:
1
7
2
5 9
3
5 9 7
5
5 4 3 2 1
2
6 -1
5
-1 6 5 1 3
总结
比起以前来说好多了,但还是菜,多练练吧。
