蓝桥杯训练day4
并查集,堆,哈希表
- 1.并查集
-
- (1)合并集合
- (2)连通块中点的数量
- (3)食物链
- (4)亲戚
- (5)银河英雄传说
- 2.堆
-
- (1)堆排序
- (2)模拟哈希表
- 3.哈希表
-
- (1)模拟散列表
- (2)字符串哈希
- (3)笨拙的手指
1.并查集
并查集:有两个庞大的家族,每个家族里面关系都很复杂且明确。每个家族有唯一的一个族长,如果给出家族所有人之间的关系,要将所有的人归类到确定的家族(有什么意义?比如我知道a是b的姑妈,但是这并不知道a是哪个家族(A,B)的,如果知道a是A族长的女儿,那么间接就知道了b是A族长女儿的侄子,那么b就是A族的成员) 这就是并查集要做的第一件事情:根据元素之间的关系给元素分类,每一类元素都一个特有的标签(也就是一个族长)
第二件事情:如果将AB连两个族合并,不需要将A族的成员的全部转移到B族,只需要将A族族长和B族族长联系起来就可以。
(1)合并集合
#include(2)连通块中点的数量
#include(3)食物链

大概思路:
带权并查集
将所有的关系都放入一个并查集,然后用d[n]来描述各个元素之间的关系。
即–建立关系,用d[n]判断关系。
食物链
#include(4)亲戚
#include(5)银河英雄传说
#include2.堆
对于堆的基础,推荐这篇博客:堆的简介
写的很基础,有基本的c基础都可以看懂。
堆是一个有特点的二叉树:对于任意一个节点,他的值大于等于他的所有孩子节点
对于堆的操作,简单介绍
-
插入元素:
将元素放入末尾,然后向上进行比较和转移,维护二叉树的性质(对于任意节点,他大于等于他的左右孩子节点) -
弹出根节点:将最后一个节点的值赋给根节点,然后从根节点开始向下比较和转换,维护二叉树。
//此代码是上述博客的,非本人的
#include
for (parent = index; (parent * 2 + 1) < heap.size; parent = child) {
child = parent * 2 + 1; //左子节点
//取两个子节点最大结点
if (((child + 1) < heap.size) && (heap.arr[child + 1] > heap.arr[child])) {
child++;
}
if (cur >= heap.arr[child])break;//不大于,跳出循环
else {
/*大于当前父节点,进行交换,然后从子节点位置继续向下调整,
即for从第二次循环开始,初始值都为上一次的子节点位置*/
heap.arr[parent] = heap.arr[child];
heap.arr[child] = cur;
}
}
}
static bool popMax(Heap& heap, int& value);
bool popMax(Heap& heap, int& value) {
if (heap.size < 1)return false;
value = heap.arr[0];
//将size-1的位置值赋给根节点,size本身又--
/*相当于
heap.arr[0] = heap.arr[heap.size-1];
heap.size--;
*/
heap.arr[0] = heap.arr[--heap.size];
adjustDown(heap, 0); //向下执行堆调整
return true;
}
bool insertHeap(Heap& heap, int value) {
if (heap.size == heap.capacity) {
fprintf(stderr, "栈空间耗尽!\n");
return false;
}
int index = heap.size;
heap.arr[heap.size++] = value;//先赋值value,再size++
adjustUp(heap, index);
}
void adjustUp(Heap& heap, int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= heap.size) {
//如果只有一个结点(插入的结点)inedx<0,或者大于堆的最大值,return掉
return;
}
int temp = heap.arr[index];//temp为插入的值
while (index > 0) {
int parent = (index - 1) / 2;
if (parent >= 0) { //如果索引没有出界,就执行想要操作
if (heap.arr[parent] < temp) {
heap.arr[index] = heap.arr[parent];
heap.arr[parent] = temp;
index = parent;
}
else break; //如果没有比父结点大,则跳出
}
else break; //越界,结束循环
}
}
int main() {
Heap hp;
int orignArry[] = { 1,2,3,87,93,82,92,86,95 };
if (!initHeap(hp, orignArry, sizeof(orignArry) / sizeof(orignArry[0]))) {
fprintf(stderr, "初始化堆失败!\n"); //输出到控制台
exit(-1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < hp.size; i++) {
cout << "第" << i << "个数为:" << hp.arr[i] << endl;
}
//向堆中插入元素
insertHeap(hp, 99);
printf("在堆中插入新的元素99,插入结果:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < hp.size; i++) {
cout << "第" << i << "个数为:" << hp.arr[i] << endl;
}
int value;
while (popMax(hp, value)) {
cout << "依次出列最大元素:" << value << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
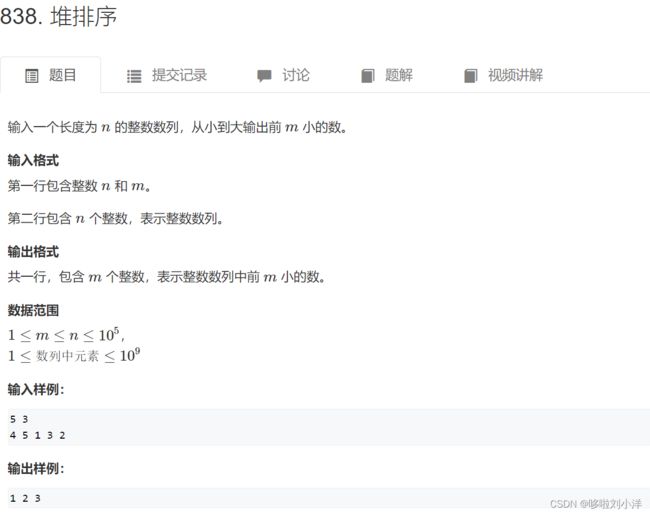
(1)堆排序
#include(2)模拟哈希表
#include3.哈希表
哈希表
a[x]=y
x叫关键字,y叫值。(key–value)
通过一系列的变换由x找到y
比如ax+by=c,则ax=c-by,x=(c-by)/a
哈希表有两个东西:
- 一个映射关系(函数)(自己定义,隐藏的逻辑)
- (key–value)(实际存储的东西,可以被看到的)
(1)模拟散列表
两种方法:拉链法和开放寻址法
两种方法的本质区别就是对于哈希冲突的解决。
什么是哈希冲突?
就是不同的x通过函数映射得到一样的y。
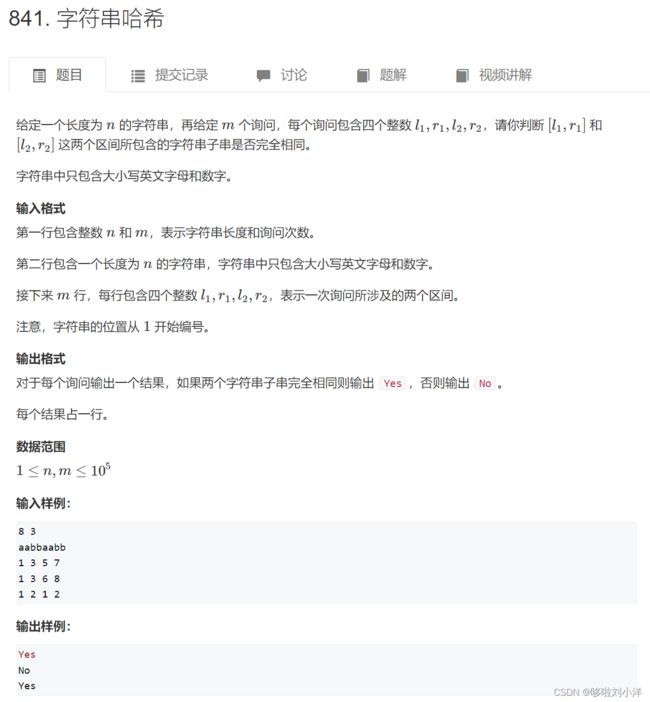
#include(2)字符串哈希
#include(3)笨拙的手指
#include