SpringBoot 全局异常处理用法及原理
SpringBoot 全局异常处理用法及原理
Springboot或springMVC项目中, 我们一般会设置一个全局异常处理, 来对异常进行兜底。 业务代码执行过程中抛出的异常, 如果业务逻辑没有主动捕获,那么异常就会一直往上抛,最后进入全局异常处理逻辑。
本文和大家探讨SpringBoot 全局异常处理用法及原理, 整体分为三个部分:第一部分,讲spring如何处理一个http请求异常;第二部分, 讲全局异常处理的几种方法; 第三部分,探究一下全局异常处理的底层原理。
1、springboot如何处理一个http请求异常
SpingBoot中,web请求由DispatcherServlet类的doDispatch方法来处理,如果处理过程抛出了异常,processDispatchResult方法会对异常进行处理。 此处省略了一些无关的代码。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// code omitted
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// this is where thrown exception is handled 处理异常的地方
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
// code omitted
}
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException)方法是异常处理的入口,然后委派给processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception)方法来处理。
/**
* Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is
* either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView.
*
*/
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
// get handler from handlerchain, in most cases the hanlder is a HanlderMethod
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
// delegate to this method 委派给processHandlerException
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// code omitted
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
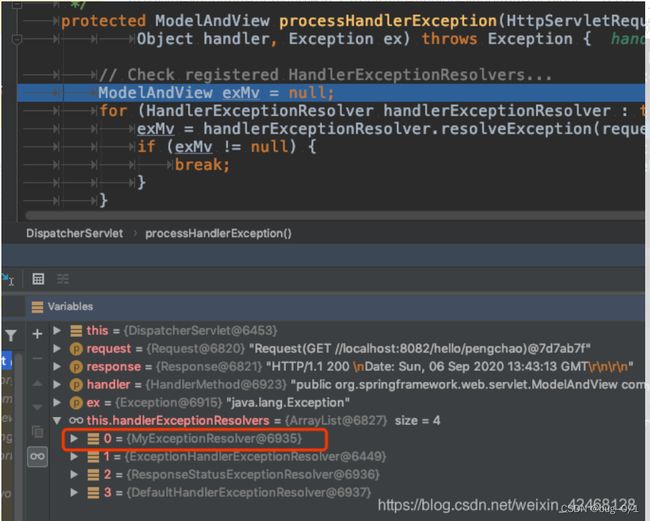
// Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers...
ModelAndView exMv = null;
// 重点代码
for (HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {
exMv = handlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
if (exMv != null) {
if (exMv.isEmpty()) {
request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
return null;
}
// We might still need view name translation for a plain error model...
if (!exMv.hasView()) {
exMv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request));
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Handler execution resulted in exception - forwarding to resolved error view: " + exMv, ex);
}
WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, getServletName());
return exMv;
}
throw ex;
}
可以看出, 这里有一组异常解析器,按照优先级由高到低排列。遍历异常解析器, 逐一调用resolveException方法来处理异常, 异常一旦得到处理,就break,这样就保证了,优先级高的处理器优先处理异常。 关于springboot如何处理http请求异常,了解这么多就够了。
至于这些handlerExceptionResolvers是怎么注册的? 第三部分会解释。
2、自定义全局异常处理的三种方法
2.1 实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口(不推荐)
看过第一部分,我们知道springboot的http请求异常由一组异常解析器来处理, 那么我们自然可以创建自己的异常解析器,然后把它加到现有的解析器中。
Spring已经为我们提供了抽象类AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver(Abstract base class for HandlerExceptionResolver implementations), 我们可以选择继承AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver来创建自己的全局异常解析器。
例如,
@Component //autowired
public class MyExceptionResolver extends AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override //异常解析器的顺序, 数值越小,表示优先级越高
public int getOrder() {
return -1;
}
@Override // write your exception-handle code
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
System.out.println("hello from MyExceptionResolver");
if(ex.instanceOf(BusinessException)){
// ...
// business code
// ...
}
}
}
这里MyExceptionResolver继承了AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver, 并重写了getOrder和doResolveException方法。在doResolveException中, 我根据异常的类型, 做相应的处理。
从图片可以看出来MyExceptionResolver注册进来了, 而且因为让getOrder方法返回了-1, 所以MyExceptionResolver排在了最前面,可以优先处理异常。
但在实际应用中,几乎没见过使用这种方法,这里提出来主要是加深大家对原理的理解。
2.2. @ExceptionHandler + BaseController(不推荐)
第二种方法, 是使用@ExceptionHandler注解 + BaseController。
例如,
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldController.class);
@Autowired
private HelloWorldService helloWorldService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello/{name:.+}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView hello(@PathVariable("name") String name) throws Exception {
logger.debug("hello--> {}", name);
throw new BusinessException();
}
@ExceptionHandler({BusinessException.class}) // 这里可以定义要处理的一组异常类型
private ModelAndView handleException(Exception e){
System.out.println("hello from in controller");
// handle BusinessException
}
@ExceptionHandler({BusinessException1.class, BusinessException2.class}) // 这里可以定义要处理的异常类型
private ModelAndView handleException1(Exception e){
System.out.println("hello from in controller");
// handle BusinessException1 and BusinessException2
}
}
这里,在HelloWorldController中, 定义了两个由@ExceptionHandler注释的方法来处理异常。如果HelloWorldController的hello方法(或者其他方法)执行过程中, 抛出BusinessException类型的异常, 那么会被handleException方法捕获到; 如果抛出了BusinessException1类型或是BusinessException2类型的异常,则会被handleException1方法捕获到。
通过@ExceptionHandler注解的方式, 我们可以通过让不同的方法处理不同的异常。
但是这种方式是不是意味着, 我们需要在每个controller中都要定义自己@ExceptionHandler方法呢? 如果各自处理自己的异常, 那叫什么全局异常处理呢?
为此, 我们其实可以写一个BaseController, 将全局、通用的异常处理方法写在BaseController里, 需要进行全局异常处理的Controller继承BaseController。而个性化的异常处理,则写在具体的controller里。
最后看一下ExceptionHandler的代码
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ExceptionHandler {
/**
* Exceptions handled by the annotated method. If empty, will default to any
* exceptions listed in the method argument list.
* 是一个数组, 表示要处理的一组异常类型。 如果为空的话, 会处理注解所修饰方法参数代表的异常类型。
*/
Class<? extends Throwable>[] value() default {};
}
方法二, 不如方法三灵活,几乎也没有人用。
2.3 @ExceptionHandler + @ControllerAdvice(推荐)
第三种方法是使用@ExceptionHandler注解 + @ControllerAdvice注解。通过给ExceptionHandler注解传入参数或者给方法添加异常类型的参数,可以让方法处理指定类型的一组异常。
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlabalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
private void handleException(Exception e){
System.out.println("hello from glabal exception handler");
// handle BusinessException
}
@ExceptionHandler({BusinessException1.class, BusinessException2.class}) // 这里可以定义要处理的一组异常类型
private ModelAndView handleException1(Exception e){
System.out.println("hello from glabal exception handler");
// handle BusinessException1 and BusinessException2
}
}
这里对于所有controller,如果有方法抛出BusinessException类型的异常, 会走到handleException方法; 如果抛出了BusinessException1类型或是BusinessException2类型的异常,则会被handleException1方法处理。
ControllerAdvice提供了灵活的方式, 来指定对哪些controller来进行异常处理。
看一下ControllerAdvice的代码
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface ControllerAdvice {
/**
* basePackages的别名,功能同下。
*/
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
/**
* 指定一组包名。
* 可以指定一组包名。 这些包(包括子包)里的所有controller,都会拥有异常处理的能力
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
...
/**
*
* 指定一组类, controller如果可以赋值给其中任意一个类(controller就是该类或者是该类的子类,对于接口来说也是一样), 则该controller会拥有异常处理的能力。
*/
Class<?>[] assignableTypes() default {};
...
}
实际应用中,多采用这种方法。
3、原理
我们进一步讨论第二部分的三种用法的原理。
3.1. 实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口的原理
我们在第一部分中已经提到,在org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#processHandlerException方法中,会有一组异常解析器来解析异常,而且第一部分末尾留下了一个问题:这一组handlerExceptionResolvers是怎么注册的?
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//调用初始异常处理器方法
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the HandlerExceptionResolver used by this class.
* If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace,
* we default to no exception resolver.
*/
private void initHandlerExceptionResolvers(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers) {
// Find all HandlerExceptionResolvers in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
// 最关键一段代码,这里
Map<String, HandlerExceptionResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils
.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = new ArrayList<HandlerExceptionResolver>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerExceptionResolvers in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerExceptionResolvers);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerExceptionResolver her =
context.getBean(HANDLER_EXCEPTION_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerExceptionResolver.class);
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = Collections.singletonList(her);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, no HandlerExceptionResolver is fine too.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least some HandlerExceptionResolvers, by registering
// default HandlerExceptionResolvers if no other resolvers are found.
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers == null) {
this.handlerExceptionResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerExceptionResolvers found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
最终是在initHandlerExceptionResolvers方法完成异常解析器的初始化, 关键代码用中文注释标出。 这里首先会从spring容器中找出所有HandlerExceptionResolver类型(包括子类)的bean, 然后按照order进行排序。这样,我们自定义的异常解析器就会被spring注册并放到指定的位置。
3.2. @ExceptionHandler + Controller、@ExceptionHandler + @ControllerAdvice的原理
我们把方法二和方法三放到一起说。
Spring是依靠自带的ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver这个异常解析器来支持这两种方式的。DispatcherServlet初始化时,会把ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver注册到handlerExceptionResolvers中。弄清楚了ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver就清楚了方法二和方法三的原理。
以下是ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的关键代码:
@Override
protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
//这里是关键
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception);
if (exceptionHandlerMethod == null) {
return null;
}
//省略其它代码
...
}
实际调用代码
protected ServletInvocableHandlerMethod getExceptionHandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
Class<?> handlerType = null;
if (handlerMethod != null) {
// Local exception handler methods on the controller class itself.
// To be invoked through the proxy, even in case of an interface-based proxy.
handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
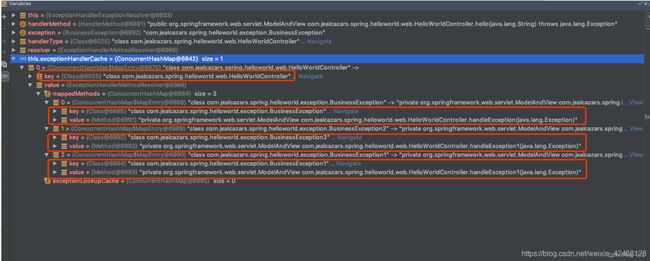
//首先尝试从exceptionHandlerCache里找ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = this.exceptionHandlerCache.get(handlerType);
if (resolver == null) {
resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(handlerType);
this.exceptionHandlerCache.put(handlerType, resolver);
}
Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception);
if (method != null) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod.getBean(), method);
}
// For advice applicability check below (involving base packages, assignable types
// and annotation presence), use target class instead of interface-based proxy.
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(handlerType)) {
handlerType = AopUtils.getTargetClass(handlerMethod.getBean());
}
}
//遍历ControllerAdvice去找异常处理方法
for (Map.Entry<ControllerAdviceBean, ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver> entry : this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.entrySet()) {
ControllerAdviceBean advice = entry.getKey();
if (advice.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = entry.getValue();
Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception);
if (method != null) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(advice.resolveBean(), method);
}
}
}
return null;
}
可以看出来:
首先会从exceptionHandlerCache中去找handlerMethod所属bean的class对应的ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver, 如果找不到则new一个ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver并缓存起来。 然后从ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver去找该exception对应的异常处理方法。
先上一张图,直观感受一下,来自第二部分方法二的例子:
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver中存的是各个Exception到各个异常处理方法映射。
我们再看一下new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(handlerType)的实现, 不详细说了, 简单说一下关键点, 直接写在代码注释里。
/**
* A constructor that finds {@link ExceptionHandler} methods in the given type.
* @param handlerType the type to introspect
*/
public ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(Class<?> handlerType) {
//找出handlerType(这里就是对应的Controller)里所有有@ExceptionHandler注解的方法,然后遍历方法
for (Method method : MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, EXCEPTION_HANDLER_METHODS)) {
// 从一个异常处理方法中提取出处理的异常,然后遍历异常
for (Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType : detectExceptionMappings(method)) {
//添加异常到方法的映射
addExceptionMapping(exceptionType, method);
}
}
}
/**
* Extract exception mappings from the {@code @ExceptionHandler} annotation first,
* and then as a fallback from the method signature itself.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private List<Class<? extends Throwable>> detectExceptionMappings(Method method) {
List<Class<? extends Throwable>> result = new ArrayList<Class<? extends Throwable>>();
//先从注解中找
detectAnnotationExceptionMappings(method, result);
if (result.isEmpty()) {
// 如果注解中没有, 才会从参数中找。 也就是说, 如果注解中设置了异常的话, 那么异常参数就没有意义。
for (Class<?> paramType : method.getParameterTypes()) {
if (Throwable.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) {
result.add((Class<? extends Throwable>) paramType);
}
}
}
if (result.isEmpty()) {
// 有 @Exceptionhandler但是找不到任何异常类型, 会抛出异常
throw new IllegalStateException("No exception types mapped to " + method);
}
return result;
}
private void addExceptionMapping(Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType, Method method) {
Method oldMethod = this.mappedMethods.put(exceptionType, method);
//如果之前已经有该异常类型的映射, 会抛异常。
if (oldMethod != null && !oldMethod.equals(method)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous @ExceptionHandler method mapped for [" +
exceptionType + "]: {" + oldMethod + ", " + method + "}");
}
}
看到这里, 相信方法二的原理大家应该清楚了。
接着往下看getExceptionHandlerMethod方法。 简单说就是遍历所有被@ControllerAdvice注解的bean, 如果该bean适用于本Controller,则去匹配异常处理方法。
关键看一下exceptionHandlerAdviceCache是如何初始化的?
private void initExceptionHandlerAdviceCache() {
if (getApplicationContext() == null) {
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for exception mappings: " + getApplicationContext());
}
//找出所有被@controllerAdvice注解的bean, 然后排序
List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = ControllerAdviceBean.findAnnotatedBeans(getApplicationContext());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(adviceBeans);
for (ControllerAdviceBean adviceBean : adviceBeans) {
//遍历bean, 然后解析其中的异常处理方法。 上面已经介绍过了。
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(adviceBean.getBeanType());
if (resolver.hasExceptionMappings()) {
this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, resolver);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected @ExceptionHandler methods in " + adviceBean);
}
}
if (ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(adviceBean.getBeanType())) {
this.responseBodyAdvice.add(adviceBean);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected ResponseBodyAdvice implementation in " + adviceBean);
}
}
}
}
写到这里方法三的原理大家也应该明白了吧。
总结一下, 对于某一个controller,如果既有采用方法二配置的异常处理,也有方法三的全局异常配置, 那么方法二优先。也就是说, 如果在controller里已经找到了异常处理方法,则不会再去controlleradvicebean中找。 只有当controller里没有对应的处理方法,才会去 controlleradvicebean找。