基于python的旅游系统_基于python的去哪儿网旅游数据分析
20011 基于python的去哪儿网旅游数据分析
运行视频、代码等:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1tw4Qvtcuwt7ys36M7HvLSg
提取码:1589
复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦
技术
Python + Pandas + Numpy + Pyecharts
功能详情
数据抽取
数据清洗
数据分析
数据展示
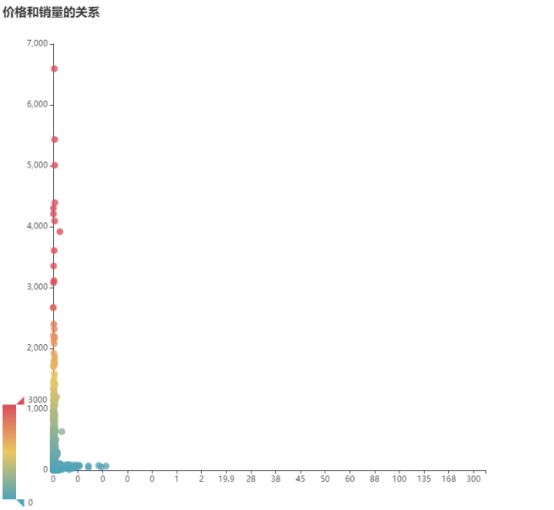
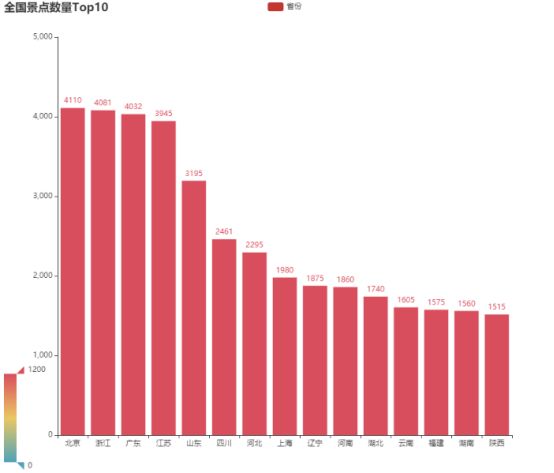
主要展示了不同时间不同城市的景区的销售情况。
系统相关截图
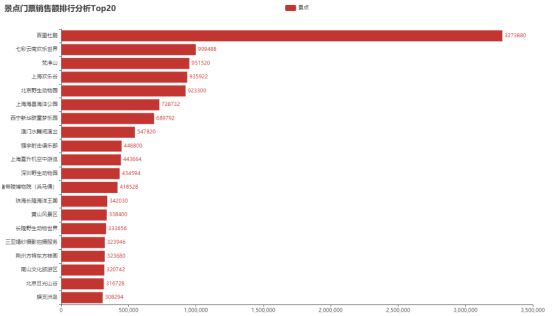
景点门票销售额排行
import random
with open('hw.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write('height\tweight\n')
for i in range(100):
height = random.randint(1600, 1900) / 10
weight = (height - 100) * 0.9 + random.randint(-50, 50) / 10
f.write('%.1f\t%.1f\n' % (height, weight))
linear_regression.py:
author = 'DivinerShi'
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def compute_error(b,m,data):
totalError = 0
#Two ways to implement this
#first way
# for i in range(0,len(data)):
# x = data[i,0]
# y = data[i,1]
# totalError += (y-(m*x+b))**2
# print('(%f*%f+%f)=%f,y=%f,loss=%f,totalError=%f' % (m,x,b,(m*x+b),y,(y-(m*x+b))**2,totalError))
#second way
x = data[:,0]
y = data[:,1]
totalError = (y-m*x-b)**2
totalError = np.sum(totalError,axis=0)
return totalError/float(len(data))
def optimizer(data,starting_b,starting_m,learning_rate,num_iter):
b = starting_b
m = starting_m
#gradient descent
for i in range(num_iter):
#update b and m with the new more accurate b and m by performing
# thie gradient step
b,m =compute_gradient(b,m,data,learning_rate)
if i%100==0:
print('iter {0}:error={1}'.format(i,compute_error(b,m,data)))
return [b,m]
def compute_gradient(b_current,m_current,data ,learning_rate):
b_gradient = 0
m_gradient = 0
N = float(len(data))
#Two ways to implement this
#first way
# for i in range(0,len(data)):
# x = data[i,0]
# y = data[i,1]
# #computing partial derivations of our error function
# #b_gradient = -(2/N)*sum((y-(m*x+b))^2)
# #m_gradient = -(2/N)*sum(x*(y-(m*x+b))^2)
# b_gradient += -(2/N)*(y-((m_current*x)+b_current))
# m_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y-((m_current*x)+b_current))
# # print('m_current=%f,b_current=%f,N=%f,x=%f,y=%f,y-((m_current*x)+b_current)=%f, b_gradient=%f, m_gradient=%f' % (m_current, b_current, N, x, y, y-((m_current*x)+b_current), b_gradient, m_gradient))
#Vectorization implementation
x = data[:,0]
y = data[:,1]
b_gradient = -(2/N)*(y-m_current*x-b_current)
b_gradient = np.sum(b_gradient,axis=0)
m_gradient = -(2/N)*x*(y-m_current*x-b_current)
m_gradient = np.sum(m_gradient,axis=0)
#update our b and m values using out partial derivations
new_b = b_current - (learning_rate * b_gradient)
new_m = m_current - (learning_rate * m_gradient)
return [new_b,new_m]
def Linear_regression():
# get train data
# data =np.loadtxt('data.csv',delimiter=',')
data =np.loadtxt('hw.txt',delimiter='\t',skiprows=True)
#define hyperparamters
#learning_rate is used for update gradient
#defint the number that will iteration
# define y =mx+b
learning_rate = 0.000001
initial_b =0.0
initial_m = 0.0
num_iter = 10000
#train model
#print b m error
print('initial variables:\n initial_b = {0}\n intial_m = {1}\n error of begin = {2} \n'\
.format(initial_b,initial_m,compute_error(initial_b,initial_m,data)))
#optimizing b and m
[b ,m] = optimizer(data,initial_b,initial_m,learning_rate,num_iter)
#print final b m error
print('final formula parmaters:\n b = {1}\n m={2}\n error of end = {3} \n'.format(num_iter,b,m,compute_error(b,m,data)))
#plottting
x = data[:,0]
y = data[:,1]
y_predict = m*x+b
plt.scatter(x, y, color = 'blue')
plt.plot(x,y_predict,'k-', color = 'red', linewidth = 4)
# plt.show()
from sklearn import linear_model
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
regr.fit(x.reshape(-1,1), y)
print(regr.coef_, regr.intercept_)
plt.scatter(x, y, color = 'blue')
plt.plot(x, regr.predict(x.reshape(-1,1)), color = 'orange', linewidth = 4)
plt.show()
def lr_by_sklearn():
from sklearn import linear_model
data =np.loadtxt('hw.txt',delimiter='\t',skiprows=True)
x = data[:,0]
y = data[:,1]
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
regr.fit(x.reshape(-1,1), y)
print(regr.coef_, regr.intercept_)
# import pandas as pd
# data = pd.read_csv('hw.txt', sep='\t')
# regr.fit(data['height'].values.reshape(-1,1), data['weight'])
# plt.scatter(data['height'], data['weight'], color = 'blue')
# plt.plot(data['height'], regr.predict(data['height'].values.reshape(-1,1)), color = 'orange', linewidth = 4)
# plt.show()
plt.scatter(x, y, color = 'blue')
plt.plot(x, regr.predict(x.reshape(-1,1)), color = 'orange', linewidth = 4)
plt.show()
if name =='main':
Linear_regression()
lr_by_sklearn()
import numpy as np
df2 = df.groupby('addr').agg([np.mean, np.var])
df2['x'] = 1
from math import pi, exp, sqrt
def f(x, mean, var):
return exp(-(x-mean)**2/(2var))/sqrt(2pi*var)
df2['p_x_min']=df2[['min','x']].apply(lambda x: f(x['x'], x['min']['mean'], x['min']['var']), axis=1)
df2['p_x_max']=df2[['max','x']].apply(lambda x: f(x['x'], x['max']['mean'], x['max']['var']), axis=1)
(df2['p_x_min']pcpa['java']).argmax()
方法二:
from numpy import genfromtxt
x = genfromtxt('51.txt', delimiter='\t', skip_header=True, usecols=(2,3))
x.shape
y = genfromtxt('51.txt', delimiter='\t', skip_header=True, usecols=(1), dtype=str)
y.shape
import numpy as np
np.unique(y)
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
clf = GaussianNB()
拟合数据
clf.fit(x, y)
print(clf.predict([[0.8, 1.2]]))
print(clf.predict_proba([[0.8, 1.2]]))
print(clf.predict_log_proba([[0.8, 1.2]]))
import urllib.request
import re
import sqlite3
def get_content(page, key):
url = 'https://search.51job.com/list/010000%2C020000%2C030200%2C040000,000000,0000,00,9,99,' + key + ',2,' + str(page) + '.html'
a = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
html = a.read().decode('gbk')
lst = re.findall(r'(北京|上海|广州|深圳).*?\s+(\d+.?\d?)-(\d+.?\d?)(万|千)/(年|月)', html)
return lst
conn = sqlite3.connect('51.db')
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute('''CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS jobs
(key text, addr text, min float, max float)''')
c.execute('''delete from jobs''')
conn.commit()
with open('51.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write('%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\n' % ('key','addr','min','max'))
for key in ('python', 'java'):
for each in range(1, 11):
for items in get_content(each, key):
min = float(items[1])
max = float(items[2])
if items[3] == "千":
min /= 10
max /= 10
if items[4] == "年":
min /= 12
max /= 12
f.write('%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\n' % (key, items[0], round(min, 2), round(max, 2)))
c.execute("INSERT INTO jobs VALUES (?,?,?,?)", (key, items[0], round(min, 2), round(max, 2)))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
if name == 'main':
lst = get_content(1, 'python')
print(lst)